Patents
Literature
52 results about "Dibenzylideneacetone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
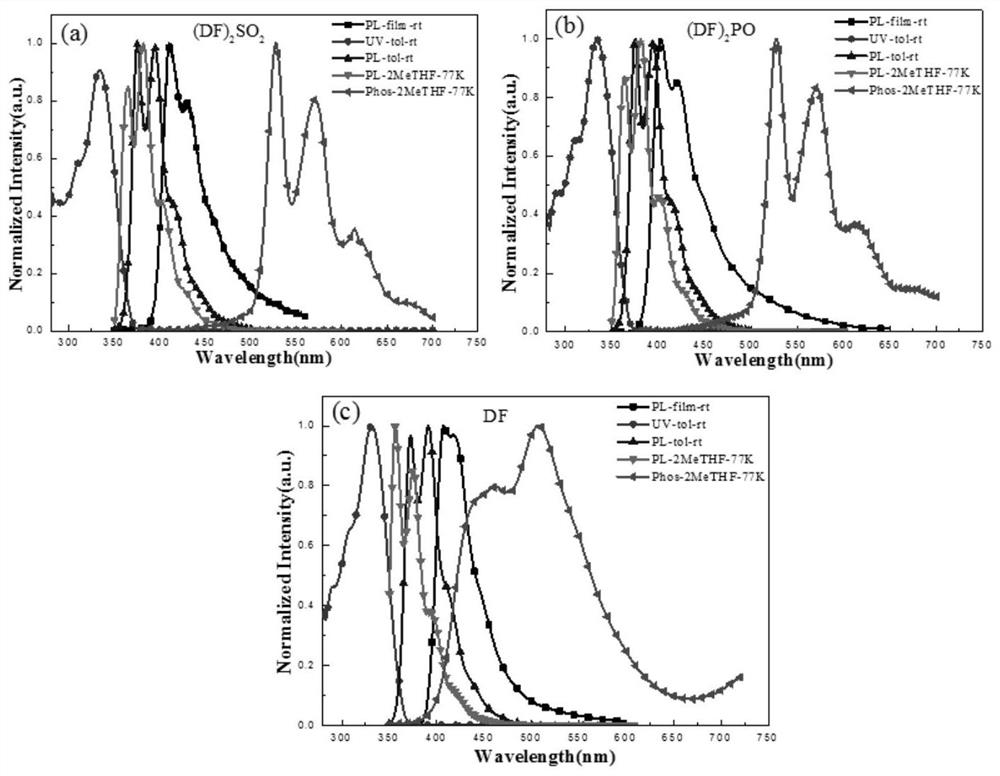
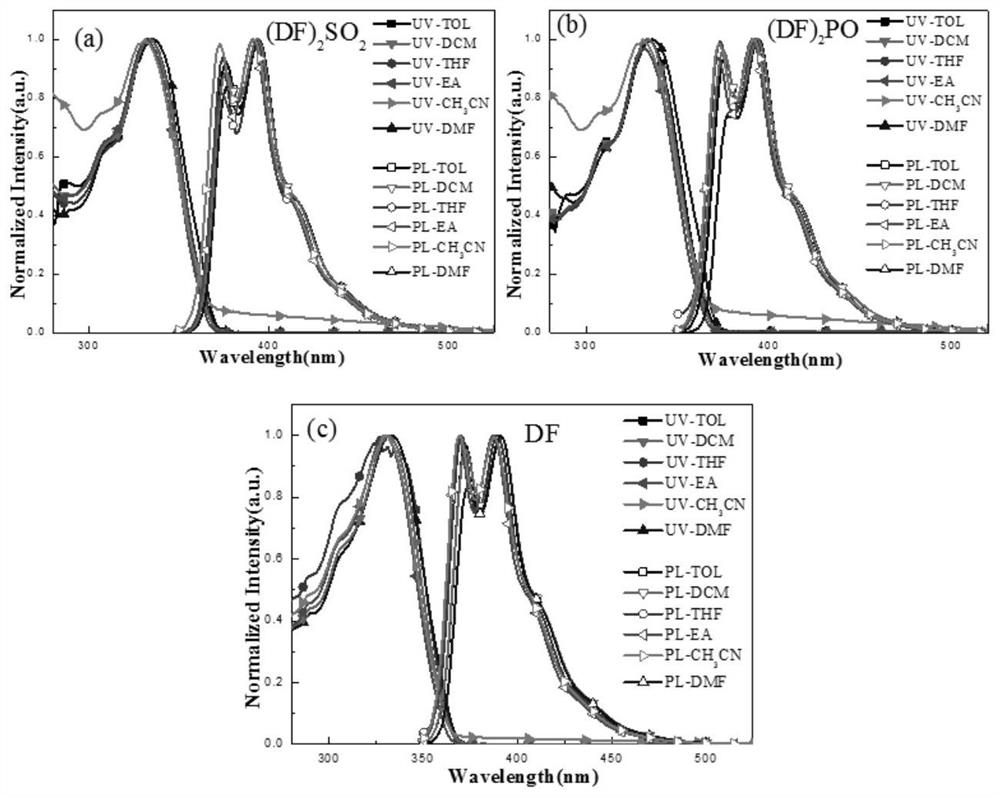
Dibenzylideneacetone or dibenzalacetone, often abbreviated dba, is an organic compound with the formula C₁₇H₁₄O. It is a pale-yellow solid insoluble in water, but soluble in ethanol. Dibenzylideneacetone is used as a component in sunscreens and as a ligand in organometallic chemistry.
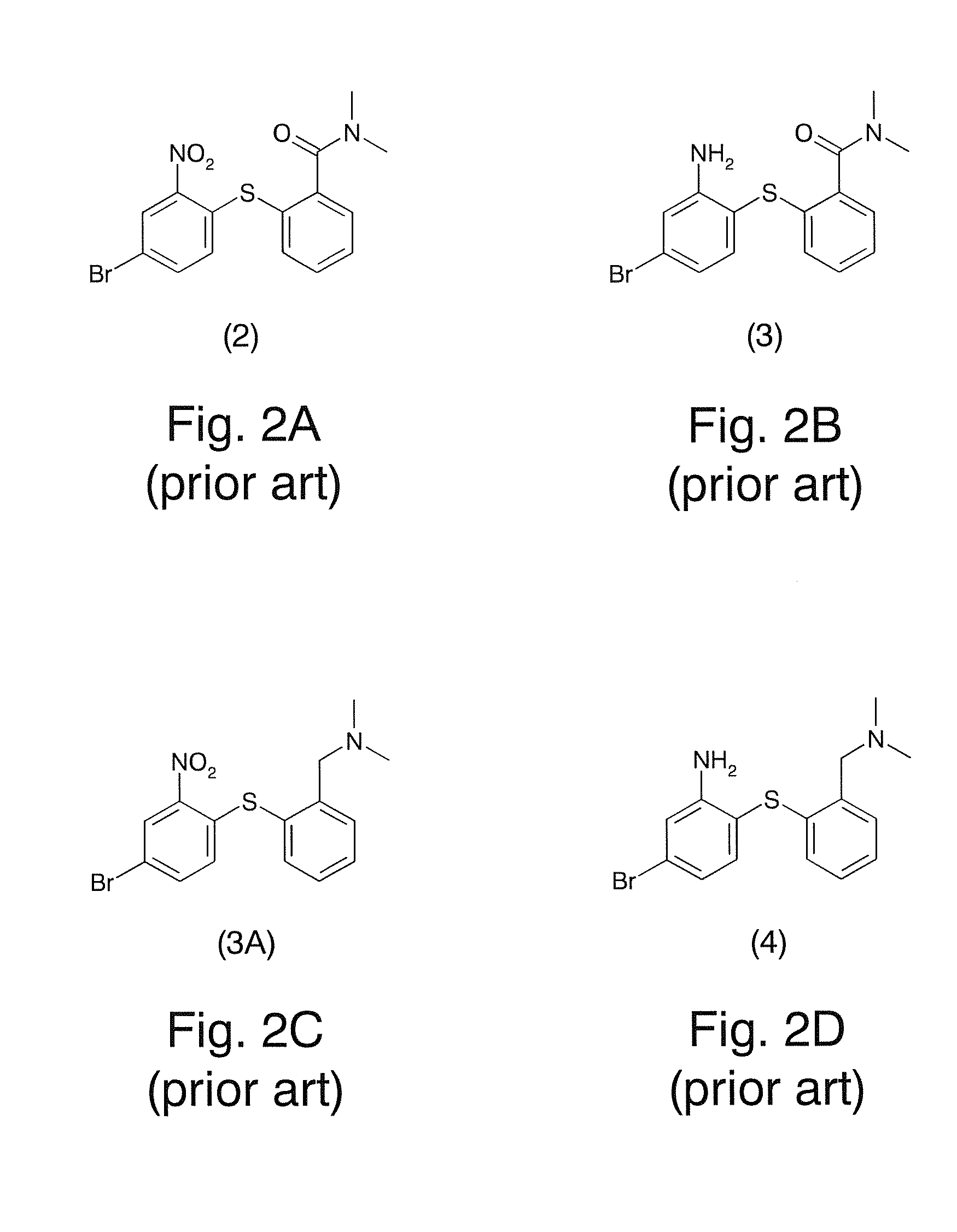
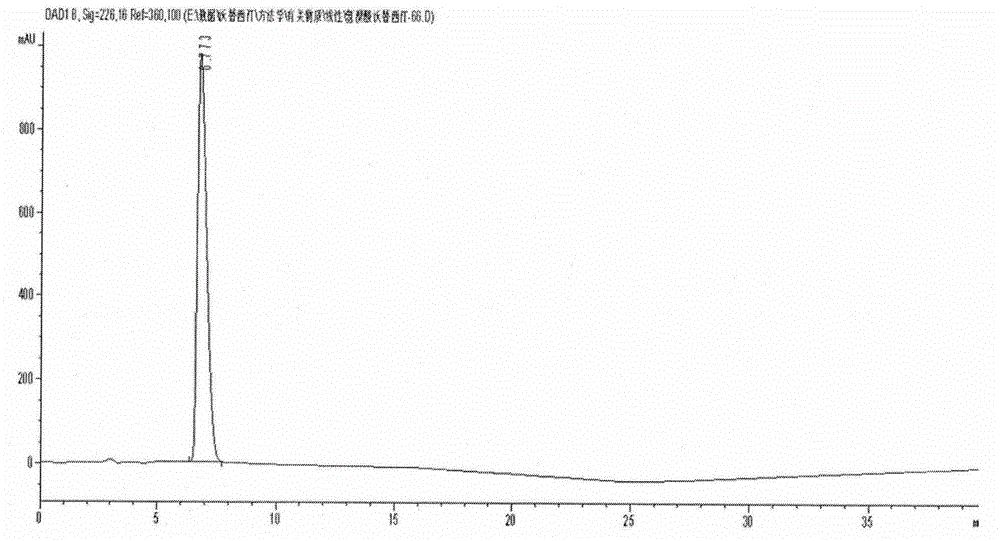
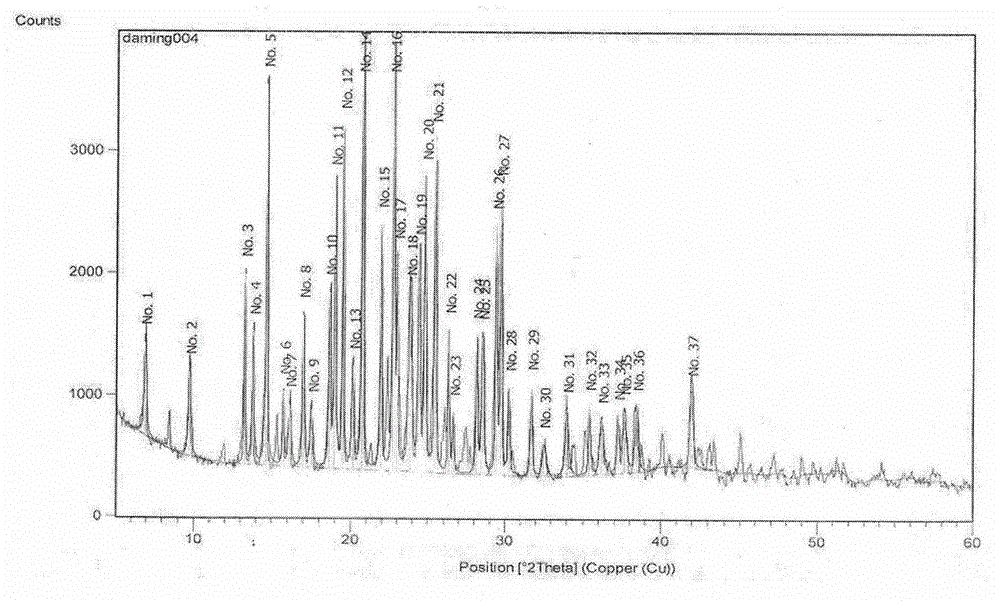
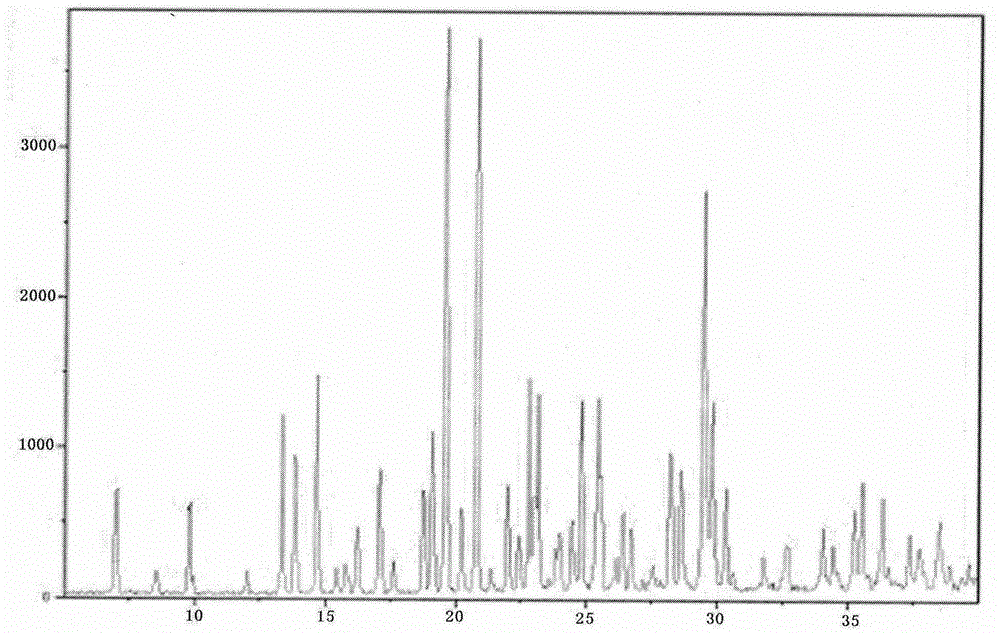
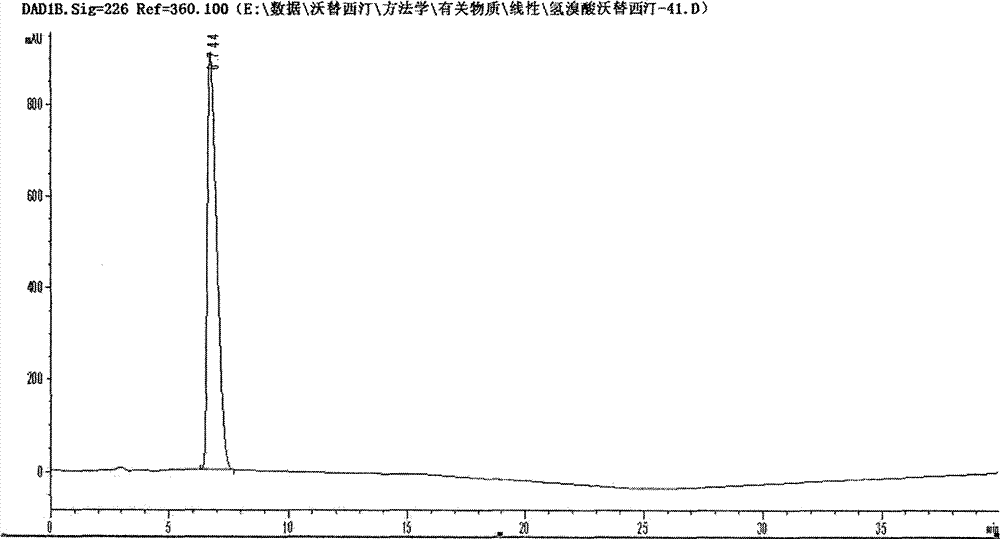
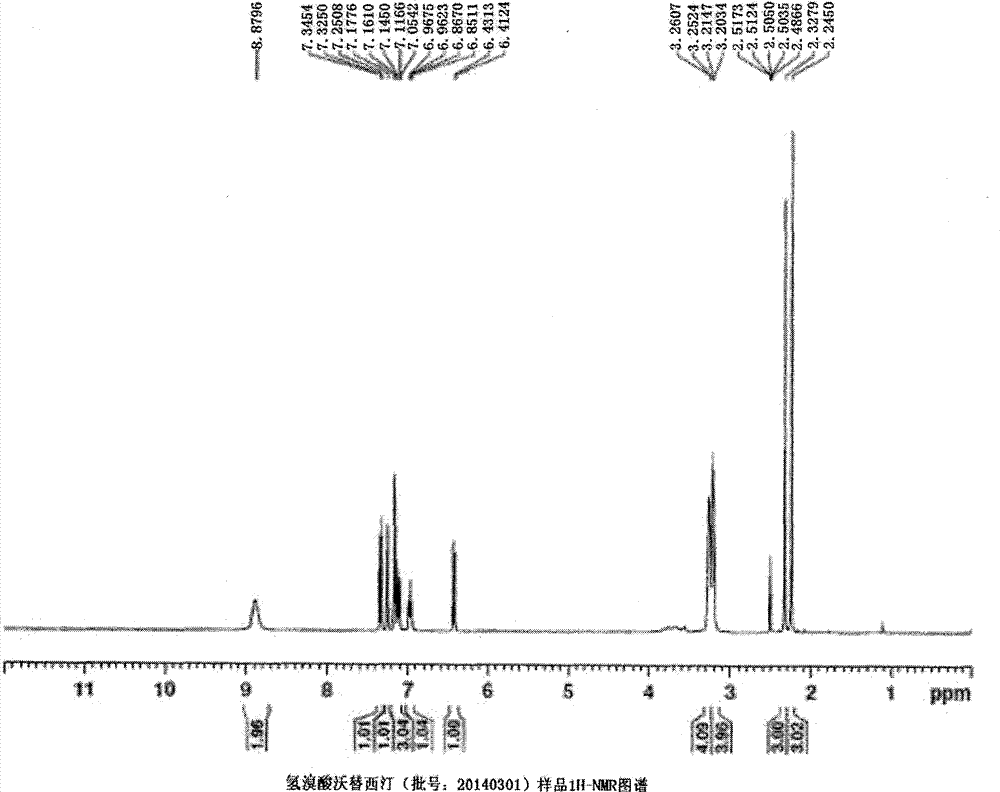
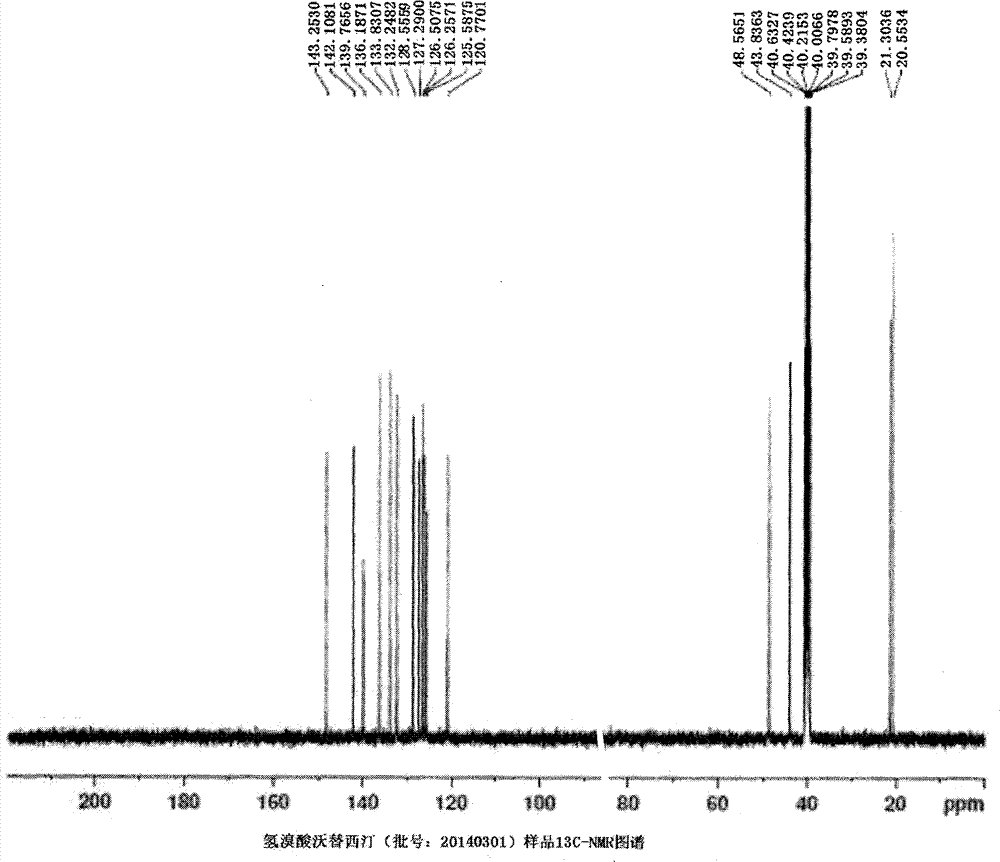
Novel preparation method of hydrobromic acid Vortioxetine beta crystalline form
The invention discloses a novel preparation method of a hydrobromic acid Vortioxetine beta crystalline form. The novel preparation method comprises the steps of firstly synthesizing 2-(2,4-dimethyl-phenylsulfanyl)chlorobenzene from 2-chlorobenzenethiol and 2,4-dimethylphenol, adding bi(dibenzylidene acetone)palladium, 1,1'-binaphthyl-2,2'-bisdiphenylphosphino, sodium tert-butoxide and toluene into a reaction bottle, mixing, adding other substances to prepare Vortioxetine, dissolving prepared Vortioxetine by virtue of ethyl acetate with the weight of 14-16 times of that of Vortioxetine to obtain rough hydrobromic acid Vortioxetine, and finally purifying rough hydrobromic acid Vortioxetine to obtain finished hydrobromic acid Vortioxetine. The preparation method has the beneficial effects that the raw materials are easily available, process reaction conditions are mild, a product is high in yield and purity, and industrial production is easily realized; prepared hydrobromic acid Vortioxetine is white crystalline powder, and the purity is more than 99.5%.
Owner:郑州大明药物科技有限公司
Norbornene, acrylonitrile and vinyl acetate ternary polymerization catalyst and ternary polymerization method
ActiveCN105924548AEasy to wash and separateGood lithography performanceAcrylonitrileCarvacryl acetate
The invention relates to a norbornene, acrylonitrile and vinyl acetate ternary polymerization catalyst and a ternary polymerization method. The preparation method of the catalyst is characterized by comprising the following steps that tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium, a ligand and titanium tetrachloride are dissolved into a first solvent in a three-mouth flask in a dry inert atmosphere, an electric stirrer is installed to stir the materials, constant-temperature stirring is conducted for 20 min to 60 min at the speed of 130 rpm to 170 rpm at the temperature of 20 DEG C to 60 DEG C, and then a palladium-titanium complex catalyst is obtained; norbornene, acrylonitrile and vinyl acetate monomers are taken according to the molar ratio of 1:1:1, added into a high-pressure kettle which is vacuumized and subjected to nitrogen filling for many times and dissolved by adding a second solvent; the palladium-titanium complex catalyst is added, and reacting is conducted for 1 hour to 8 hours at the temperature of 20 DEG C to 150 DEG C under the pressure of 0.1 MPa to 8 MPa; a product obtained through reacting is poured into an ethanol solution containing 4 wt%-5 wt% of hydrochloric acid, an obtained precipitate is washed with ethanol until the precipitate is neutral, vacuum drying is conducted, and then the norbornene, acrylonitrile and vinyl acetate terpolymer is obtained.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Palladium catalyst system comprising zwitterion and/or acid-functionalized ionic liquid
