Synbiotic micro-ecological preparation for pigs and preparation method and application of synbiotic micro-ecological preparation
A probiotic and synbiotic technology, applied in applications, animal feed, additional food elements, etc., can solve the problems of unguaranteed strain stability and unclear probiotic promotion effect, and achieve healthy and stable development, improve Pig growth performance and the effect of improving bacterial flora environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] 1. Isolation and screening of lactic acid bacteria
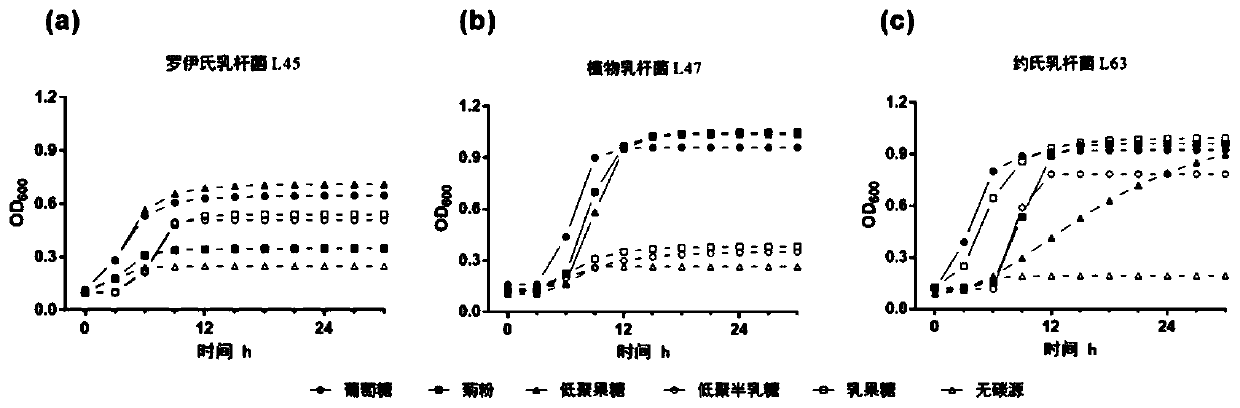
[0028] 155 pig lactic acid bacteria were preliminarily screened from the intestinal mucosa, chyme, and feces of pigs at different growth stages (piglets, growing and finishing pigs, and sows), and 4 strains with strong acid-producing ability were screened out through routine biochemical identification and acid-producing ability. of lactic acid bacteria.
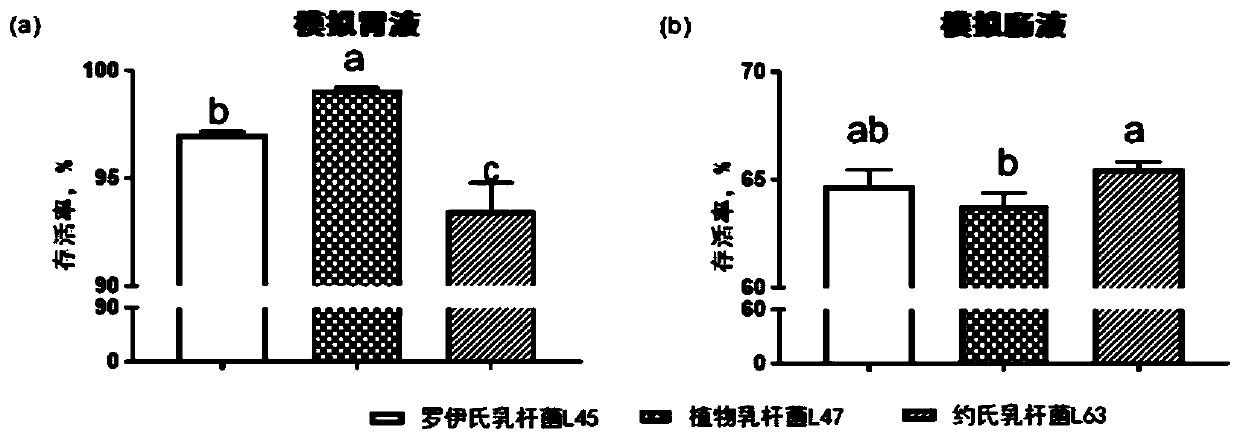
[0029] 2. Simulated gastrointestinal digestion
[0030] Artificial gastric juice: Add 3.0 g / L pepsin to sterile physiological saline with a pH of 2.5. After fully dissolving, filter and sterilize with a sterile microporous membrane (0.22 μm) to obtain artificial gastric juice for future use. Artificial intestinal juice: Add 1.0g / L trypsin and 1.8g / L bile salt to sterile saline with a pH of 8.0, fully dissolve, filter and sterilize for later use. The activated bacterial solution was inserted into the above-mentioned artificial gastric juice at an inoculum amount of ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2 Screening of the most suitable ratio of prebiotics and probiotics
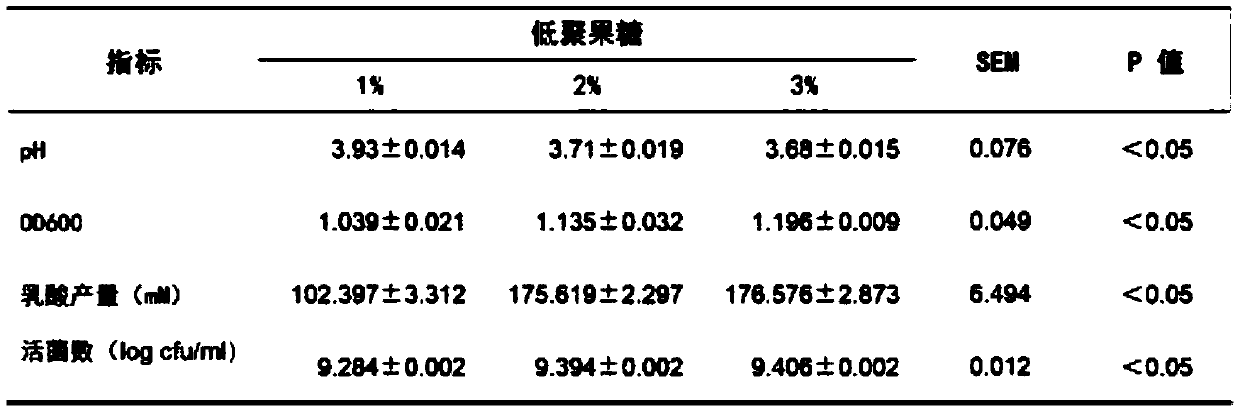
