Polyamide thermofuse with low melting point and preparation method thereof
A low-melting, hot-melt filament technology, applied in rayon manufacturing, single-component polyamide rayon, fiber chemical characteristics, etc. problems, to achieve high strength and elongation, improve polymerization rate and quality, and accelerate the effect of polymerization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
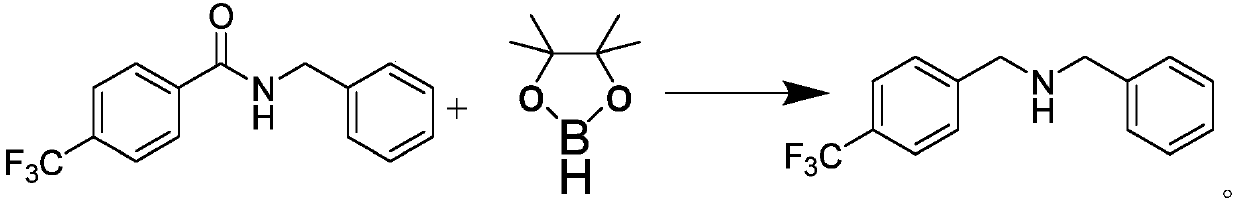
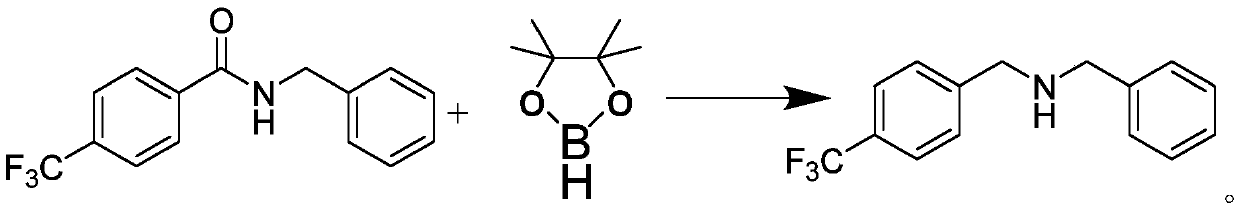
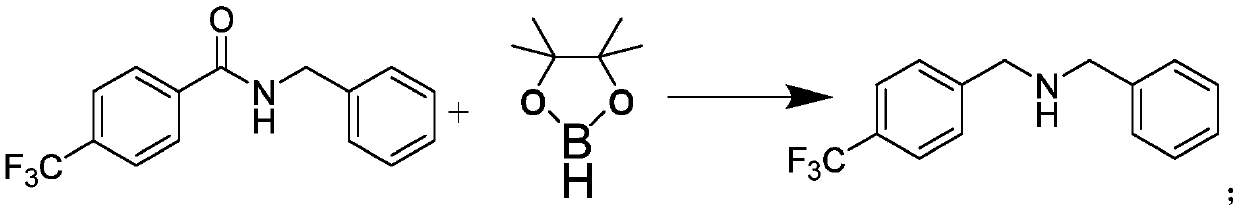
[0038] Preparation of N-benzyl-4-trifluoromethylphenylmethylamine:
[0039] Under nitrogen protection, N-benzyl-4-trifluoromethylbenzamide (0.5mmol), pinacol borane (4.0mmol), rare earth catalyst bis Trimethylsilylamino yttrium (0.05mmol) was stirred and mixed; after mixing evenly, reacted at a temperature of 120°C for 23h to obtain N-benzyl-4-trifluoromethylphenylmethylamine;
[0040] Characterization data: 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ,500MHz,ppm):δ7.60(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.47(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.38-7.33(m,4H),7.31-7.26(m,1H), 3.86(s,2H),3.82(s,2H),1.76(brs,1H). 13 C NMR (CDCl 3,125MHz,ppm):δ144.6,140.1,129.3(q,J=32.3Hz),128.5,128.3,128.2,127.0,125.2(q,J=3.8Hz),124.4(q,J=271.9Hz),53.2, 52.6. The structural formula of N-benzyl-4-trifluoromethylphenylmethylamine is Its reaction formula is:
[0041]
Embodiment 2
[0043] A low-melting nylon hot-melt yarn, comprising the following components by weight:
[0044] 100 parts of polybasic acid;
[0045] 80 parts of polyamine;
[0046] 15 parts of modifier;
[0047] 2 parts of palladium catalyst;
[0048] 3 parts of dispersant;
[0049] Anti-aging agent 2 parts;
[0050] 1 part of defoamer;
[0051] Described polybasic acid is the mixture of oxalic acid, sebacic acid and dodecanedioic acid, and its mass ratio is 1:4:2;
[0052] The polyamine is a mixture of decanediamine, 12-lactam and N-(3-aminopropyl)-N-dodecyl-1,3-propanediamine, the mass ratio of which is 3:1:1.
[0053] The modifier is a mixture of N-benzyl-4-trifluoromethylphenylmethylamine and 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether, and its mass ratio is 1:1;
[0054] The structural formula of the 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether is
[0055] The N-benzyl-4-trifluoromethylphenylmethanamine is prepared from Example 1.
[0056] The palladium catalyst is two (dibenzylideneacetone) palladium;
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0069] A low-melting nylon hot-melt yarn, comprising the following components by weight:
[0070] 100 parts of polybasic acid;
[0071] 80 parts of polyamine;
[0072] 12 parts of modifier;
[0073] 1 part of palladium catalyst;
[0074] 2 parts of dispersant;
[0075] 1 part anti-aging agent;
[0076] 1 part of defoamer;
[0077] Described polybasic acid is the mixture of oxalic acid, sebacic acid and dodecanedioic acid, and its mass ratio is 1:4:2;
[0078] The polyamine is a mixture of decanediamine, 12-lactam and N-(3-aminopropyl)-N-dodecyl-1,3-propanediamine, the mass ratio of which is 3:1:1.
[0079] The modifier is a mixture of N-benzyl-4-trifluoromethylphenylmethylamine and 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether, and its mass ratio is 1:1;
[0080] The structural formula of the 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether is The N-benzyl-4-trifluoromethylphenylmethanamine is prepared from Example 1.
[0081] The palladium catalyst is tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium.
[0082] The di...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com