InactiveCN102625731AOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPalladium catalystIonic liquid
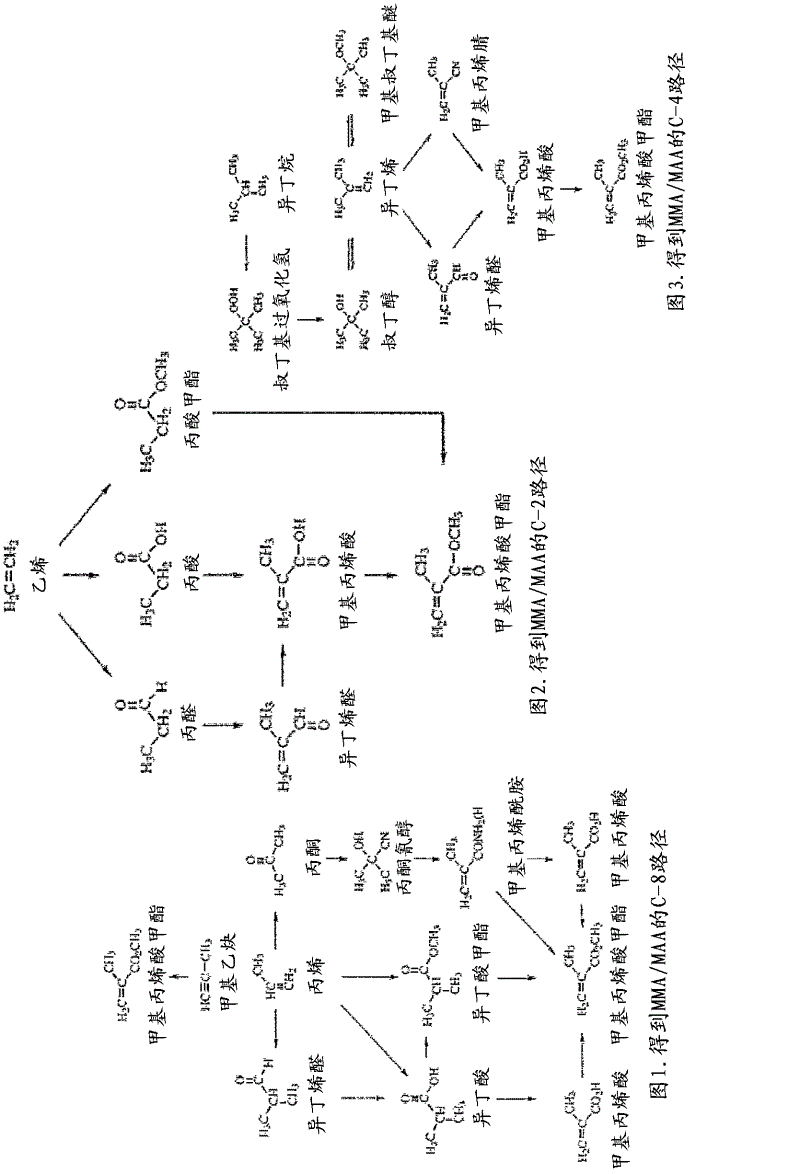
The present invention concerns a catalyst system in particular a catalyst system comprising Palladium (Pd), a zwitterion and / or an acid-functionalized ionic liquid, and one or more phosphine ligands, wherein the Pd catalyst can be provided by a complex precursor, such as Pd(CH3COO)2, PdCI2, Pd(CH3COCHCOCH3), Pd (CF3COO)2, Pd(PPh3)4 or Pd2(dibenzylideneacetone)3. Such catalyst systems can be used for e.g. alkoxycarbonylation reactions, carboxylation reactions, and / or in a co-polymerization reaction, e.g. in the production of methyl propionate and / or propanoic acid, optionally in processes forming methyl methacrylate and / or methacrylic acid. Catalyst systems according to the invention are suitable for reactions forming separable product and catalyst phases and supported ionic liquid phase SILP applications.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
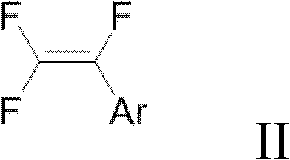
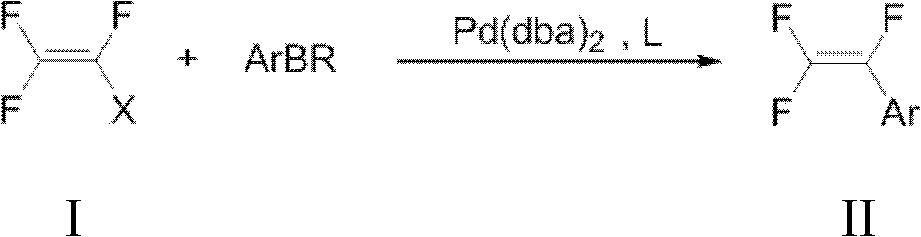
Preparation method of trifluorostyrene compound
ActiveCN103373897AAmino preparation from aminesCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationArylDibenzylideneacetone
The invention provides a synthesis method of a trifluorostyrene compound. According to the method provided by the invention, the trifluorostyrene compound can be synthesized from an accessible fluorin containing raw material and various substituted arylboronic acid compounds in an alkali condition by using a phosphine ligand or a multiphosphine ligand and using bis(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium as a catalyst. By adopting the method provided by the invention, the fluorine spectrum yield is extremely improved, while the use amount of the catalyst is obviously reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of high-purity vortioxetine hydrobromide
ActiveCN104725335ARaw materials are easy to getProcess reaction conditions are mildOrganic chemistryChlorobenzene2-Chlorophenol
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-purity vortioxetine hydrobromide. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, synthesizing 2-(2,4-dimethyl phenyl sulfanyl) chlorobenzene from 2-chlorophenol and 2,4-dimethylbenzenethiol; then, adding di(dibenzylideneacetone)palladium, 1,1'-binaphthyl-2,2'-bis(diphenyl phosphine), sodium tert-butoxide, and methylbenzene into a reaction bottle to mix, and adding other materials so as to prepare vortioxetine; and dissolving the prepared vortioxetine by using 14-16 times of ethyl acetate, so that a vortioxetine hydrobromide coarse product is obtained; and finally, purifying the coarse product so as to obtain a vortioxetine hydrobromide fine-product. The method disclosed by the invention is easily-obtained in raw materials, mild in process reaction conditions, high in product yield, high in product purity, and convenient for industrial production. Prepared vortioxetine hydrobromide is white crystalline powder, and the purity is more than 99.5%.