[0033] By adding different proportions (1-3%) of inulin or fructooligosaccharides to the medium, the concentration that has the greatest impact on the acid production performance and growth rate of Lactobacillus plantarum L47 is selected as the added concentration of the synbiotic probiotics. It can be seen from Table 1 and Table 2 that when the addition amount is 3%, the lactic acid production and the number of viable bacteria of Lactobacillus plantarum L47 are the largest, so 3% is selected as the compatible addition content of prebiotics.
[0034] Table 1 Effects of different fructo-oligosaccharide addition ratios on Lactobacillus plantarum
[0035]
[0036] Table 2 Effects of different inulin addition ratios on Lactobacillus plantarum
[0037]
Embodiment 3
[0038] The preparation of embodiment 3 synbiotics probiotics
[0039] ① Lactobacillus plantarum was enriched by culturing in MRS medium at 37°C for 24 hours, centrifuged and resuspended to obtain a pure bacterial liquid. The composition of the MRS medium: peptone 10.0g, beef extract 10.0g, yeast extract 5.0 g, 2.0 g of diammonium hydrogen citrate, 20.0 g of glucose, 1.0 mL of Tween-80, 5.0 g of sodium acetate, 2.0 g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.58 g of magnesium sulfate, 0.25 g of manganese sulfate, and 1000 mL of distilled water.
[0040] ② Add 3% inulin and (or) 3% fructo-oligosaccharide of the mass of the bacterial liquid to the Lactobacillus plantarum bacterial liquid with a viable count greater than 10.0 log cfu / mL, and add 5-10% of the bacterial liquid mass Cell protection agent (skimmed milk powder, glycerin or gelatin), freeze-dried after mixing. Wherein the degree of polymerization of fructo-oligosaccharides is DP=2-9, and the degree of polymerization of inul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com