Method for reducing biogenic amine through cyclic rice soaking by inoculating lactobacillus plantarum not generating biogenic amine
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and microbial agent, which is applied in the field of food processing and manufacturing, can solve the problems such as the inability to effectively realize the multiple recycling of rice soaking water, the generation of thick slurry, and the difficulty in handling, so as to shorten the time required for rice soaking and reduce the Biogenic amine content and the effect of stabilizing physical and chemical indicators
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
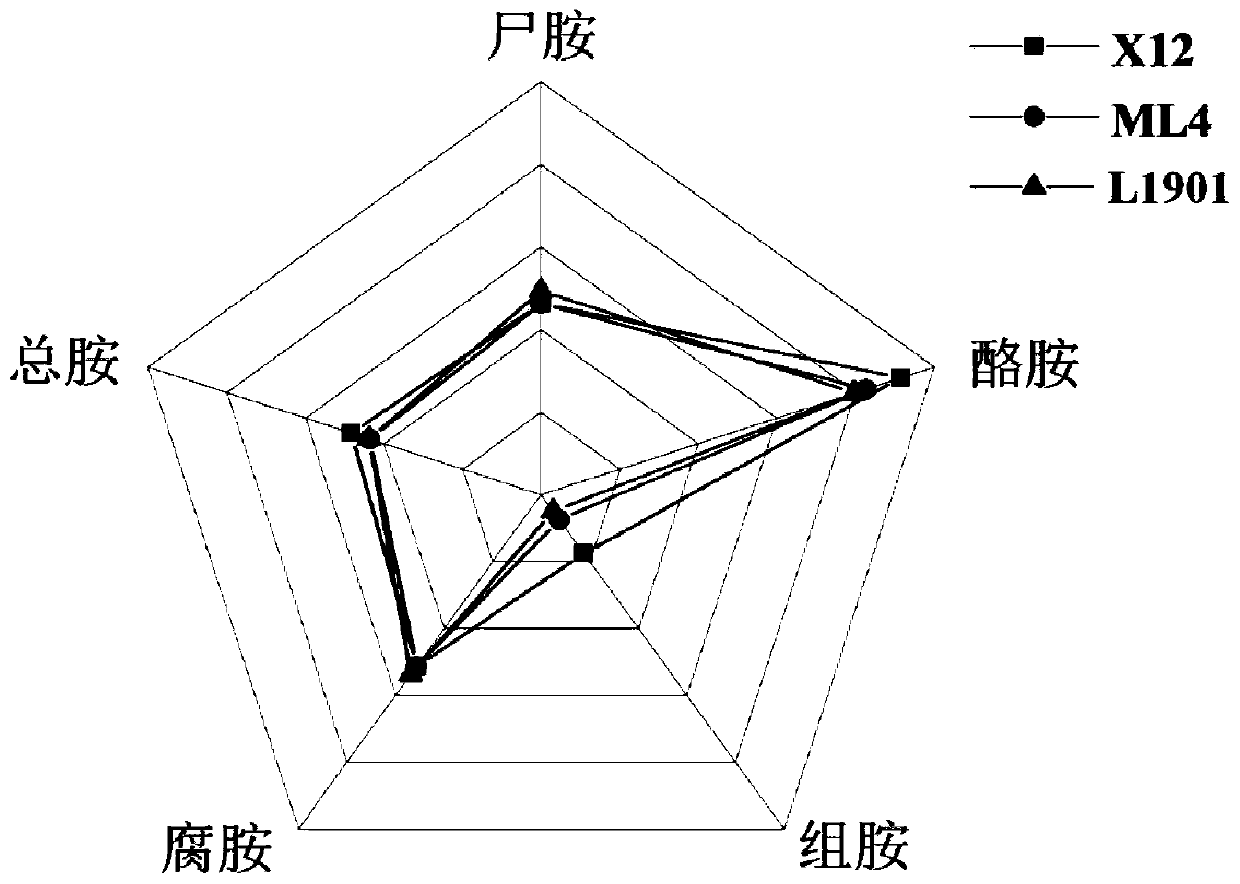
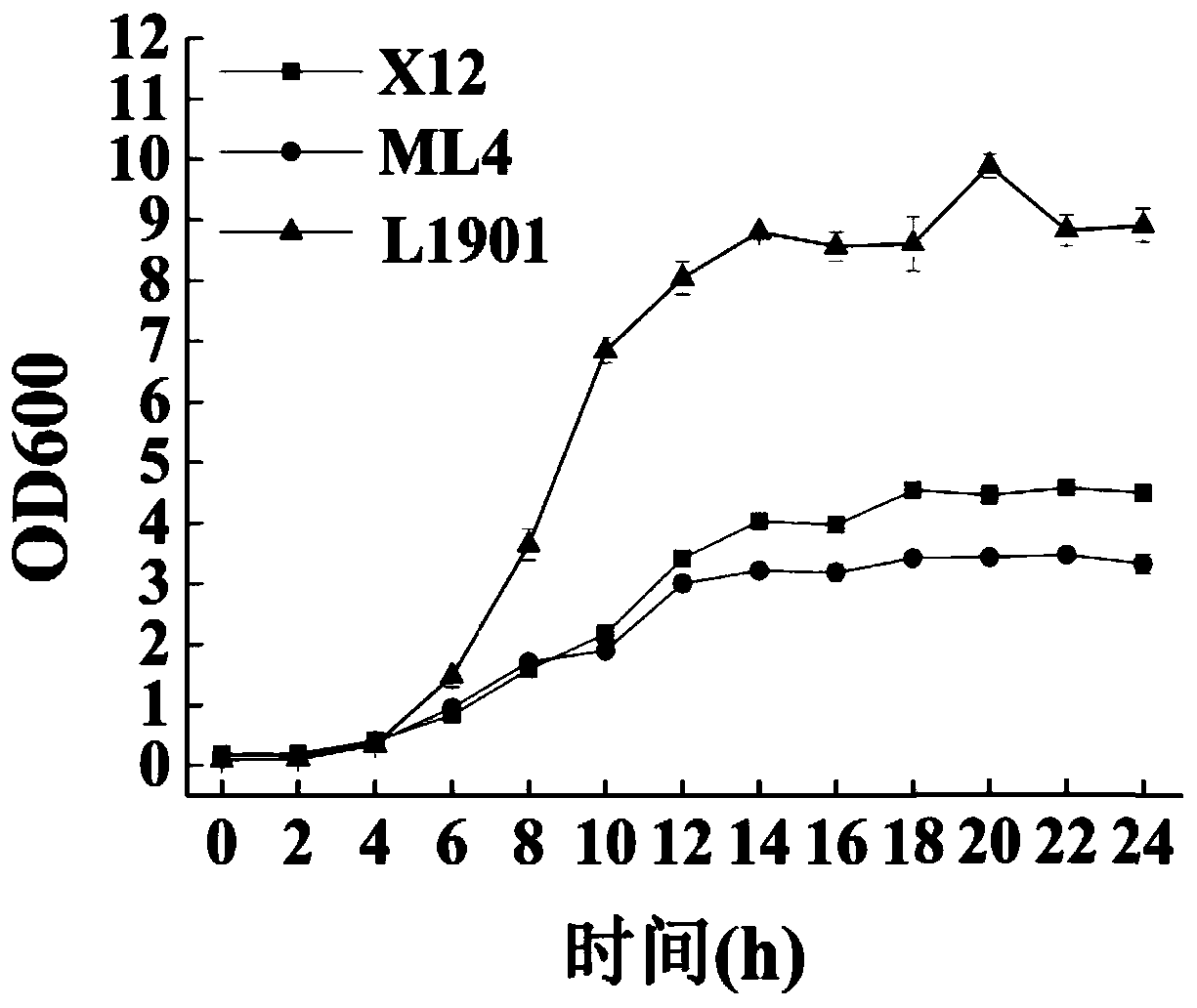
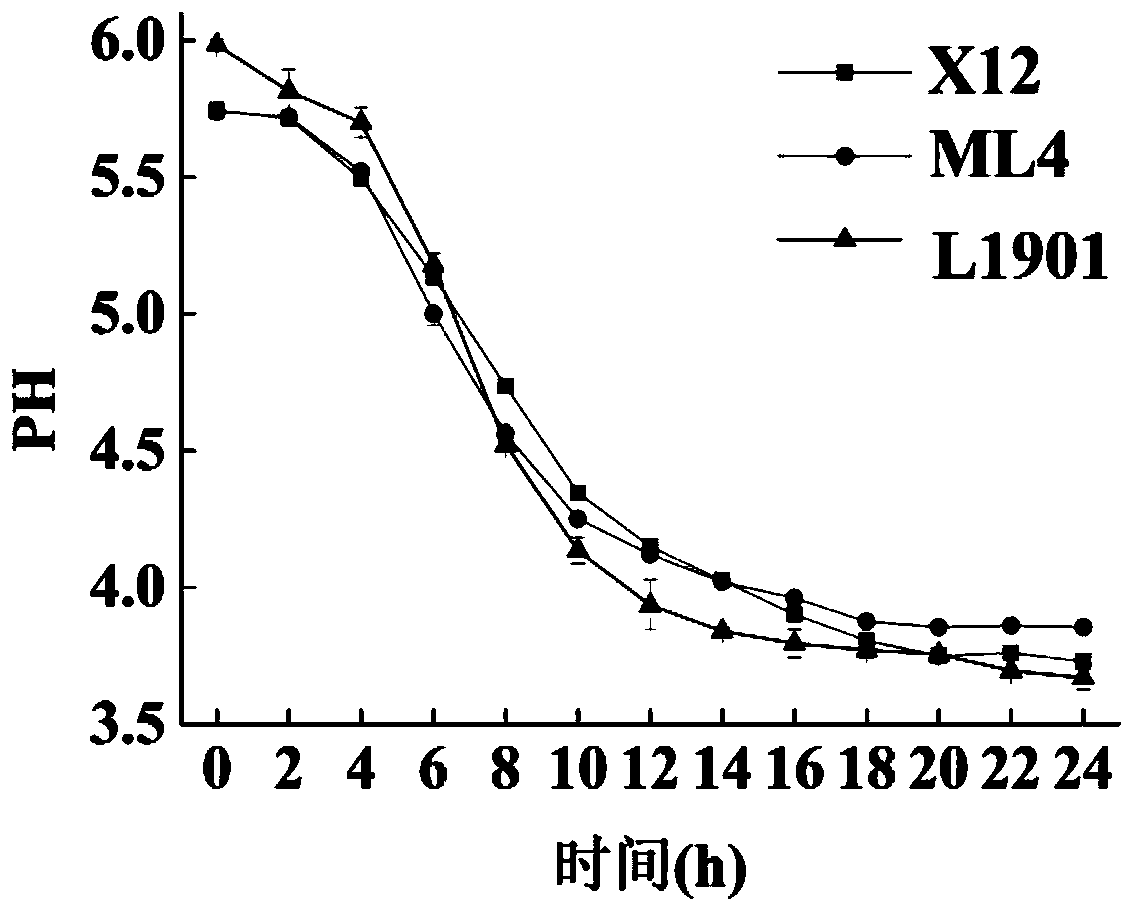
[0031] Embodiment 1: Screening of Lactobacillus plantarum L1901
[0032] Three strains of Lactobacillus L. mindensis ML4, L. plantarum L1901 and L. casei X12, which do not produce and have the ability to degrade biogenic amines, were isolated from rice wine soaked rice water and fermented mash in the early stage of the laboratory. In order to screen out a strain that meets the needs of soaking rice and can reduce the content of biogenic amines during rice soaking, the biogenic amine degradation ability, growth and acid production characteristics, and pH tolerance of the above three Lactobacillus strains were further analyzed.