Owner:郑州大明药物科技有限公司
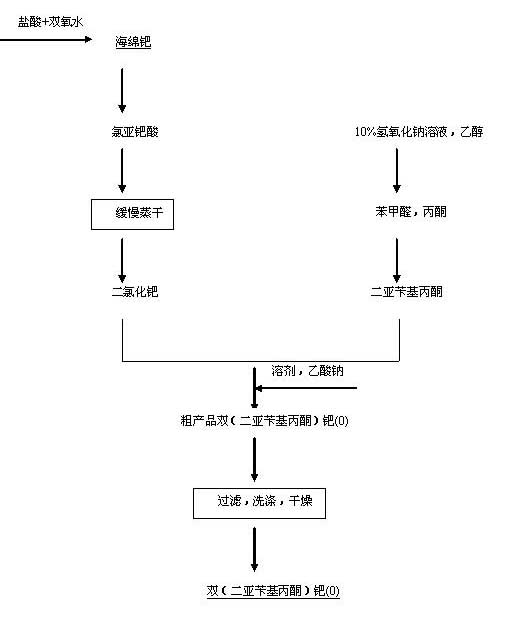
Preparation method of di(dibenzalacetone)palladium(0)
ActiveCN102010445ASimple production processGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsOrganic synthesisPalladium catalyst
A preparation method of di(dibenzalacetone)palladium(0) relates to a preparation method of a zerovalent palladium catalyst, namely di(dibenzalacetone)palladium(0) which is used in the catalytic hydrogenation, coupling, carbonylation, cyclotrimerization of alkynes and other aspects of the organic synthesis. The invention is characterized in that the preparation process is as follows: under nitrogen atmosphere, palladium dichloride and ligand dibenzalacetone are stirred to react in absolute alcohol, suction filtering is performed, absolute alcohol, water and acetone are used for cleaning, and finally the product can be obtained through drying. In the preparation method in the invention, palladium dichloride, dibenzalacetone and anhydrous sodium acetate are fed at once to synthetize di(dibenzalacetone)palladium(0) in absolute alcohol solvent through one pot method; and the key point of the technology is as follows: the molar ratio of palladium dichloride and dibenzalacetone is strictly controlled so as to obtain the pure di(dibenzalacetone)palladium(0) product. By adopting the method in the invention, the production technology can be effectively simplified and the method is environment-friendly.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
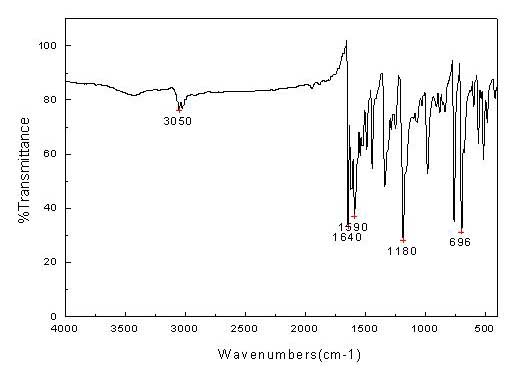
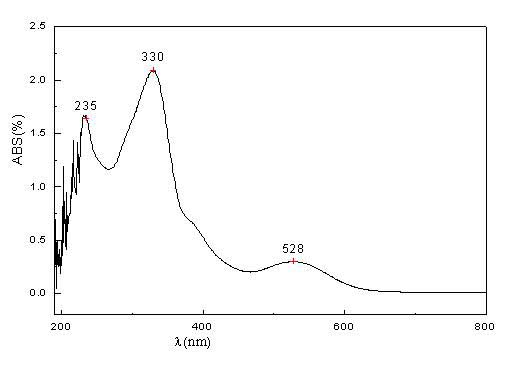
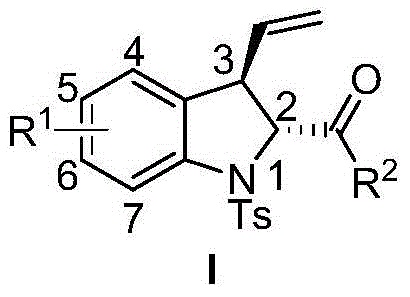
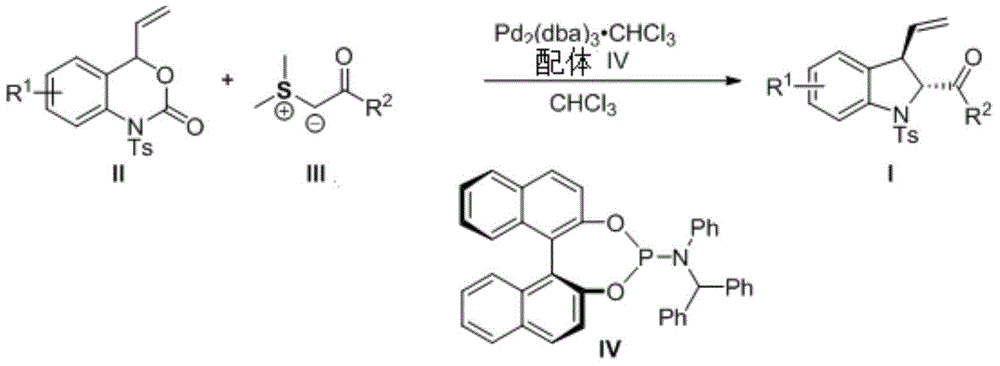
3-vinyl indoline derivatives with optical activity and asymmetric synthesis method of same
The invention relates to 3-vinyl indoline derivatives with optical activity and an asymmetric synthesis method of the same. The 3-vinyl indoline derivatives have a structural formula as shown in a general formula I (described in the specification), wherein R1 is hydrogen, 4-fluorine, 5-methyl, 5-methoxyl, 5-bromine, 6-chlorine and 7-fluorine; and R2 is phenyl, p-methoxyphenyl, p-methylphenyl, p-fluorophenyl, p-chlorphenyl, o-fluorophenyl, m-bromophenyl, 2-thiophene, 2-furan, ethyoxyl, styryl and isobutyl. The synthesis method of the 3-vinyl indoline derivatives comprises the step of carrying out a decarboxylation allylation / cyclizing series reaction on compounds which are as shown in a general formula II and a general formula III in a chloroform solvent in presence of a metal catalyst tris(dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium chloroform adduct and a ligand IV. The synthesis method of the 3-vinyl indoline derivatives has the advantages that a cycloaddition manner is adopted, the 3-vinyl indoline derivatives with the optical activity can be efficiently synthesized with high enantioselectivity through one-step operation only, the yield is 63-99%, dr is more than 99.5% and ee is 83-99%.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method of high-sterically-hindered arylborate compound
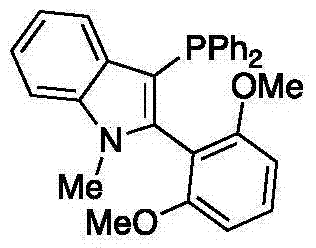
InactiveCN104327106AAir stabilizationEasy to synthesizeGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsCaesium acetateAldehyde
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-sterically-hindered arylborate compound. The preparation method includes following steps: in the presence of a catalyst of a catalyst tri(dibenzalacetone)dipalladium with a phosphine ligand (wherein the phosphine ligand is 3-diphenylphosphine-2-(2,6-dimethoxylphenyl)-N-methylindole), adding an aryl chloride, bis(neopentyl glycolato)diboron, and an additive ceseium acetate to a 1,4-dioxane solution; and carrying out a reaction at 100-130 DEG C for 12-48 hours to obtain the arylborate compound. In the invention, the employed substrate is stable, is low in cost and is easy to obtain and the catalyst is unique, is easy to prepare and is suitable for the reaction of the high-sterically-hindered aryl chloride. The system is compatible of existences of functional groups, such as an ester group, an aldehyde group, methoxyl and the like so that range of the substrate is greatly developed. The catalyst system is stable, is high in catalytic activity, is wide in suitable scope, is good in selectivity and is mild in reaction conditions. The high-sterically-hindered arylborate compound can be widely applied in cross coupling reaction catalyzed by transition metal, thereby preparing various compounds, such as biaromatic hydrocarbons. The preparation method has a great application potential in synthesis of natural medicines and drug intermediates.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV SHENZHEN RES INST
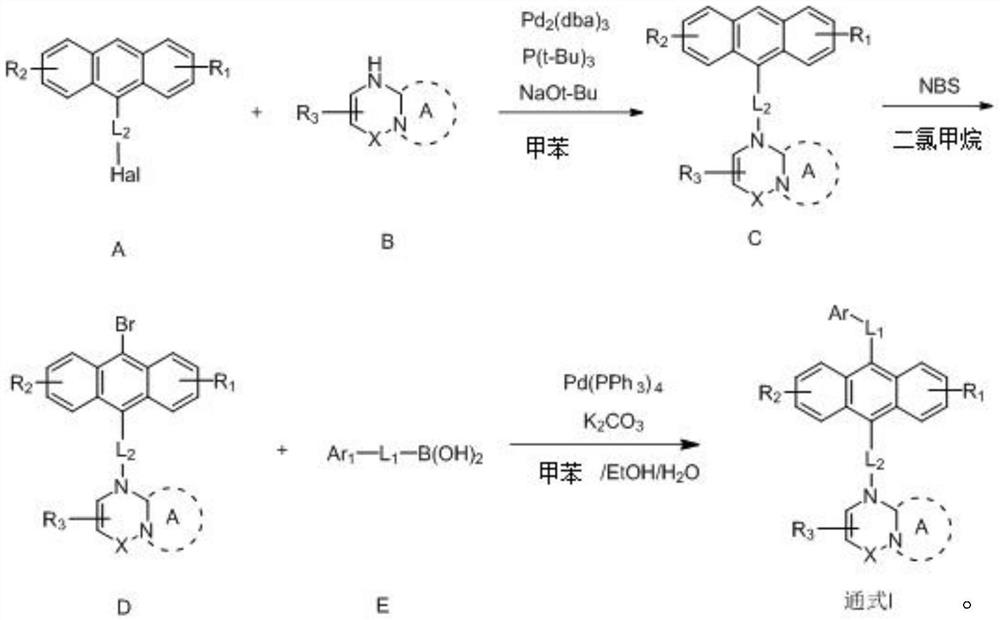
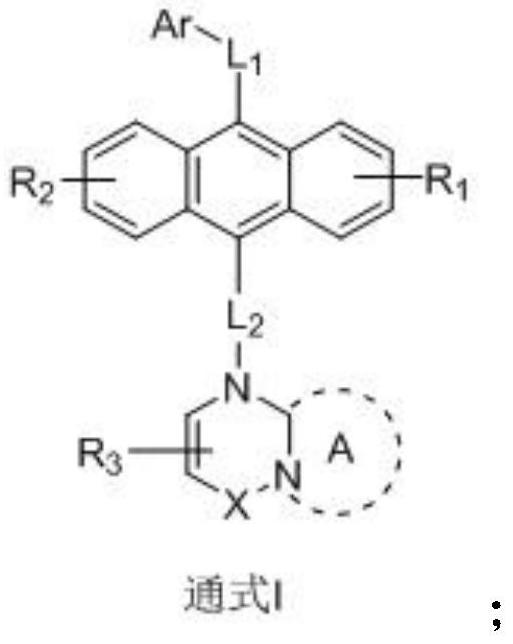
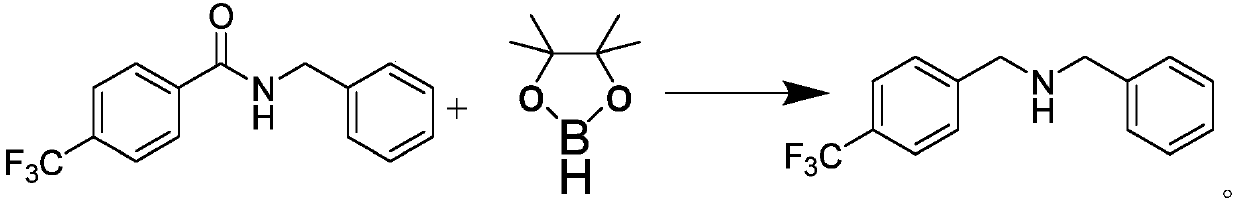
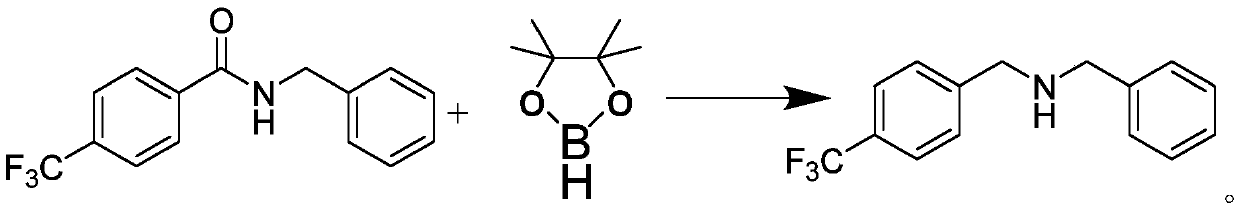
Anthracene nitrogen-containing organic light-emitting compound and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112142672AGood electron transport propertiesImprove luminous performanceOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesBenzylideneacetoneTert butyl
The invention discloses an anthracene nitrogen-containing organic light-emitting compound and a preparation method and application thereof, the specific structure of the anthracene nitrogen-containingorganic light-emitting compound is as shown in the general formula 1 in the specification, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: taking methylbenzene as a solvent; reacting the raw material A with the raw material B in the presence of sodium tert-butoxide, tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium and tris(tert-butyl)phosphorus to obtain an intermediate product C, reacting the intermediate product C with NBS by taking dichloromethane as a solvent to obtain an intermediate product D, and reacting the intermediate product D with a mixed solution of methylbenzene, ethanol and water by taking a mixed solution of methylbenzene, ethanol and water as a solvent; and reacting the intermediate product D with a raw material E in the presence of potassium carbonate and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium to finally obtain the compound shown in the general formula I. The anthracene derivative provided by the invention has relatively high electron transmission performance, and can improve the electron transmission efficiency of a device and can prolong the service life of the device when being applied to an organic electroluminescent device. In addition, the preparation method provided by the invention is simple, easy to operate and suitable for industrial popularization.
