Method for preparing zinc ferrite from waste batteries and application of zinc ferrite in degradation of bisphenol A
A zinc ferrite, waste technology, applied in the field of photocatalyst material preparation, can solve the problems of catalyst structure change, secondary pollution of water, increase treatment cost, etc., and achieve the effects of good crystallinity, easy separation, and improved service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
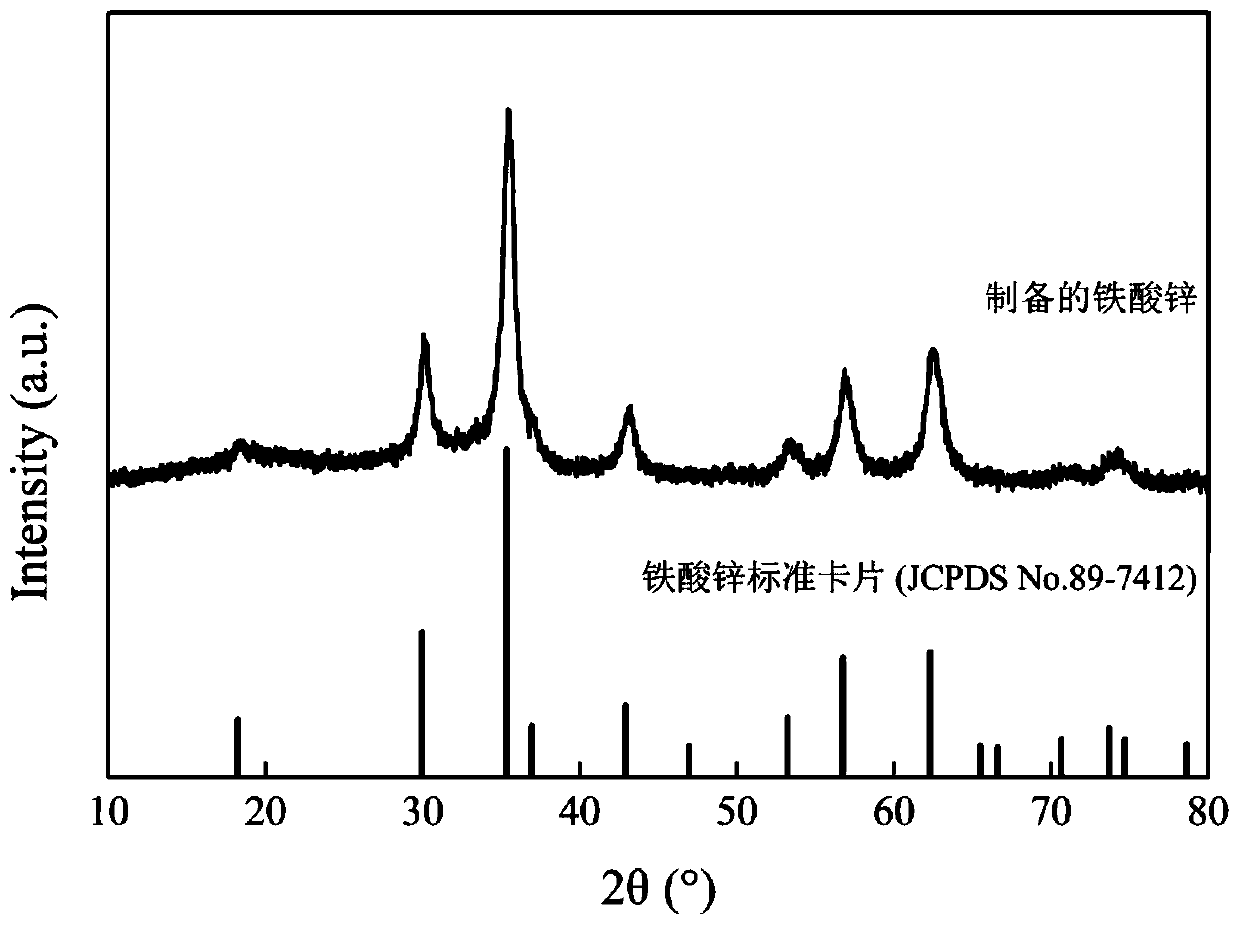
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] A method for preparing zinc ferrite by utilizing waste alkaline zinc-manganese batteries, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0032] (1) Dismantling the waste alkaline zinc-manganese battery to obtain the steel shell of the battery outer layer and the battery cathode zinc paste;
[0033] (2) Dissolve the steel shell and zinc paste in step (1) separately, the solution is 3mol / L sulfuric acid, heat and reflux in a water bath at 80°C for 1 hour, and the solid-to-liquid ratio of the steel shell and sulfuric acid is 1:20 , the solid-to-liquid ratio of zinc paste to sulfuric acid is 1:10;
[0034] (3) the lysate of step (2) is suction-filtered while hot to obtain iron-containing filtrate and zinc-containing filtrate, and respectively measure zinc and iron ion contents in the solution;
[0035] (4) get step (3) gained iron-containing filtrate and zinc-containing filtrate to mix, and add monohydrate citric acid to dissolve and mix, wherein the mol ratio of elemental...