[0033] The formula of MRS medium: peptone 10.0g / L; beef extract 10.0g / L; yeast extract 5.0g / L; diammonium hydrogen citrate 2.0g / L; glucose 20.0g / L; Tween 80 1.0mL / L ; Sodium acetate (sodium oxalate) 5.0g / L; Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 2.0g / L; Magnesium sulfate 0.58g / L; Manganese sulfate 0.25g / L; Agar 18.0g / L (added in solid MRS medium); pH 6.2-6.6. ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2: Application of Lactobacillus plantarum L1901 in soaking rice in single batches of rice wine
[0044] 1. Activation of the strain
[0045]Medium formula: MRS medium: peptone 10.0g / L; beef extract 10.0g / L; yeast extract 5.0g / L; diammonium hydrogen citrate 2.0g / L; glucose 20.0g / L; Tween 80 1.0mL / L; sodium acetate (sodium oxalate) 5.0g / L; dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 2.0g / L; magnesium sulfate 0.58g / L; manganese sulfate 0.25g / L; agar 18.0g / L (added to solid MRS medium) ; pH 6.2-6.6.
[0046] Glutinous rice saccharification solution: mix rice (glutinous rice), malt powder, and water at a ratio of 1:0.2:4 (m / m / v), add liquefaction enzyme 2‰, glucoamylase 2, and wheat koji 10%, keep saccharification at 60°C for 4 hours, Stir once every 1 hour. After saccharification, sterilize at 115°C for 15 minutes.
[0047] Lactic acid bacteria strain L1901 was streaked on a solid MRS medium for activation once, cultured in liquid MRS medium at 37°C for 24 hours, and activat...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Example 3: The application of adding Lactobacillus plantarum L1901 in the rice wine circulatory soaking process
[0059] 1. Activation of the strain
[0060] The lactic acid bacteria strains were streaked on the solid MRS medium for activation once, cultured in the liquid MRS medium at 37°C for 24 hours, and activated twice. Afterwards, inoculate the glutinous rice saccharification solution with 4‰ inoculum, and culture at 37°C for 24 hours to complete the activation.
[0061] 2. Inoculation of Lactobacillus plantarum L1901 in the process of circulating rice soaking
[0062] Take glutinous rice in a beaker, add water at a ratio of solid to liquid 1:1.5, put the activated strain into rice-soaking water with an inoculum volume fraction of 7.5%, and use non-inoculated clean water-soaked rice as a control. After soaking the rice for 21 days, treat the rice soaking water inoculated with Lactobacillus plantarum. The specific method is as follows: collect the rice soaking wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com