Owner:JILIN OPTICAL & ELECTRONICS MATERIALS
Polyamide thermofuse with low melting point and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111074370ALow melting pointMeet the needs of actual production and lifeArtifical filament manufactureMonocomponent polyamides artificial filamentPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
The invention discloses polyamide thermofuse with a low melting point and a preparation method thereof. A polymerization reaction is conducted by using polyatomic acid and polyamine as reagents, and meanwhile auxiliaries such as modifier, palladium catalyst and defoamer are added; the polyatomic acid is the mixture of oxalic acid, sebacic acid and dodecanedioic acid; the polyamine is the mixture of decamethylene diamine, PA-12 and N-(3-aminopropyl)-N-dodecyl-1; the modifier is the mixture of N-benzyl-4-trifluoromethyl phenylmethylamine and 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether; the palladium catalyst isbis(dibenzylideneacetone)palladium or tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium; and the defoamer is polydimethylsiloxane or ethylene glycol siloxane. The prepared thermofuse has the low melting point, and meanwhile has large intensity and elongation, still has the large intensity and elongation even being irradiated with ultraviolet light for a long time, and can meet actual needs of production and life.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Novel palladium complexes inhibit n-myristoyltransferase activity in vitro and cancer growth in vivo
ActiveUS20100076076A1BiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsTris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladiumBiological activation
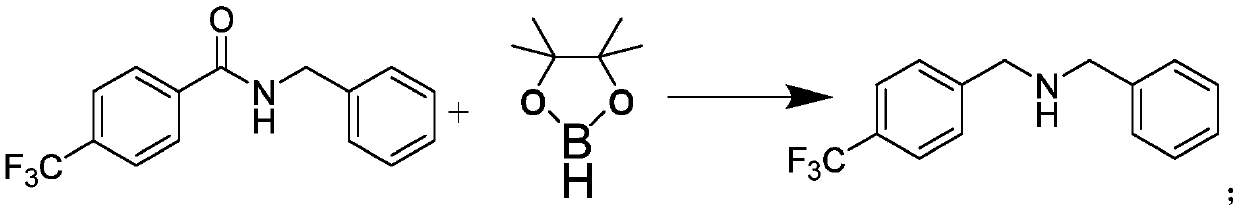
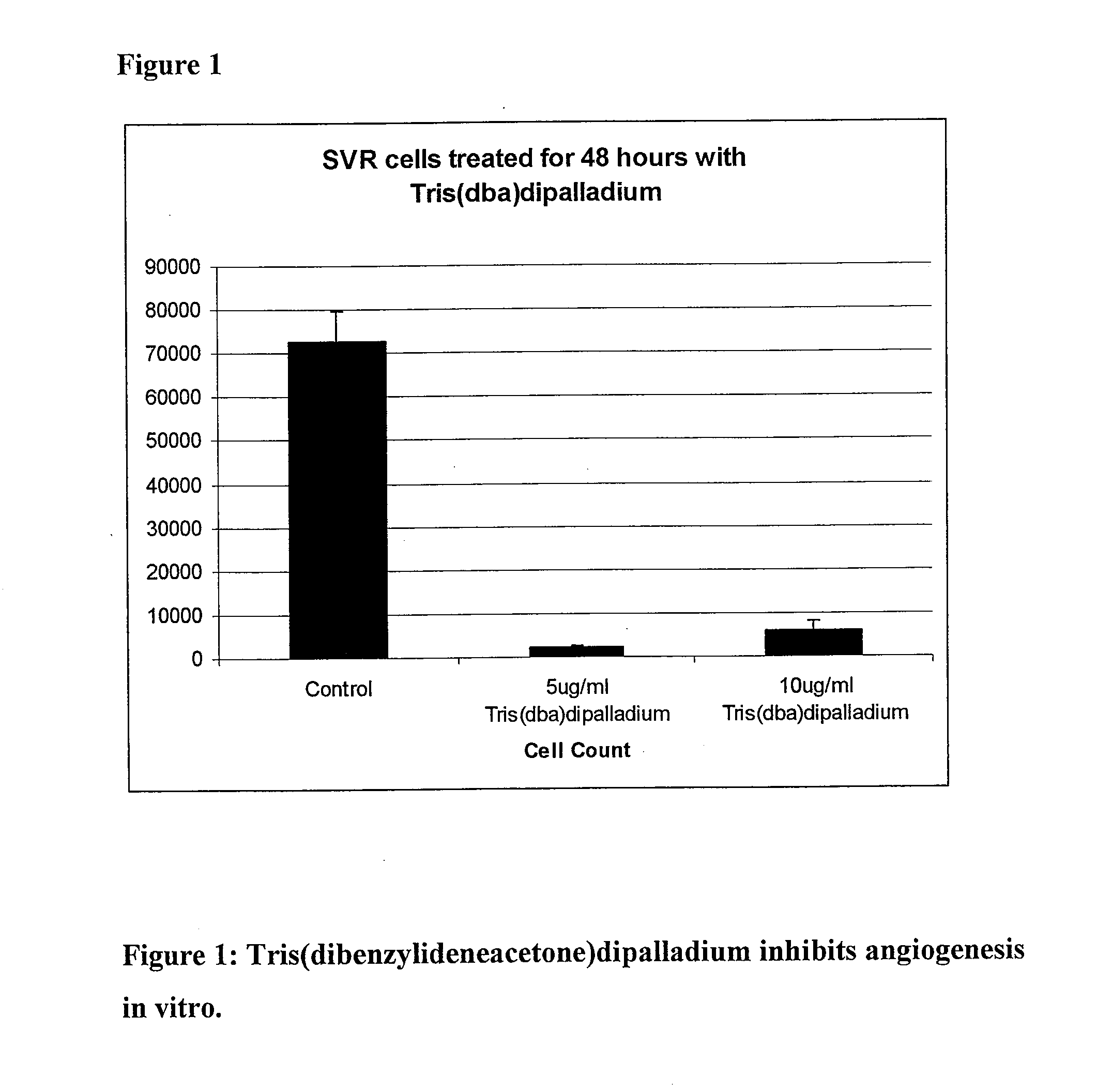
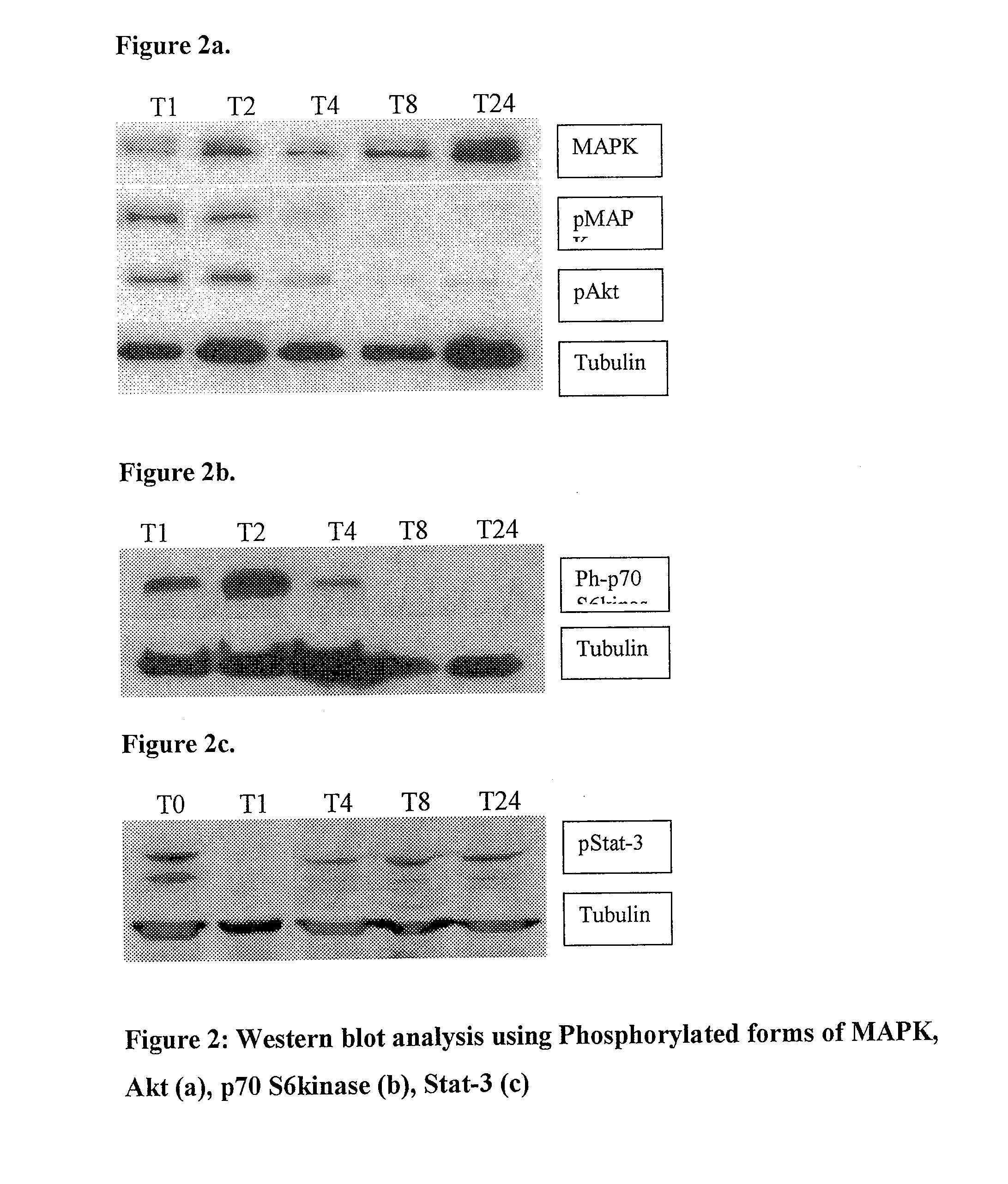
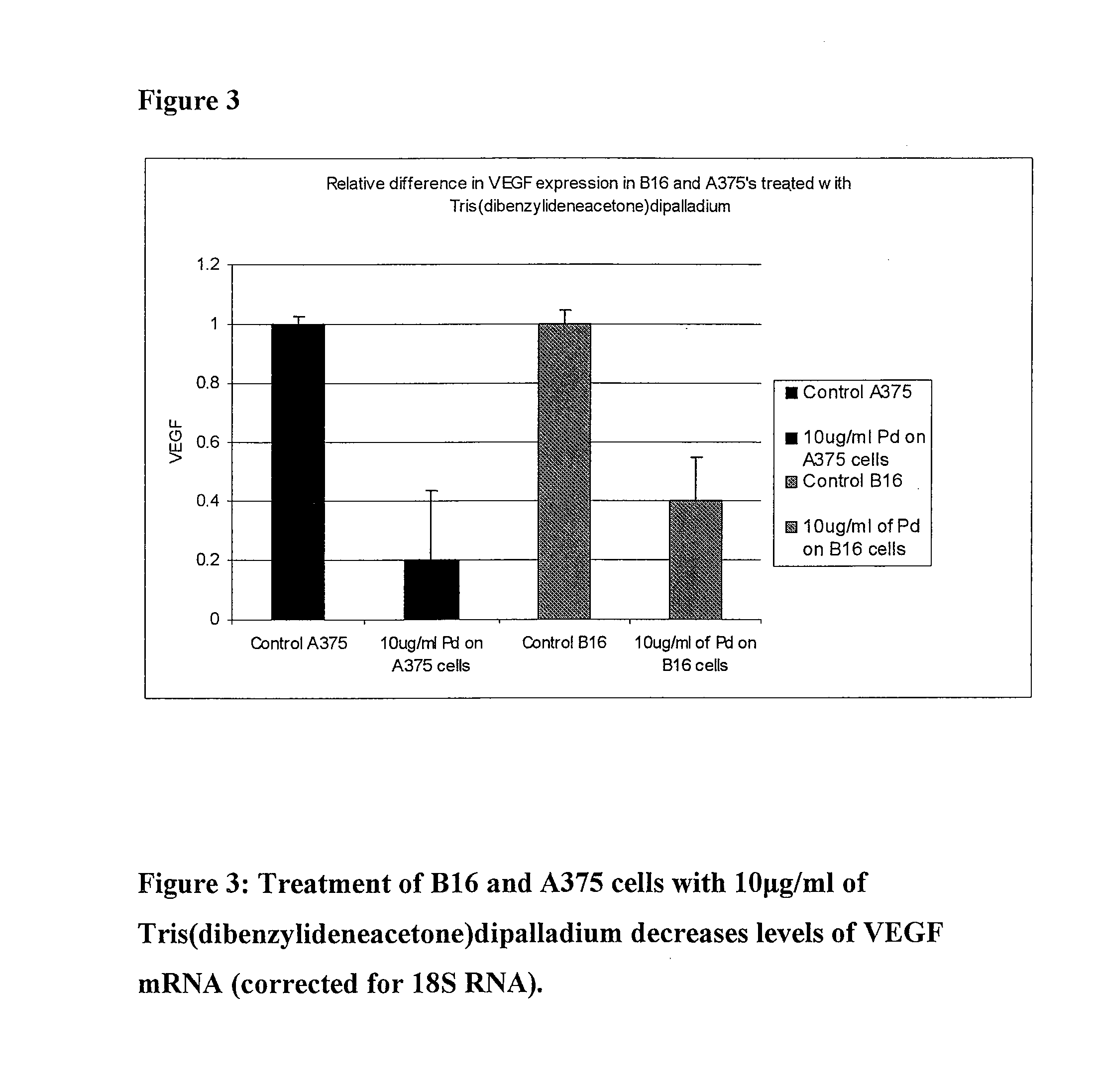
Melanoma is a solid tumor that is notoriously resistant to chemotherapy, and its incidence is rapidly increasing. Recently, several signaling pathways have been demonstrated to contribute to melanoma tumorigenesis, including constitutive activation of MAP kinase, Akt and stat-3. The activation of multiple pathways may account in part for the difficulty in treatment of melanoma. In a recent screen of compounds, we found that an organopalladium complex showed significant antiproliferative activity against melanoma cells. This complex, tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium (Tris DBA), has activity against B16 murine and A375 human melanoma in vivo. Tris DBA inhibits several signaling pathways including activation of MAP kinase, Akt, stat-3 and S6 kinase activation. Tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium is thus a novel compound that is a member of a class of noble metal complexes with potential antitumor activity. Further preclinical evaluation of TrisDBA and related complexes is warranted.
Owner:ARBISER JACK
Dibenzo[c,e]azepine derivative and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110590666AReduce consumptionProtect healthOrganic chemistryN dimethylformamideReaction temperature
The invention discloses a dibenzo[c,e]azepine derivative and a preparation method thereof. The derivative is prepared by using [1,1'-biphenyl]-2,2'-dinitrile and an aryl boronic acid as reactants; thereagents are easy to prepare, have relatively wide sources, relatively low cost, and relatively low toxicity, and is not easy to affect human health. The reaction is performed in a solvent, and the solvent is any one of toluene, xylene, methanol, tetrahydrofuran, N,N-dimethylformamide, and N,N-dimethylacetamide. When the reaction is carried out, a palladium catalyst and an acid promoter are added, wherein the palladium catalyst is any one of palladium trifluoroacetate, tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) palladium, diacetylacetone palladium, bis(dibenzylideneacetone) palladium, and tris(dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium. A reaction temperature is 100-120 DEG C, a reaction time is 20-30 h, and reaction conditions are mild, easy to reach, and safe. The method can directly synthesize a target product without separating intermediate products, and the yield can be up to 95%.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
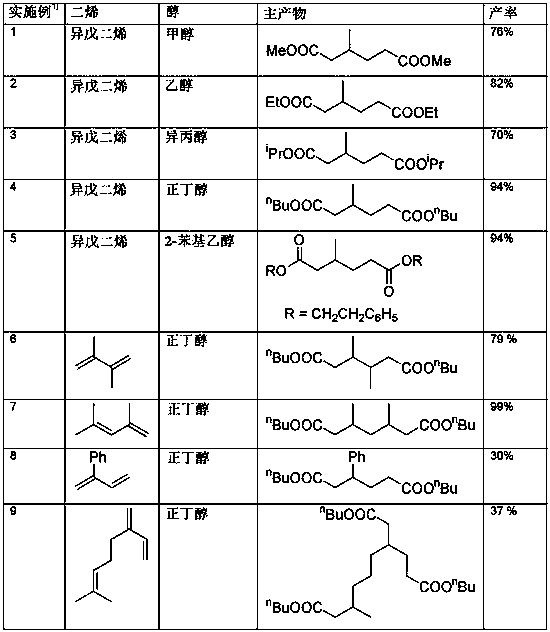
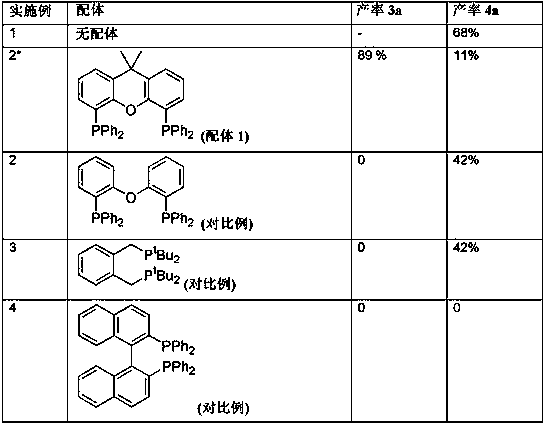
Method for preparing di- or tricarboxylic esters by alkoxycarbonylation of dienes having conjugated double bonds
ActiveCN107628953AEasy to manufactureOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsDibenzylideneacetoneAlcohol
The invention relates to a method for preparing di- or tricarboxylic esters by alkoxycarbonylation of dienes having conjugated double bonds. The method steps of: a) initially charging a diene having two conjugated double bonds; b) adding a phosphine ligand and a catalyst precursor selected from palladium dichloride, palladium dibromide, palladium diiodide, palladium(II) acetylacetonate, palladium(II) acetate, bis(dibenzylideneacetone)palladium, bis(acetonitrile)dichloropalladium(II), palladium (cinnamyl) dichloride; c) adding an alcohol; d) feeding in CO; and e) heating the reaction mixture, with conversion of the diene to a di- or tricarboxylic ester.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Crosslinkers based on dibenzalacetone derivatives
The present invention relates to the composition, process of preparation, and use of novel derivatives prepared from 1,5-bis-(4'-carbomethoxyphenyl)-1,4-pentadien-3-one. These novel compositions can act as crosslinkers with polyfunctional monomeric, oligomeric, and / or polymeric anhydrides, esters, carboxylic acids, isocyantes, epoxies, carbonates, acetoacetates, and alkoxylated melamines.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Preparation method of indolo [2, 3-A] carbazole
ActiveCN112250685ARaw materials are easy to getShort reaction stepsOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPtru catalystOrganic base
The invention discloses a preparation method of indolo [2, 3-A] carbazole, which belongs to the technical field of chemistry. The preparation method comprises the following steps of carrying out C-N coupling and C-C coupling cascade reaction on o-dibromobenzene and o-phenylenediamine under the action of a catalyst, a ligand and alkali to obtain indolo [2, 3-A] carbazole, wherein the catalysts area palladium salt catalyst and a copper salt catalyst, the palladium salt catalyst comprises palladium chloride, palladium acetate, tetra(triphenylphosphine) palladium, palladium trifluoroacetate, palladium acetylacetonate or tri(dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium, and the copper salt catalyst comprises cuprous iodide, cuprous chloride, cuprous bromide, cuprous oxide, copper sulfate, copper chloride, copper acetate or copper trifluoroacetate, the ligand is a phosphine ligand, and the alkali is organic alkali or inorganic alkali. According to the method, o-phenylenediamine and o-dibromobenzene which are cheap and easily available are used as raw materials, and compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of short reaction steps, easily available raw materials, low production cost, environmental friendliness and the like.
