Preparation method of water-soluble alginate for in-vivo implantation
A kind of alginate and water-soluble technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of water-soluble alginate implanted in the body, can solve the problems of difficult removal, limited application, and inability to meet the needs of mass production, so as to avoid adverse effects and have high purity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
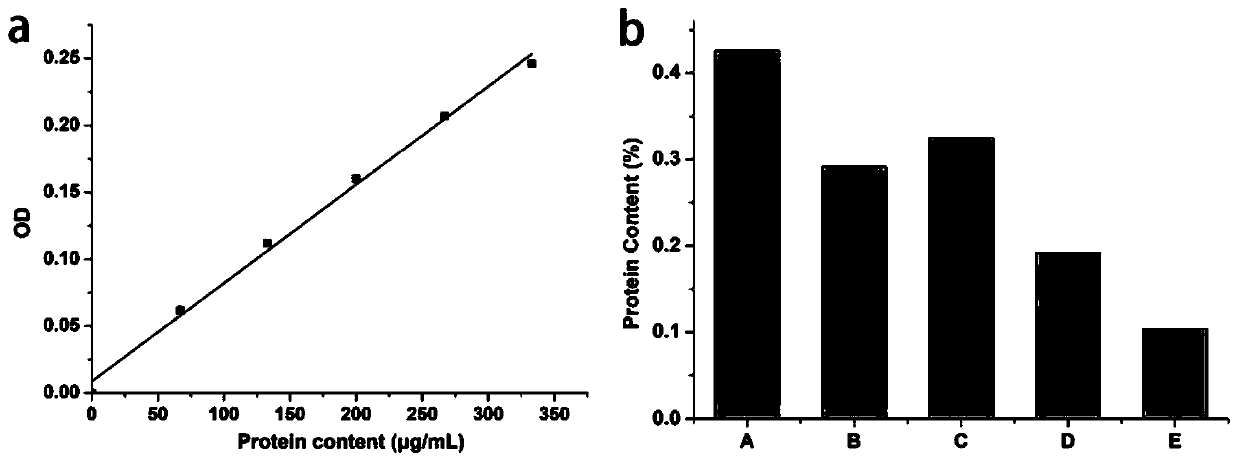
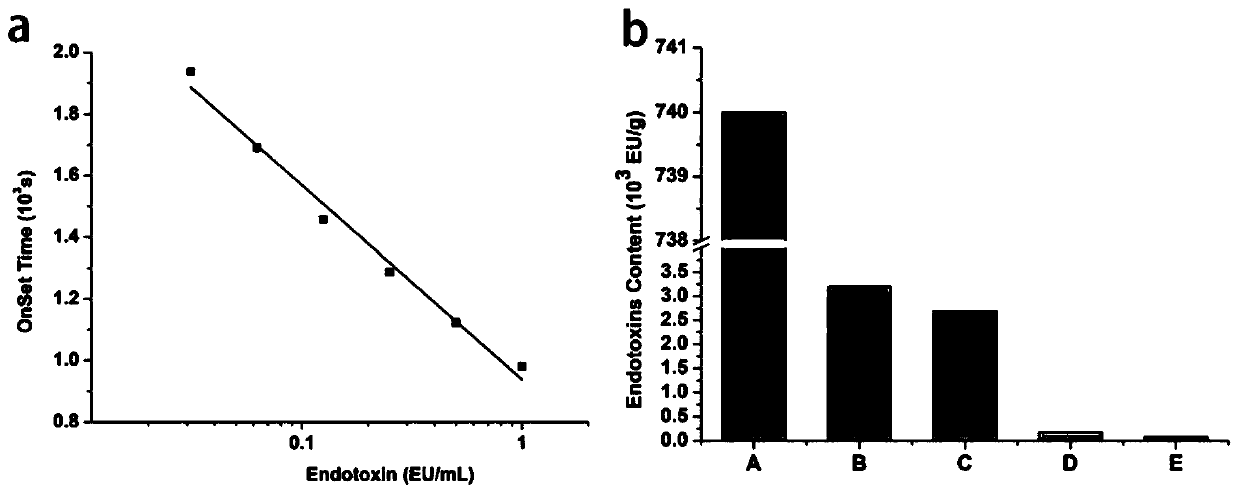
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0031] A preparation method for implanting water-soluble alginate in vivo, comprising the following steps:
[0032] (1) Dissolve commercially available food-grade or pharmaceutical excipient-grade water-soluble alginate (sodium alginate, potassium alginate and / or ammonium alginate) in purified water to obtain a water-soluble alginate solution with a concentration of 0.3% ~3% (w / v, g / ml);
[0033] (2) Pass the water-soluble alginate solution through a microporous folded membrane filter element (polypropylene filter element (PP), polyethersulfone filter element (PES) or polytetrafluoroethylene filter element (PTFE) with a pore size of 0.8 μm, 0.45 μm, and 0.22 μm. ) after filtering and adding activated carbon for adsorption, the mass ratio of water-soluble alginate to activated carbon is 5:1 to 0.1:1, and mechanically stirred at room temperature for 0.5 to 20 hours;
[0034] (3) decarburize the solution adsorbed by activated carbon in step (2) using a microporous folded membran...
Embodiment 1
[0041] 1. Add 10 g of commercially available pharmaceutical excipient grade sodium alginate into 2 L of distilled water, and dissolve it with mechanical stirring at a speed of 1500 rpm for 6 hours to obtain alginic acid with a content of 0.5% (g / ml) sodium solution.
[0042] 2. The solution obtained in step 1 was filtered through a microporous folded membrane filter element with a pore size of 0.8 μm, and then 50 g of activated carbon was added, and mechanically stirred for 6 hours at room temperature.
[0043] 3. The solution containing activated carbon is filtered through a microporous folded membrane filter element with a pore size of 0.8 μm to remove the activated carbon, and activated carbon is added to the obtained solution again, and the adsorption and decarbonization filtration process is repeated twice.
[0044] 4. Spray the alginate solution obtained in step 3 into a 0.5M hydrochloric acid solution to form alginate gel microspheres. After soaking for 8 hours, fully w...
Embodiment 2
[0053] 1. Add 10 g of commercially available food-grade potassium alginate into 1 L of distilled water, and dissolve it with mechanical stirring at a speed of 1500 rpm for 8 hours to obtain a potassium alginate solution with a content of 1.0% (g / ml) .
[0054] 2. The solution obtained in step 1 was filtered through a microporous folded membrane filter element with a pore size of 0.45 μm, then 30 g of activated carbon was added, and mechanically stirred for 4 hours at room temperature.
[0055] 3. Same as embodiment 1
[0056] 4. Drop the alginate solution obtained in step 3 into a 0.2M sulfuric acid solution to form alginate gel microspheres. After soaking for 12 hours, fully wash the gel microspheres with purified water.
[0057] 5. Soak the alginate gel microspheres in 2L, 100mM potassium carbonate solution for 20 hours, then take out the gel microspheres and wash them thoroughly with purified water.
[0058] 6. Add pH 12.0 potassium bicarbonate solution to the eluted algi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com