Embodiment 1
[0043] The application of the photocatalyst zinc ferrite prepared in embodiment 1 in the treatment of organic wastewater endocrine disruptor bisphenol A (BPA), the specific steps are as follows:
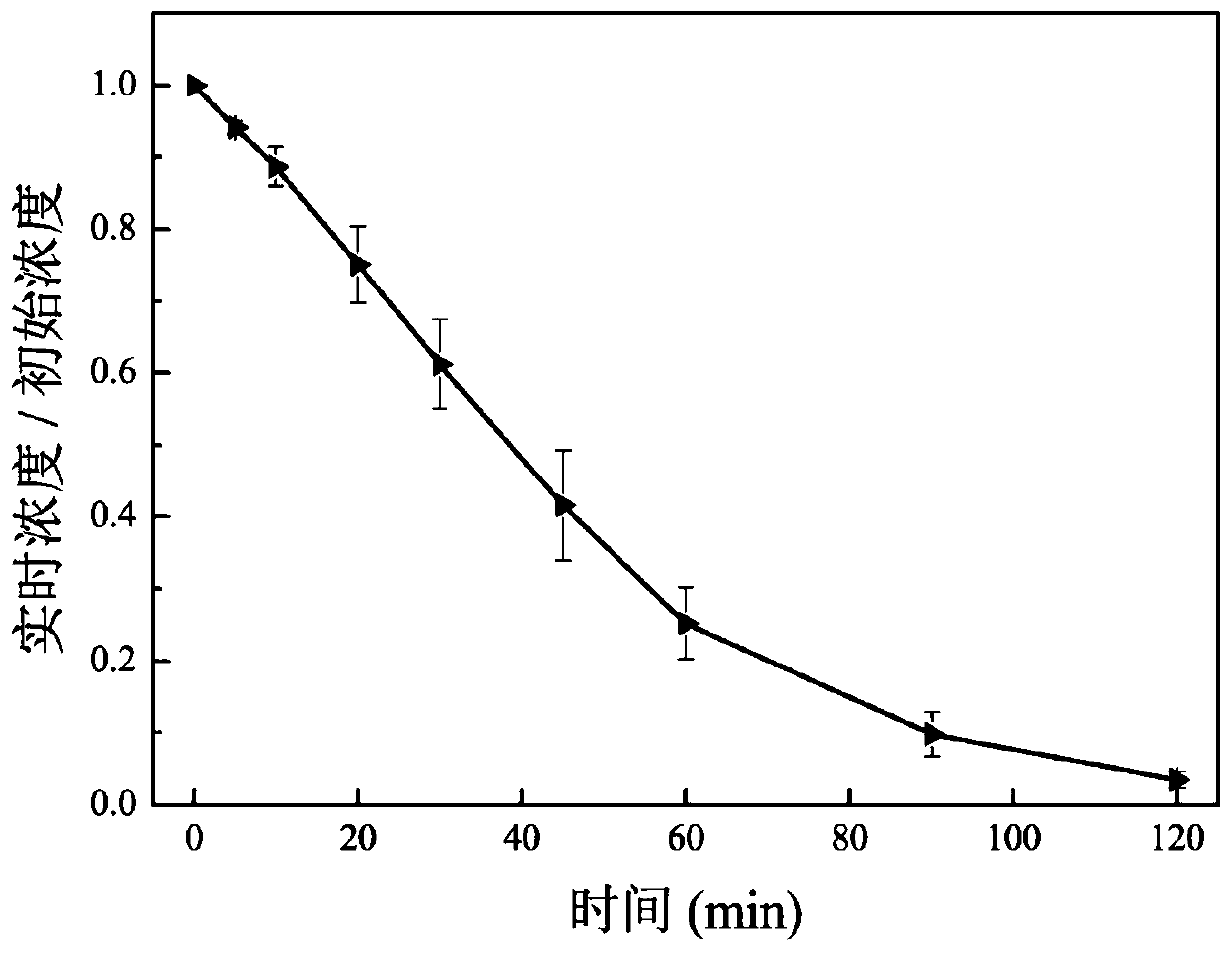
[0044] Put 100mL of simulated wastewater containing BPA (the initial concentration of BPA is 0.1mmol / L) in the photocatalytic reactor, add sodium persulfate (0.5mmol) and zinc ferrite (0.05g), and continuously feed the reactor with circulating cooling Water, react under light conditions (the wavelength of the light source is not less than 400nm) for 120 minutes. During the reaction period, the system was sampled and the content of BPA was determined, and its changes were recorded.