Owner:SINOSTEEL NANJING NEW MATERIALS RES INST CO LTD
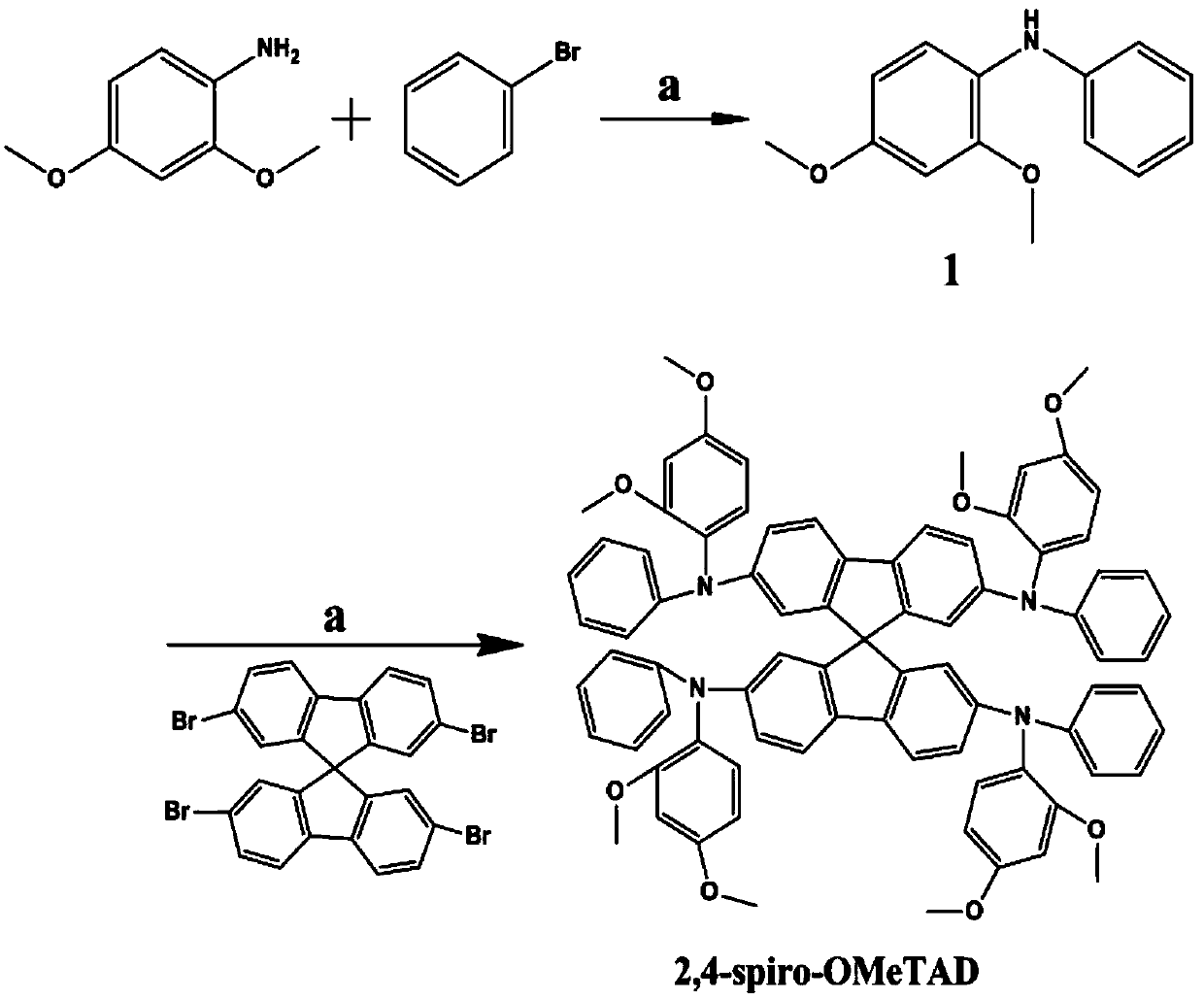
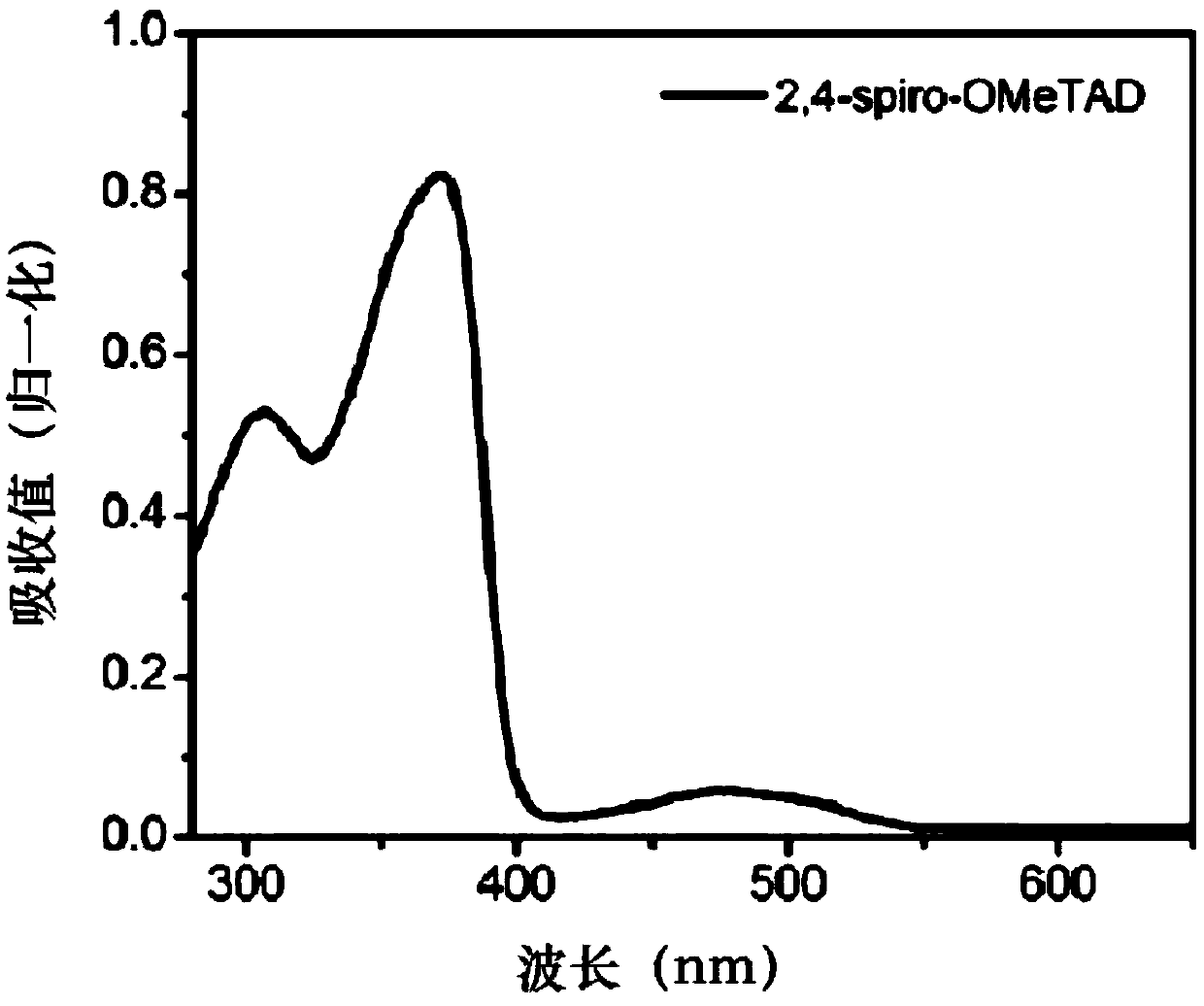
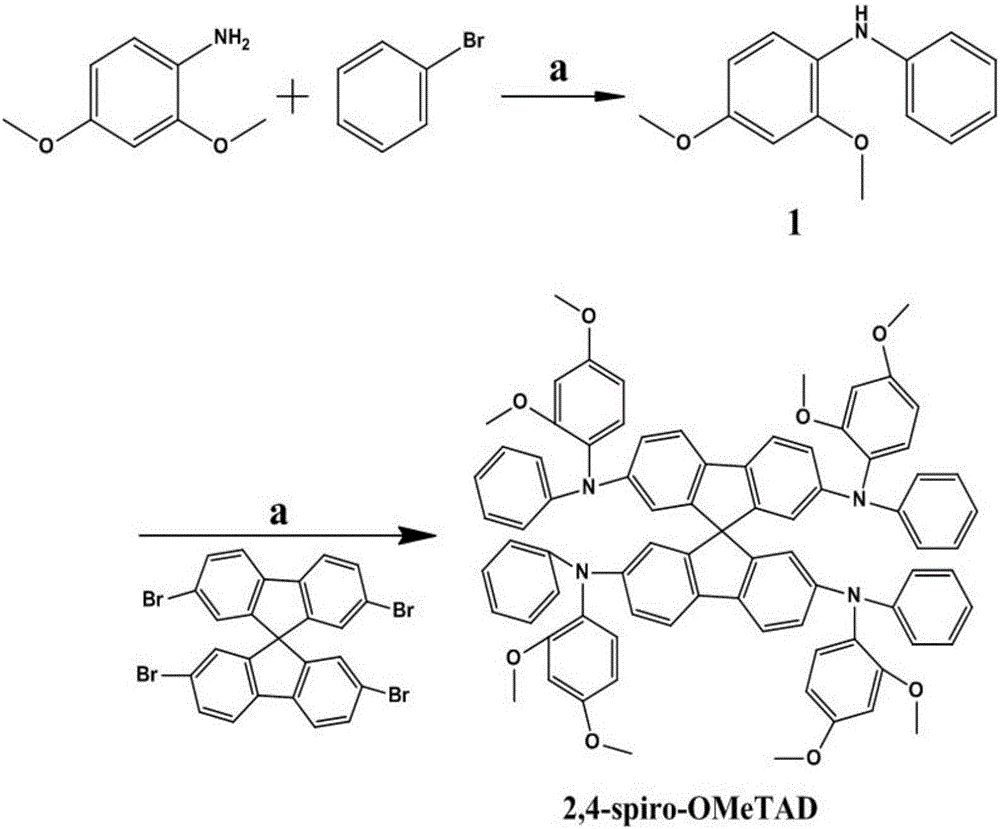
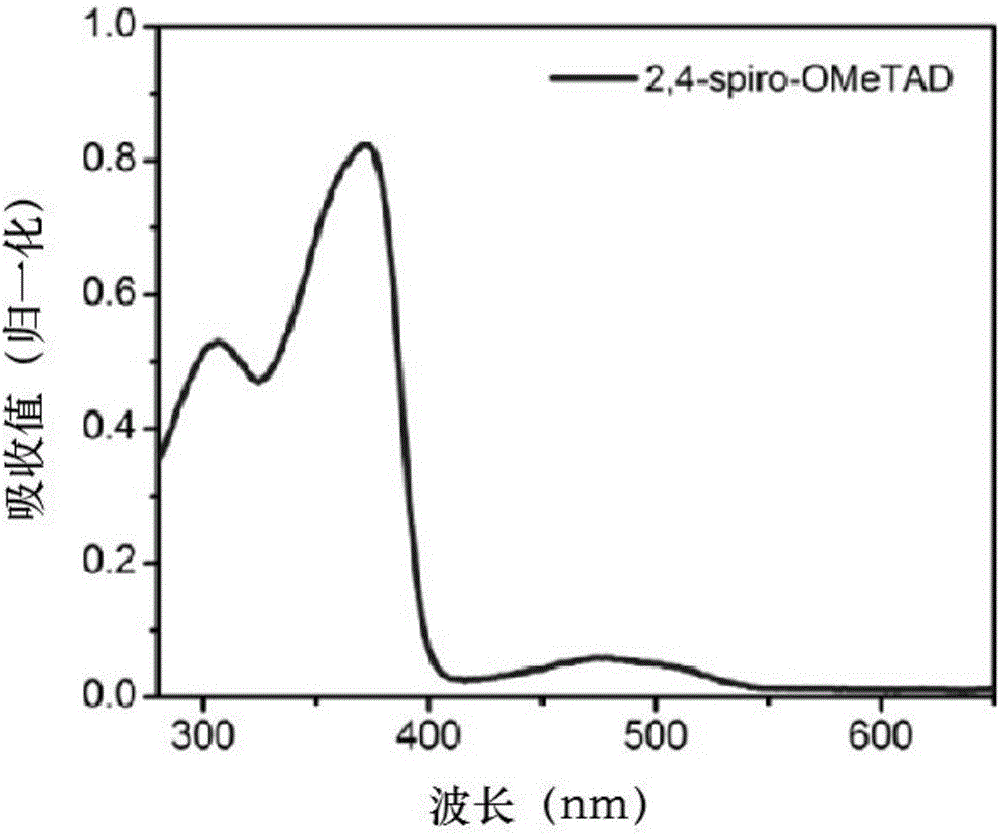
Structure, synthesis and application of spirobifluorene hole-transport materials (2,4-spiro-OMeTAD)
ActiveCN106800517AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyPromote absorptionOrganic compound preparationSolid-state devicesUltraviolet lightsSolar battery
The invention discloses a structure, synthesis and application of spirobifluorene hole-transport materials (2,4-spiro-OMeTAD). The hole-transport materials are spirobifluorene hole-transport materials; a preparation method of the spirobifluorene hole-transport materials comprises the steps of heating a mixed system, which is formed by a compound 1, spirobifluorene, sodium tert-butoxide, tri-tert-butylphosphine, tris(dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium and anhydrous toluene, up to 105-115 DEG C under the protection of argon, maintaining the temperature and reacting for 10-14h; cooling, then extracting to obtain an organic phase by using ethyl acetate, drying and concentrating the obtained organic phase, and then carrying out silica gel column chromatography to obtain a target product 2,4-spiro-OMeTAD. The hole-transport material 2,4-spiro-OMeTAD is high in hole mobility, has an HOMO energy level matched with the valence band of a perovskite material, is good in stability and dissolving capacity, and high in molar extinction coefficient; a perovskite solar battery prepared from the 2,4-spiro-OMeTAD is high in photoelectric converting efficiency; due to the flexible change of a methyl position, the structural modification can be conveniently carried out at the later period, and the spectrum absorption from an ultraviolet light area to a near infrared light area is easily realized; the commercialization cost is low.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
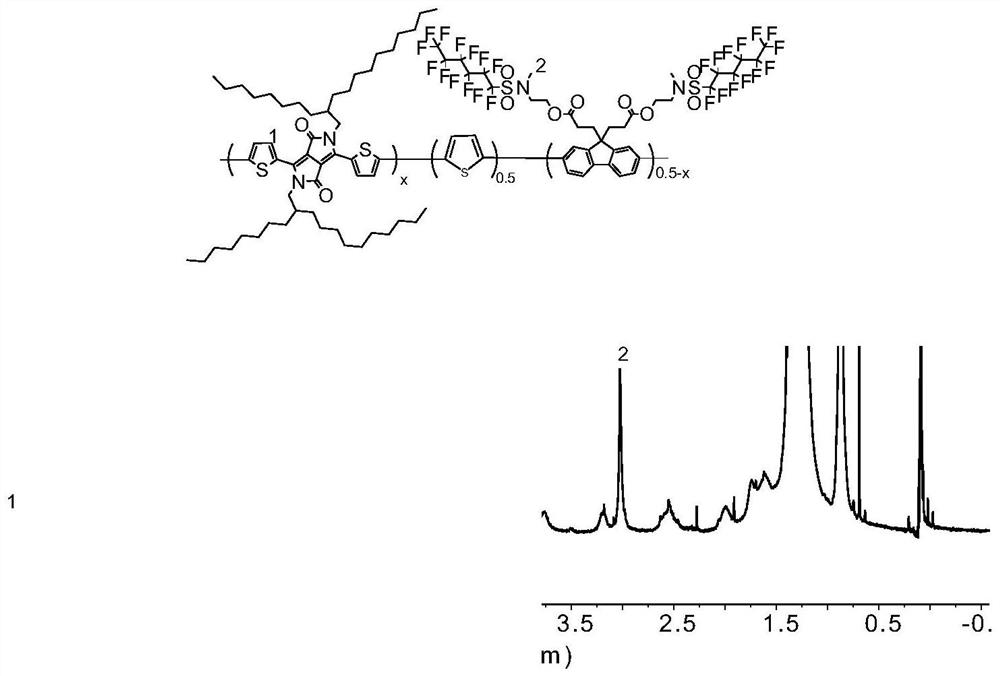
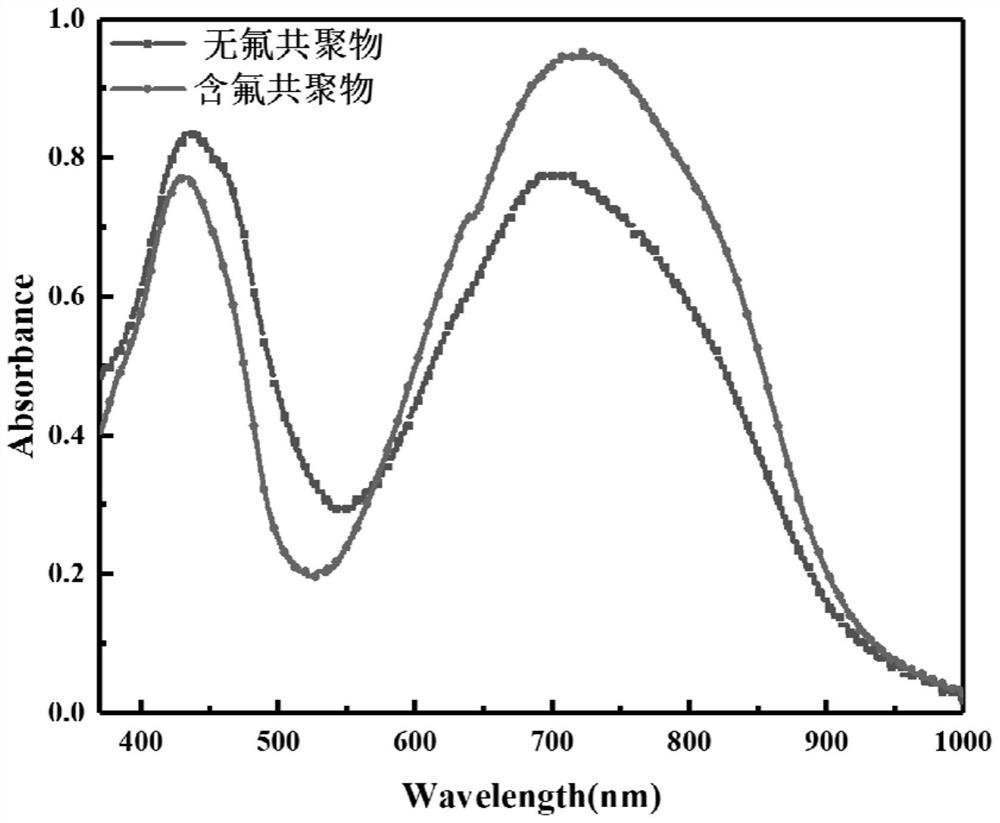
Fluorine-containing near-infrared absorption conjugated polymer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN114507336AHigh singlet oxygen efficiencyIncreased photodynamic therapy efficiencyPhotovoltaic energy generationBenzylideneacetoneSide chain
The invention belongs to the field of functional materials, and particularly relates to a fluorine-containing near-infrared absorption conjugated polymer and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a 3, 6-bis (5-bromothiophene-2-yl)-2, 5-bis (alkyl) pyrrolo [3, 4-c] pyrrole-1, 4-diketone monomer, then preparing dibromo fluorine-containing fluorene, and finally, reacting the 3, 6-bis (5-bromothiophene-2-yl)-2, 5-bis (alkyl) pyrrolo [3, 4-c] pyrrole-1, 4-diketone monomer with the dibromo fluorine-containing fluorene to prepare the fluorine-containing fluorene dibromo fluorine-containing fluorene. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a 1, 4-diketone monomer, dibromo fluorine-containing fluorene, a bis (trimethyltin) compound, tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium and tris (o-tolyl) phosphine in toluene, and reacting at 110 DEG C for 48 hours in an inert gas atmosphere to obtain the fluorine-containing fluorene and diketopyrrolopyrrole copolymer. The fluorine-containing fluorene and diketopyrrolopyrrole copolymer disclosed by the invention has strong absorption in a near-infrared region, and contains a perfluoro side chain, so that the efficiency of generated singlet oxygen is higher, and the photodynamic therapy efficiency can be improved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Method for preparing 1-[2-(2,5-dimethylphenylthio)phenyl]piperazine
The invention discloses a method for preparing 1-[2-(2,5-dimethylphenylthio)phenyl]piperazine. The method comprises the following steps: S1, in an inert gas atmosphere, 1,1'-binaphthyl 2,2'-bis(diphenylphosphine), sodium tert-butoxide, toluene, bis (dibenzylideneacetone) palladium are evenly mixed and stirred at room temperature for 10-15 minutes, a solution A is added dropwise, reflux is performed for 12-16 hours, the temperature is reduced to room temperature, and a filtrate is obtained by filtering, wherein a solute of the solution A is 2,5-dimethylthiophenol and o-iodobromobenzene, and a solvent is toluene; S2, 1,1'-binaphthyl-2,2'-bis(diphenylphosphine), sodium tert-butoxide, bis(dibenzylideneacetone)palladium and piperazine are added to the filtrate obtained in S1, the mixed solutionis subjected to reflux for 3-5 h in an inert gas atmosphere and cooled to the room temperature, water is added for uniform mixing, a product is purified, and 1-[2-(2,5-dimethylphenylthio)phenyl]piperazine is obtained.
Owner:安徽源久源科技有限公司
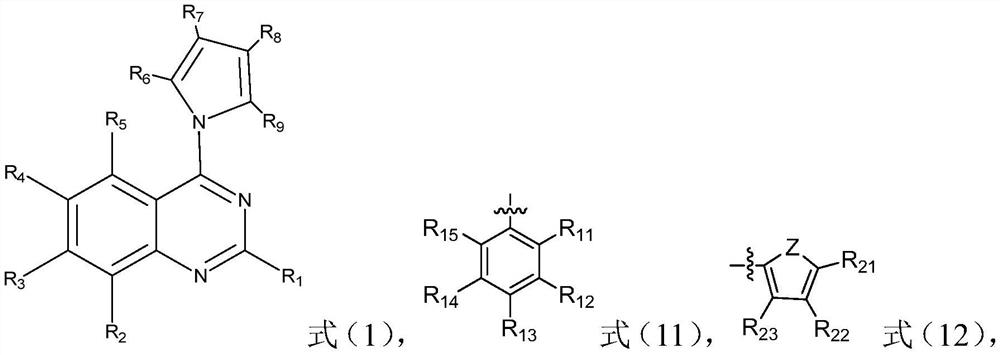
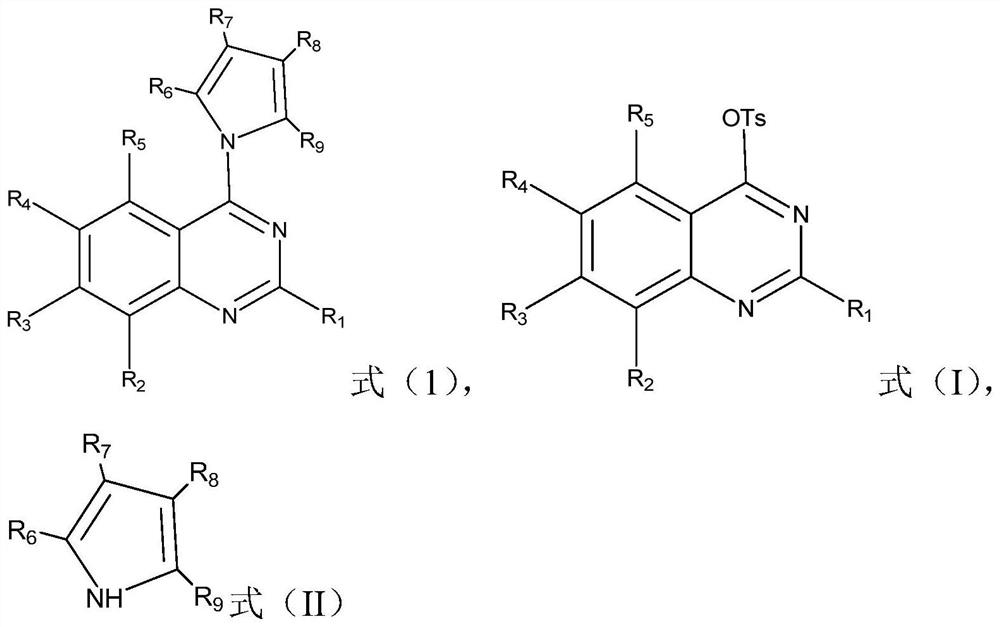
Quinazoline derivatives and their preparation methods and applications
ActiveCN109096254BWide applicabilityHigh selectivityOrganic chemistryAntiinfectivesBenzylideneacetonePtru catalyst
The invention relates to the field of organic chemistry, and discloses a quinazoline derivative, a preparation method and application thereof. The derivative has a structure represented by formula (1). The method provided by the invention comprises: under alkaline condition, in ligand and selected from palladium trifluoroacetate, tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium, bistriphenylphosphine palladium dichloride, three (dibenzylidene acetone) ) In the presence of at least one catalyst in dipalladium and palladium acetate, the compound shown in formula (I) is reacted with the compound shown in formula (II), and the ligand is 2-bicyclohexylphosphine-2', 6'-Dimethoxybiphenyl. The quinazoline derivatives provided by the invention have excellent antibacterial activity and antitumor activity. The preparation method provided by the invention has high yield, wide substrate applicability, mild reaction conditions, simple operation, low cost, few by-products, high product purity, is applicable to large-scale preparation, and has considerable application prospects.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
A kind of preparation method of diphenyl[c,e]azepine derivative
The invention discloses a diphenyl[c,e]azepine derivative and a preparation method thereof, by reacting [1,1'-biphenyl]-2,2'-dinitrile and arylboronic acid The reactant is prepared by the reaction of the reactant; the reactant is easy to prepare, has wide sources, low cost, low toxicity, and is not easy to affect human health. The reaction is carried out in a solvent, and the solvent is any one of toluene, xylene, methanol, tetrahydrofuran, N,N-dimethylformamide and N,N-dimethylacetamide; Added palladium catalyst and acid accelerator; palladium catalyst is palladium trifluoroacetate, palladium tetraphenylphosphine, bisacetylacetonate palladium, bis(dibenzylideneacetone) palladium and tris(dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium Any one; the reaction temperature is 100-120°C, the reaction time is 20-30 hours, the reaction conditions are mild, easy to achieve, and safe. The invention can directly synthesize the target product without separating intermediate products, and the highest yield can reach 95%.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIV
Chemical tin plating technology for crystalline silicon heterojunction solar cell
ActiveCN111926314AReasonable formulaImprove long-term stabilityLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingHeterojunctionChemical plating
The invention relates to the technical field of metal surface treatment and particularly relates to a chemical tin plating technology for a crystalline silicon heterojunction solar cell, wherein a chemical tin plating solution takes deionized water as a solvent and contains components of the following concentrations: 10-20 g / L of tin salt, 0.25-0.5 g / L of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, 0.1-0.25g / L of ethoxylated naphthol sulphonic acid, 0.05-0.2 g / L of stachyose, 0.06-0.12 g / L of Dibenzylideneacetone, 0.5-1 g / L of a grain refiner, 50-100 g / L of a reducing agent and 0.5-2.5 g / L of a dispersing agent. The technology provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that the chemical tin plating solution adopted is not easily influenced by a temperature which is too high or too low andis high in low-temperature stability and high-temperature stability; creatively, the stachyose and the Dibenzylideneacetone are used as a stabilizer through coordination, so that tolerance of the chemical tin plating solution to temperatures is obviously enhanced; and duration of the chemical tin plating technology is short, and production efficiency is high.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SANFU NEW MATERIALS TECH
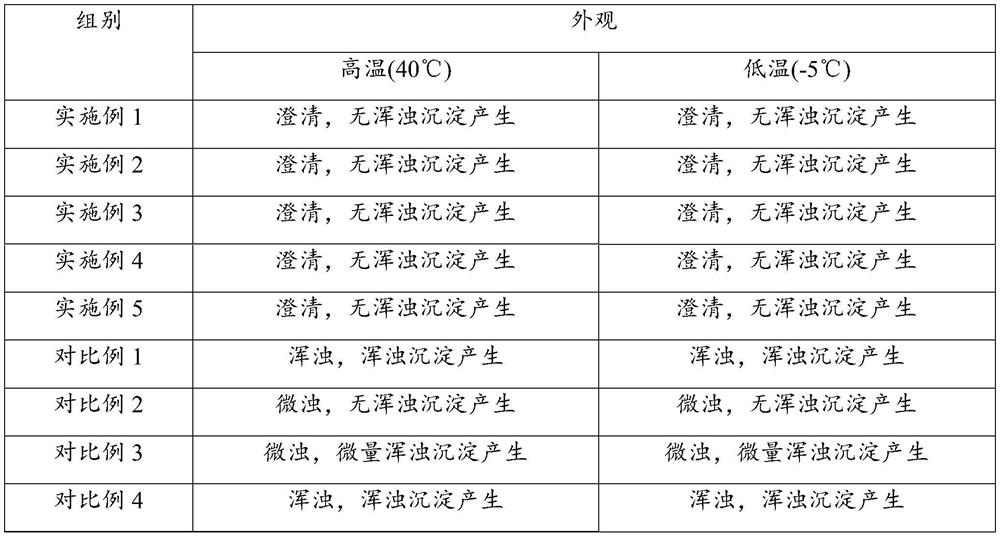
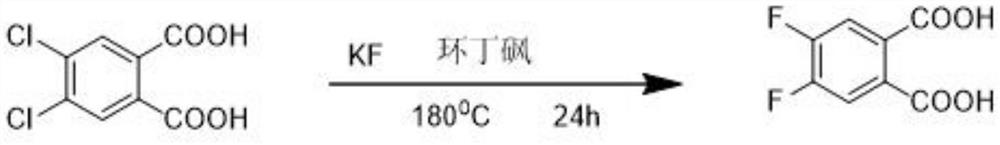
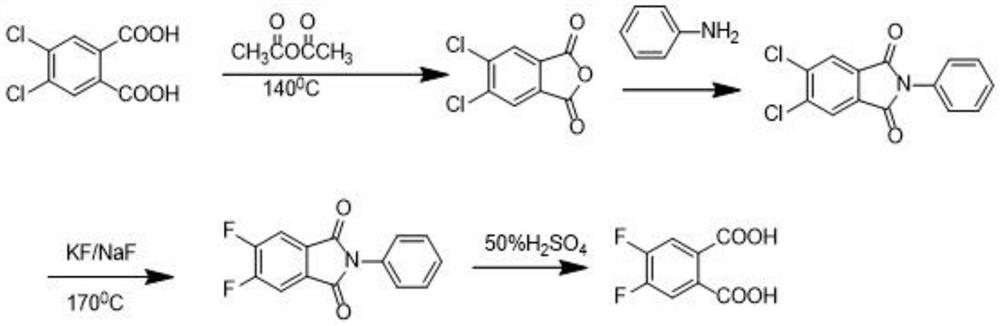
The preparation method of 4,5-difluorophthalic acid
ActiveCN112707807BLow costSafe and efficient processFinal product manufacturePreparation by cyanide reactionSodium bicarbonateBenzylideneacetone
Owner:苏州当量生物医药有限公司
Process
ActiveUS20130109877A1Convenient and economic and efficientLarge scalePalladium organic compoundsHalide preparation methodsAlcoholBenzylideneacetone
The present invention provides a process for the preparation of Pd2(dba)3.CHCl3 comprising the steps of: (a) reacting a Pd(II) complex with an alkali metal halide in at least one alcohol solvent; and (b) reacting the product of step (a) with a mixture comprising dibenzylideneacetone, chloroform and an inorganic base to form Pd2(dba)3.CHCl3.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
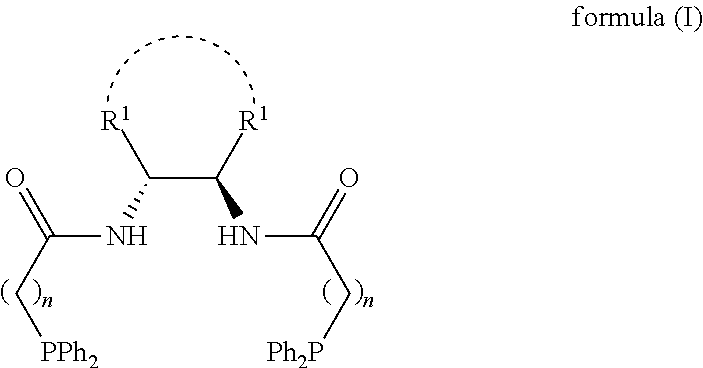
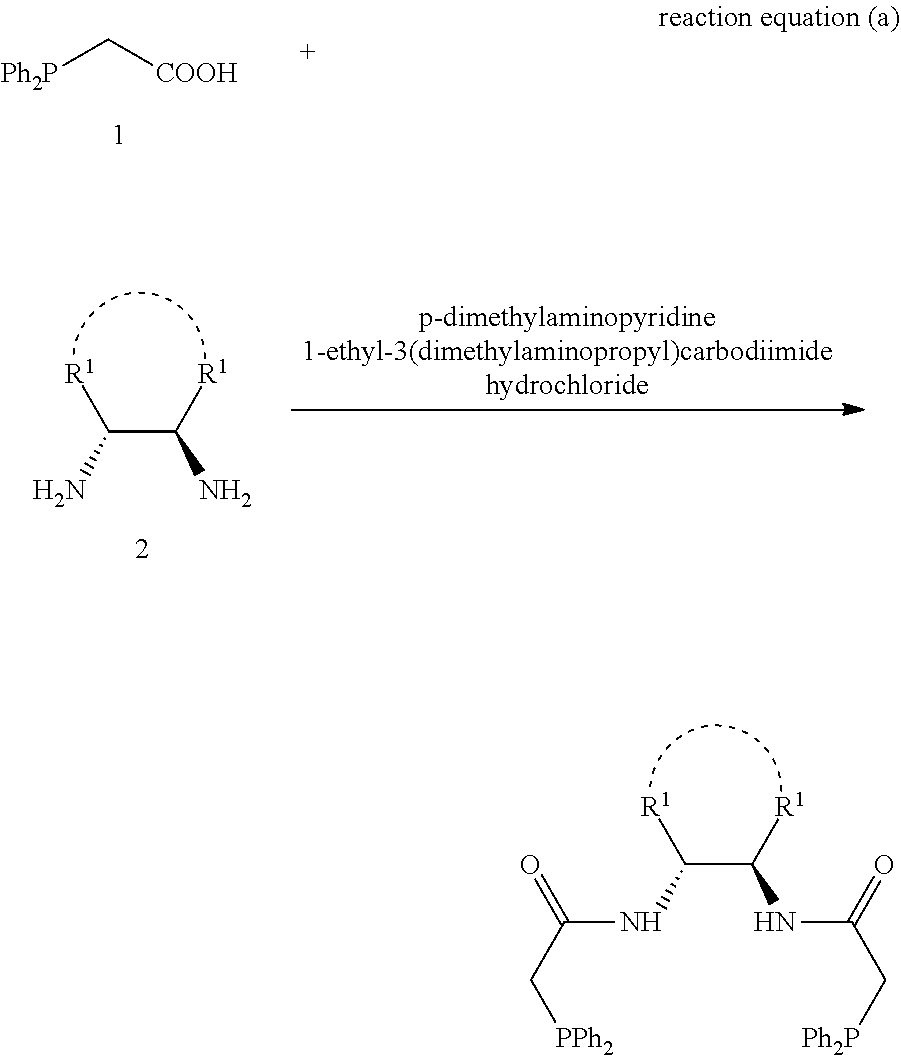
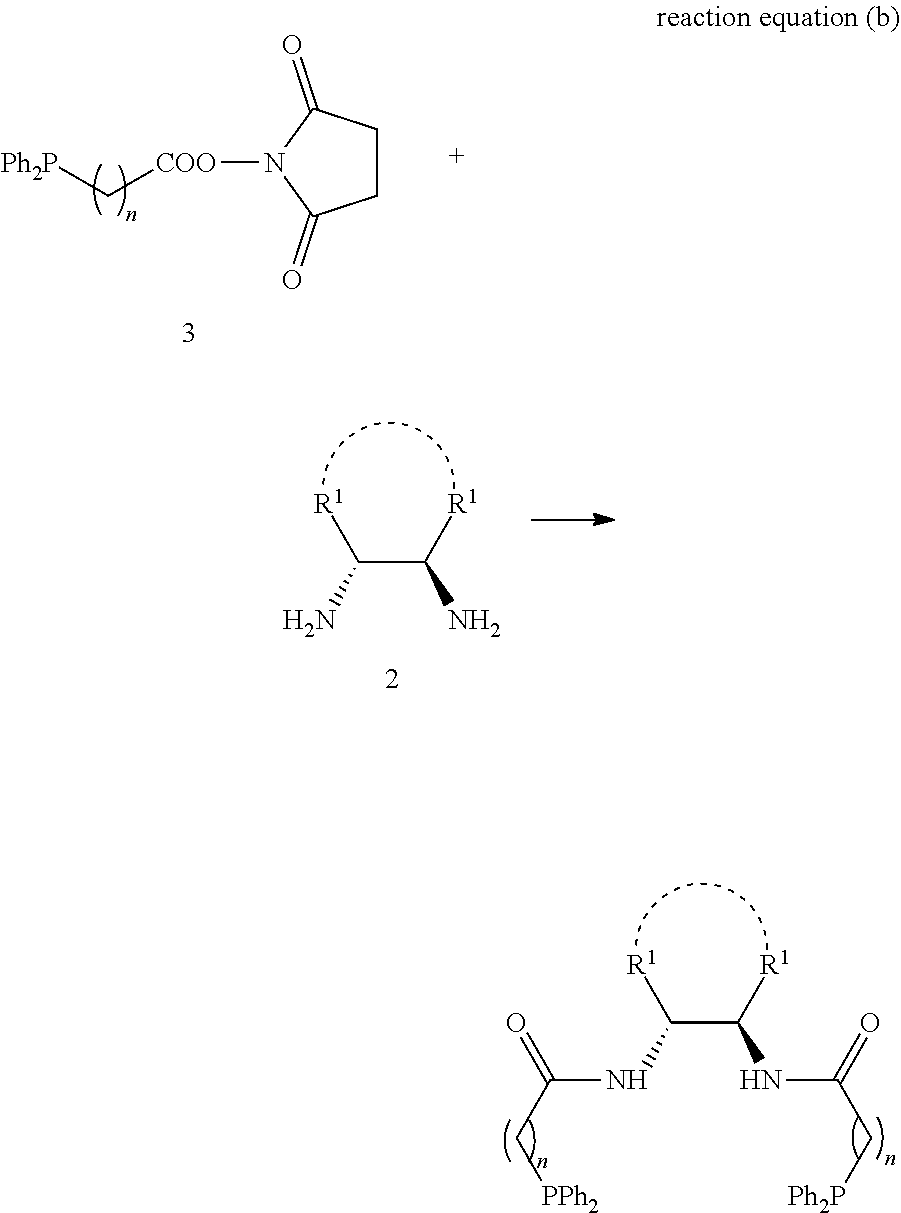
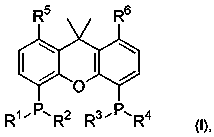
1,2-bis(diphenylphosphinoalkylamido)-1,2-disubstituted ethane, and its synthesis and application
PendingUS20220242892A1Easy to operateEasy accessGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAsymmetric synthesesBenzylideneacetonePtru catalyst
The present invention relates to the design and synthesis of a class of novel chiral phosphine ligand, 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphinoalkylamido)-1,2-disubstituted ethane, and use in asymmetric catalytic reactions, such as asymmetric catalytic synthesis of pyrazoline-5-one with a chiral quaternary carbon center, i.e., highly enantioselective synthesis of 3-methyl-4-benzyl-4-(2-butyl-2,3-butadienyl)pyrazoline-5-one by using 3-methyl-4-benzylpyrazoline-5-one and benzyl (2-butyl-2,3-butadienyl) carbonate with tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium-chloroform adduct and this novel ligand as catalysts. The ligand designed by this present invention has the following advantages: the structure is novel, the synthesis and enlarge are simple, the enantioselective control effect in the practical reaction is excellent, which has a broad application prospect in chiral catalysis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of trifluorostyrene compound