[0045] figure 2 It is the effect diagram of the oxidative degradation of BPA by zinc ferrite in the photoactivated persulfate system in this example. Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that the zinc ferrite photocatalyst activates the persulfate system under visible light conditions, and the degradati...
Embodiment 3
[0047] The application of the photocatalyst zinc ferrite prepared in embodiment 1 in the treatment of organic wastewater endocrine disruptor bisphenol A (BPA), the specific steps are as follows:
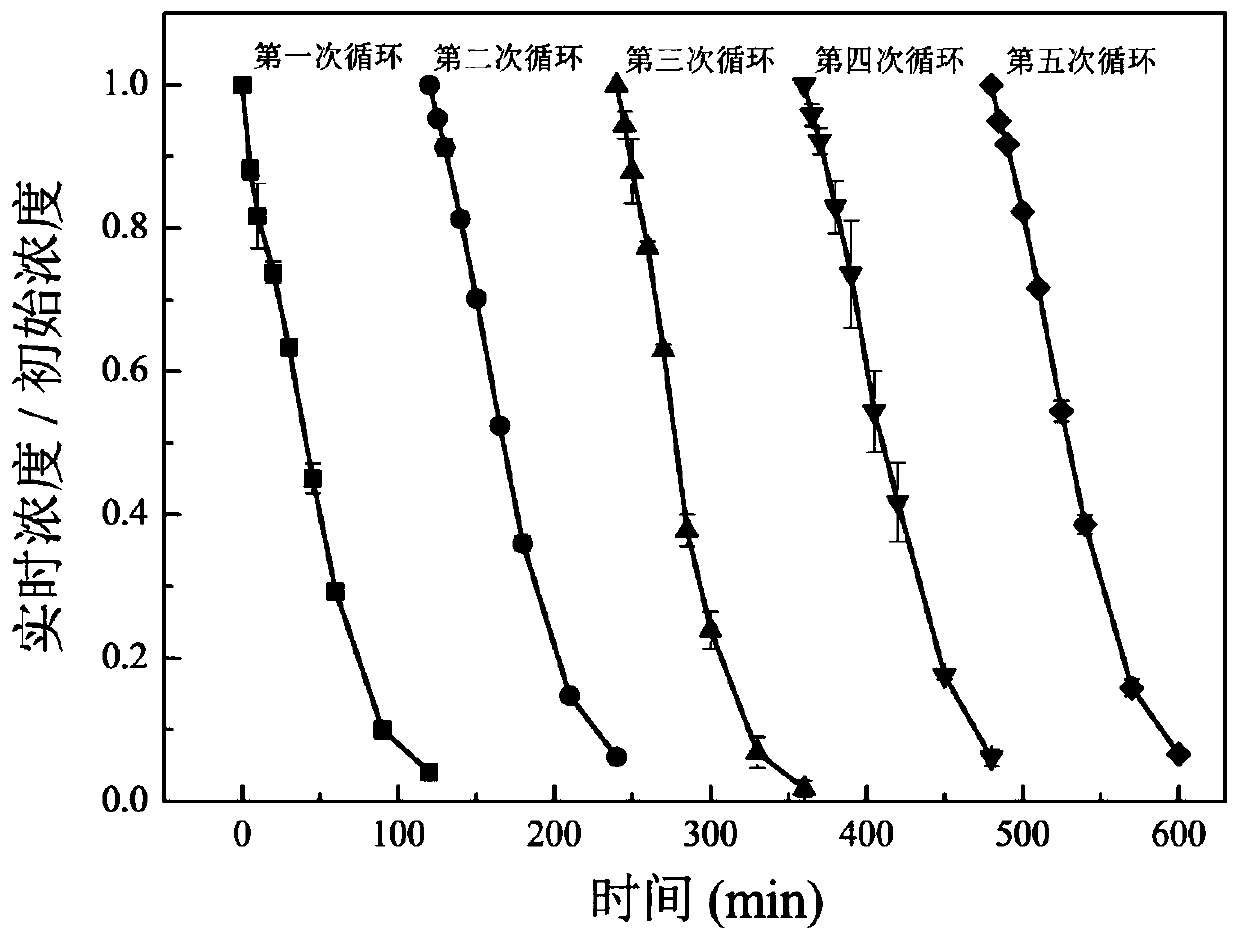
[0048] 100mL of simulated wastewater containing BPA (the initial concentration of BPA is 0.1mmol / L) was placed in the photocatalytic reactor, sodium persulfate (0.1mmol) and zinc ferrite (0.03g) were added, and the reactor was continuously fed with circulating cooling Water, react under light conditions (Xe light source wavelength not less than 400nm) for 120 minutes. During the reaction period, the system was sampled and the content of BPA was determined, and its changes were recorded.
[0049] After the reaction, the solution in the reactor was filtered with suction, and the filter cake was retained and cleaned, dried overnight in an oven at 70°C, collected and stored, and used as a photocatalyst in the second repeated experiment. The catalyst used in the third repeated experiment w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com