ActiveCN103373897BCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationAmino preparation from aminesDibenzylideneacetoneSynthesis methods
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Structure, synthesis and application of a spirobifluorene-based hole-transporting material
ActiveCN106800517BImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyPromote absorptionOrganic compound preparationSolid-state devicesMeth-Ultraviolet
The invention discloses the structure, synthesis and application of a spirobifluorene hole transport material. The hole transport material is a spirobifluorene hole transport material. The preparation steps are as follows: compound 1, spirobifluorene, t- The mixed system of sodium butoxide, tri-tert-butylphosphine, tris(dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium and anhydrous toluene is heated to 105-115°C under the protection of argon, and the temperature is maintained for 10-14 hours; after cooling The organic phase was extracted with ethyl acetate, and the organic phase was dried and concentrated, followed by silica gel column chromatography to obtain the target product 2,4‑spiro‑OMeTAD. The hole transport material 2,4-spiro-OMeTAD of the present invention has high hole mobility, the HOMO energy level matches the valence band of perovskite, good stability, good solubility, and high molar extinction coefficient, and the perovskite made of it The photoelectric conversion efficiency of the mineral solar cell is high; the flexible change of its methyl position facilitates structural modification in the later stage, and it is easy to realize spectral absorption in the ultraviolet to near-infrared light region; and the commercialization cost is low.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Method of synthesis for organic semiconducting polymers
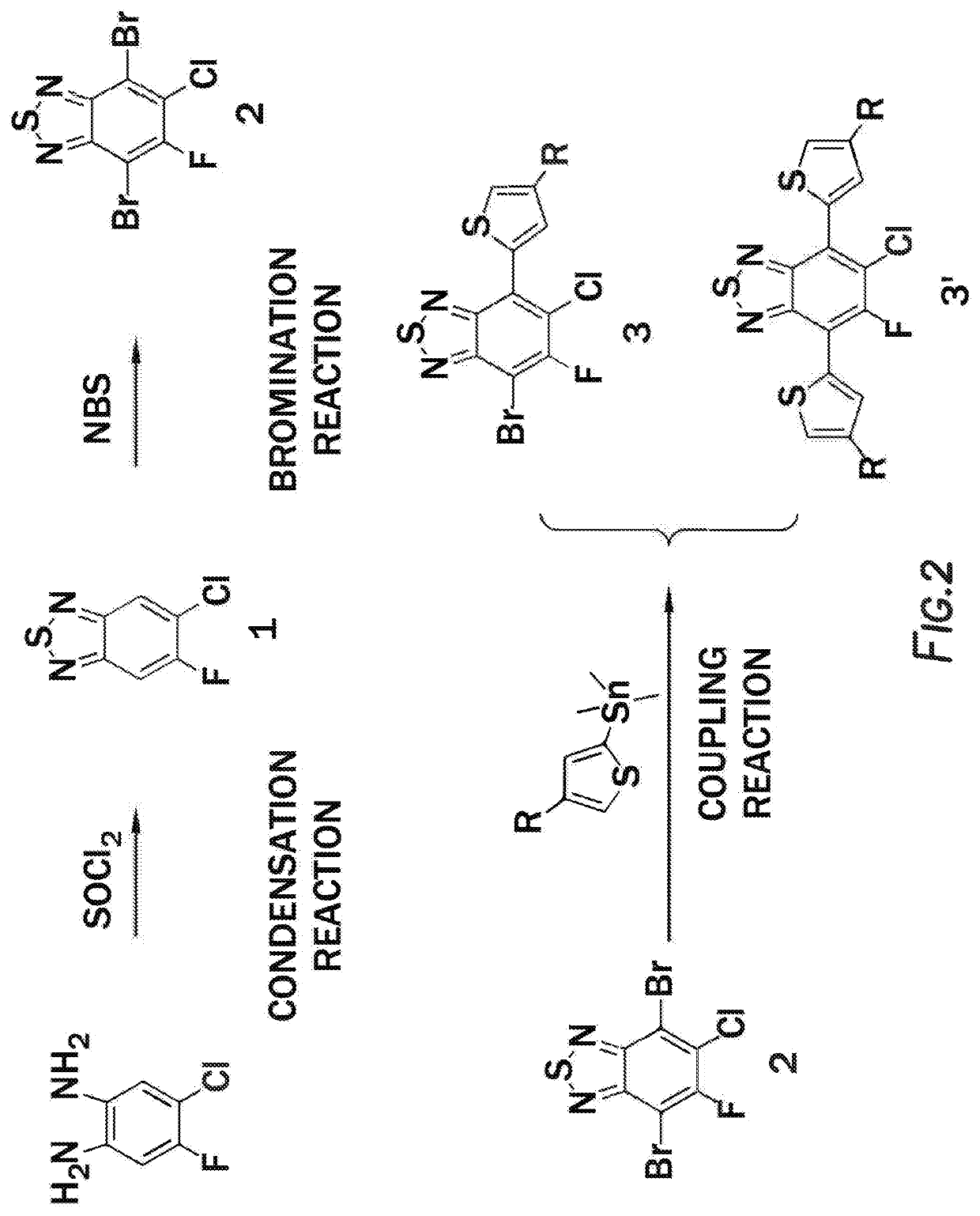
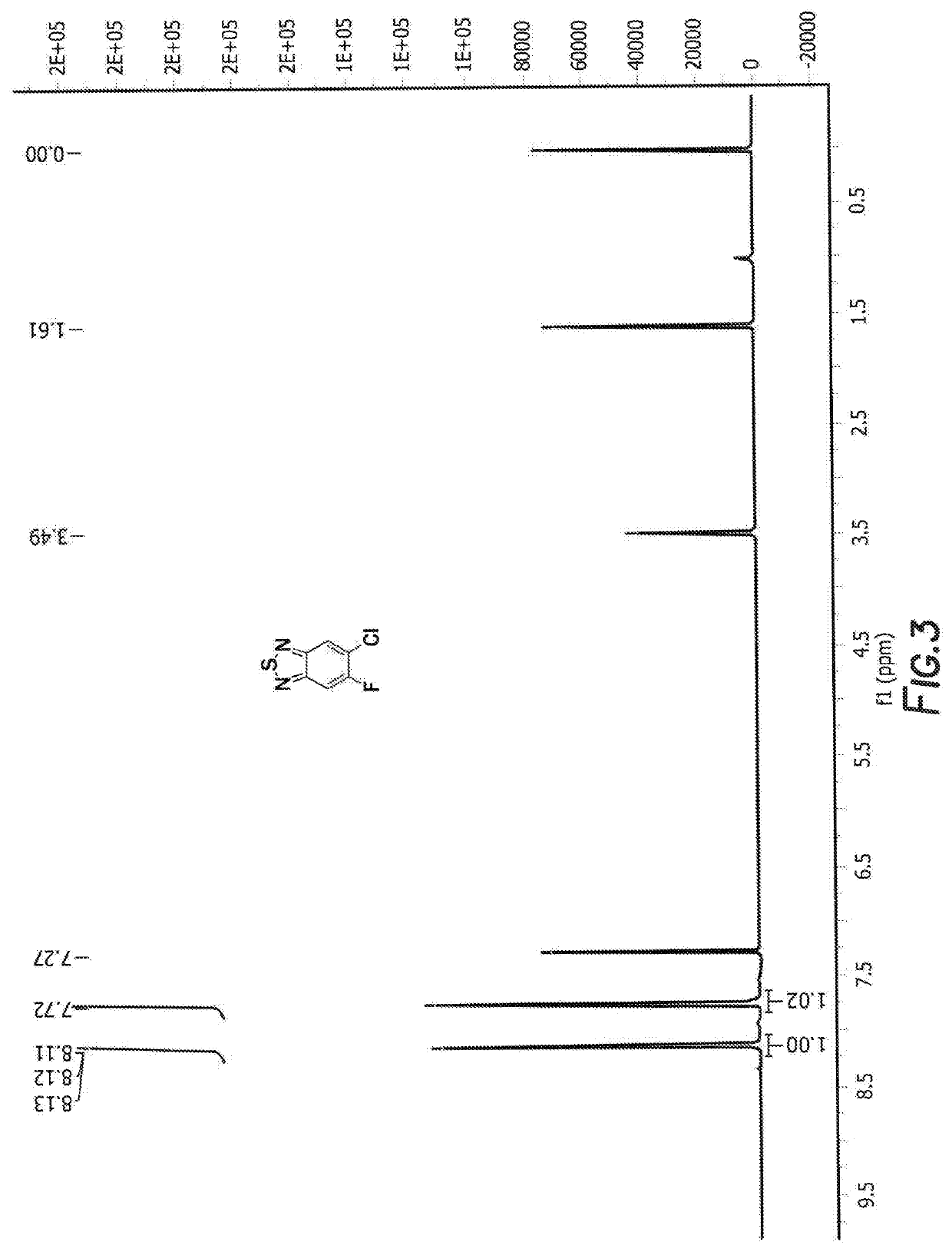
ActiveUS20210066609A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolymer scienceThiadiazoles
A method of forming a polymer, the method comprising combining 4-bromo-7-[5-bromo-4-(alkyl)thiophen-2-yl]-6-chloro-5-fluoro-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole, (3,3′-difluoro-[2,2′-bithiophene]-5,5′-diyl)bis(trimethylstannane), [4-(alkyl)-5-[5-(trimethylstannyl)thiophen-2-yl]thiophen-2-yl]trimethylstannane, tris(dibenzylideneacetone), and dipalladium P(o-tol)3 tris(2-methylphenyl)phosphane to form the polymer:In this polymer, W is selected from the group consisting of: S, Se, O, and N-Q. Additionally, Q is selected from the group consisting of: a straight-chain carbyl, silyl or hydrocarbyl, branched, cyclic alkyl with 1 to 30 atoms, and fused aromatic rings. Furthermore in this polymer, R1, and R4 are independently selected from the group consisting of: F, Cl, I, Br, CN, —NCO, —NCS, —OCN, —SCN, —OX, —SX, —NH2, —C(═O)X, —C(═O)—OX, —OX, —NHX, —NXX′, —C(═O)NHX, —C(═O)NXX′, —SO3X, —SO2X, —OH, —NO2, CF3, —SF5, a straight-chain or branched carbyl, silyl, or hydrocarbyl, a branched or cyclic alkyl with 1 to 30 atoms, a fused substituted aromatic ring, and a fused unsubstituted aromatic ring. This polymer can also have R2 and R3 are independently selected from F, Cl, Br and I. Additionally, in this polymer, the fused aromatic rings can be independently fused with groups consisting of: a straight-chain or branched carbyl, silyl, or hydrocarbyl, a branched or cyclic alkyl with 1 to 30 atoms, a fused substituted aromatic ring, and a fused unsubstituted aromatic ring. Lastly, in this polymer, h+j is between 0.2 to 0.6 and i+k is between 0.4 and 0.8.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
A kind of preparation method of three (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (0)
ActiveCN110256503BHigh purityEasy to preparePalladium organic compoundsSodium acetateBenzylideneacetone
The invention discloses a preparation method of tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0). The method comprises: 1. Under a nitrogen atmosphere, the ligand dibenzylideneacetone, palladium dichloride and anhydrous Sodium acetate is added in the dehydrated alcohol of stirring state and heated reaction, obtains solid bis (dibenzylidene acetone) palladium (0) after filtration; Two, under nitrogen atmosphere, the solid bis (dibenzylidene acetone) that obtains in step Acetone)palladium(0) was added into acetone in a stirring state for reaction, the retentate was washed after filtration, and the washed retentate was dried to obtain tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0). The present invention adopts dehydrated alcohol, dibenzylidene acetone, palladium dichloride and anhydrous sodium acetate to first prepare bis(dibenzylidene acetone) palladium (0), and then obtains tris(dibenzylidene acetone) through acetone solution treatment ) dipalladium (0), the three (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (0) obtained has higher purity.
Owner:XIAN CATALYST NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Blue luminescent materials based on bifluorene derivative
PendingCN113897193AEnhanced conjugated structureImprove thermal stabilityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsLuminescent compositionsQuantum yieldMaterials science
The invention discloses blue luminescent materials based on a bifluorene derivative, different electron withdrawing groups are introduced into a ninth reaction site of bifluorene through a C-H coupling reaction in presence of tri (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (0) to obtain a series of blue luminescent materials with distorted structures; reaction raw materials are wide in source and are common organic small molecular materials, the synthesis cost is low, and industrialization is facilitated; the luminescent material has the advantages of wide energy gap, stable luminescence wavelength, good thermal stability, high fluorescence quantum yield, good solubility in general organic solvents, and suitableness for preparing corresponding electroluminescent devices through a solution processing mode. The material still maintains excellent blue light emission in a solid film state, and can improve the luminous efficiency of an organic electroluminescent device, maintain blue light emission and improve the color purity and saturation of blue light emission of the device when being applied to the organic electroluminescent device.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
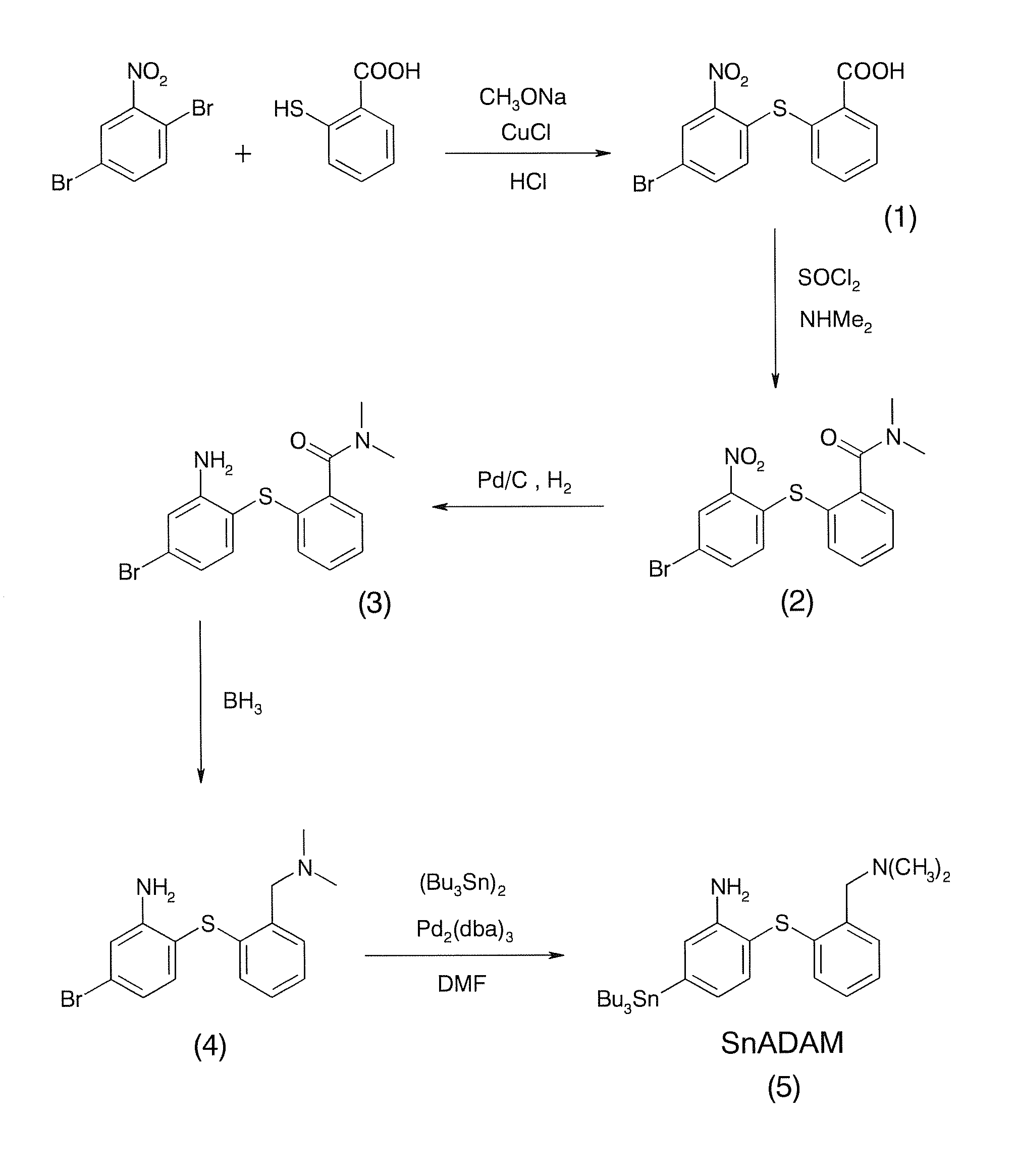
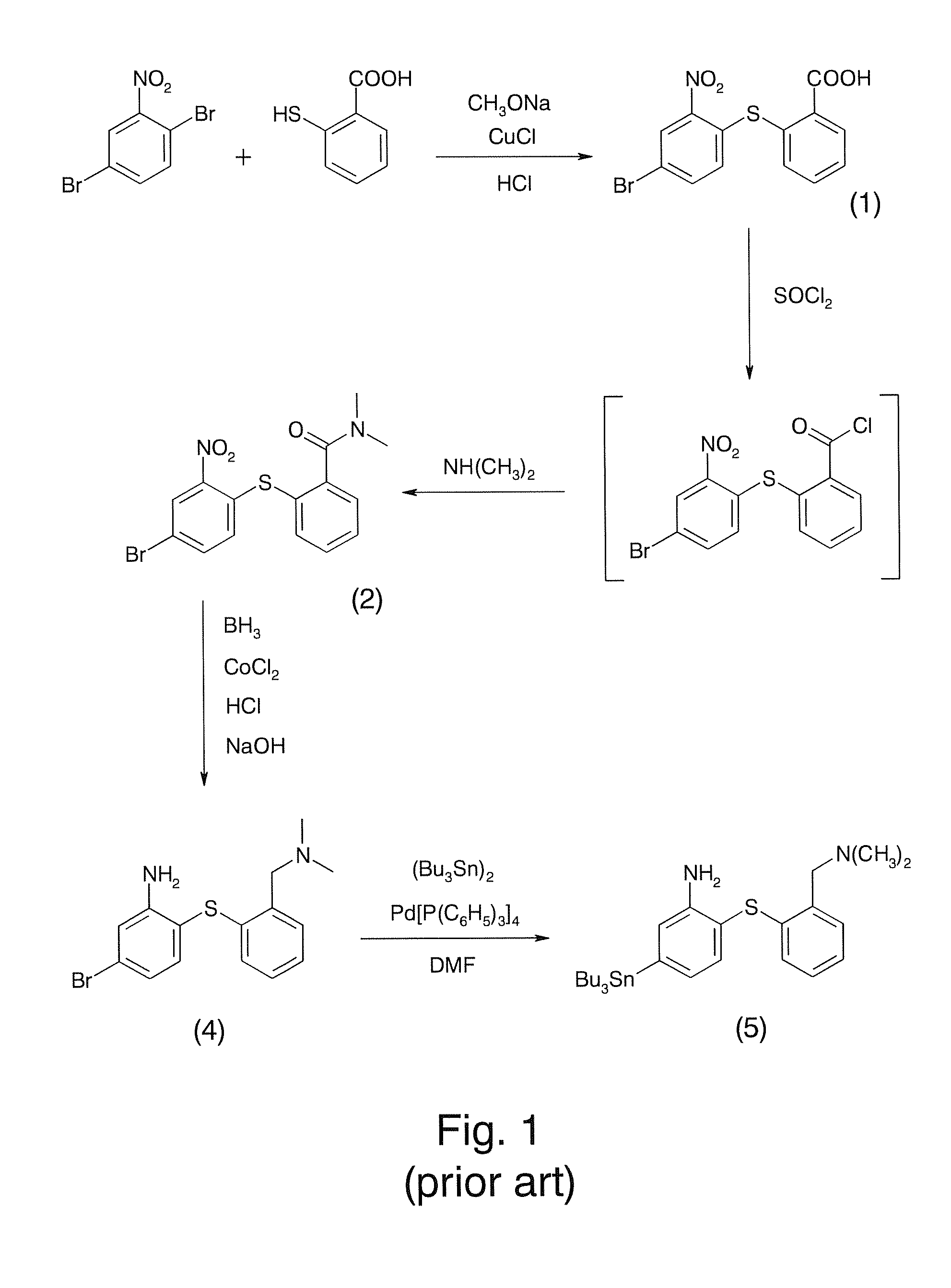
Method for preparing radiotracer precursor SnADAM
InactiveUS9096623B1Improve yieldHigh yield rateTin organic compoundsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsRadioactive tracerDibenzylideneacetone
A method for preparing a radiotracer precursor SnADAM is revealed. The method overcomes shortcomings of conventional synthesis methods including lower yield rate and time-consuming. Moreover, Pd / C catalyst and hydrogen gas are used to catalyze reduction reaction for avoiding the generation of a large amount of intermediate products with similar structures. Thus there is no need to perform isolation and purification processes. The yield rate of the intermediate products is also increased so that its impact on the low yield rate of the final product SnADAM is minimized. A part of the reaction is significantly accelerated by using tris(dibenzylideneacetone)-dipalladium(0) (Pd2(dba)3) as a catalyst. Thus the production time of SnADAM is shortened.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

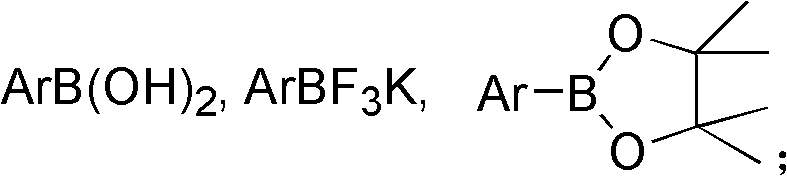

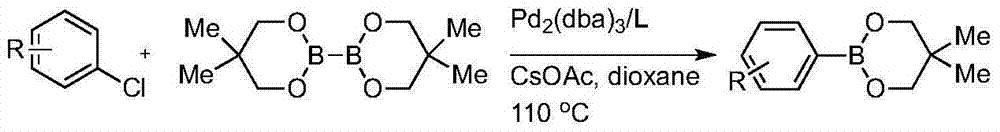

![Dibenzo[c,e]azepine derivative and preparation method thereof Dibenzo[c,e]azepine derivative and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1ee0426e-2e2d-4ecf-86b3-30e7ee69aa73/FDA0002211633130000012.png)
![Dibenzo[c,e]azepine derivative and preparation method thereof Dibenzo[c,e]azepine derivative and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1ee0426e-2e2d-4ecf-86b3-30e7ee69aa73/FDA0002211633130000013.png)
![Dibenzo[c,e]azepine derivative and preparation method thereof Dibenzo[c,e]azepine derivative and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1ee0426e-2e2d-4ecf-86b3-30e7ee69aa73/FDA0002211633130000014.png)
![Preparation method of indolo [2, 3-A] carbazole Preparation method of indolo [2, 3-A] carbazole](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/6d40720a-7965-4281-ab4e-f761deaff0c1/HDA0002797569190000011.png)
![Preparation method of indolo [2, 3-A] carbazole Preparation method of indolo [2, 3-A] carbazole](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/6d40720a-7965-4281-ab4e-f761deaff0c1/BDA0002797569180000011.png)
![Preparation method of indolo [2, 3-A] carbazole Preparation method of indolo [2, 3-A] carbazole](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/6d40720a-7965-4281-ab4e-f761deaff0c1/BDA0002797569180000012.png)
![Method for preparing 1-[2-(2,5-dimethylphenylthio)phenyl]piperazine Method for preparing 1-[2-(2,5-dimethylphenylthio)phenyl]piperazine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/ef104332-5365-4229-82df-b45a9ddc2522/BDA0001516059820000011.png)
![Method for preparing 1-[2-(2,5-dimethylphenylthio)phenyl]piperazine Method for preparing 1-[2-(2,5-dimethylphenylthio)phenyl]piperazine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/ef104332-5365-4229-82df-b45a9ddc2522/BDA0001516059820000041.png)
![A kind of preparation method of diphenyl[c,e]azepine derivative A kind of preparation method of diphenyl[c,e]azepine derivative](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/24d28a89-0c3c-4a54-9b26-99d9a2f5d53d/FDA0002562696540000012.png)
![A kind of preparation method of diphenyl[c,e]azepine derivative A kind of preparation method of diphenyl[c,e]azepine derivative](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/24d28a89-0c3c-4a54-9b26-99d9a2f5d53d/FDA0002562696540000013.png)
![A kind of preparation method of diphenyl[c,e]azepine derivative A kind of preparation method of diphenyl[c,e]azepine derivative](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/24d28a89-0c3c-4a54-9b26-99d9a2f5d53d/FDA0002562696540000014.png)