Method for intensively removing heavy metals in sludge by utilizing electroosmosis dehydration device
A dewatering device and electro-osmosis technology, applied in dewatering/drying/concentrating sludge treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of low heavy metal removal rate and unfavorable sludge resource disposal and utilization, high moisture content of mud cake
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
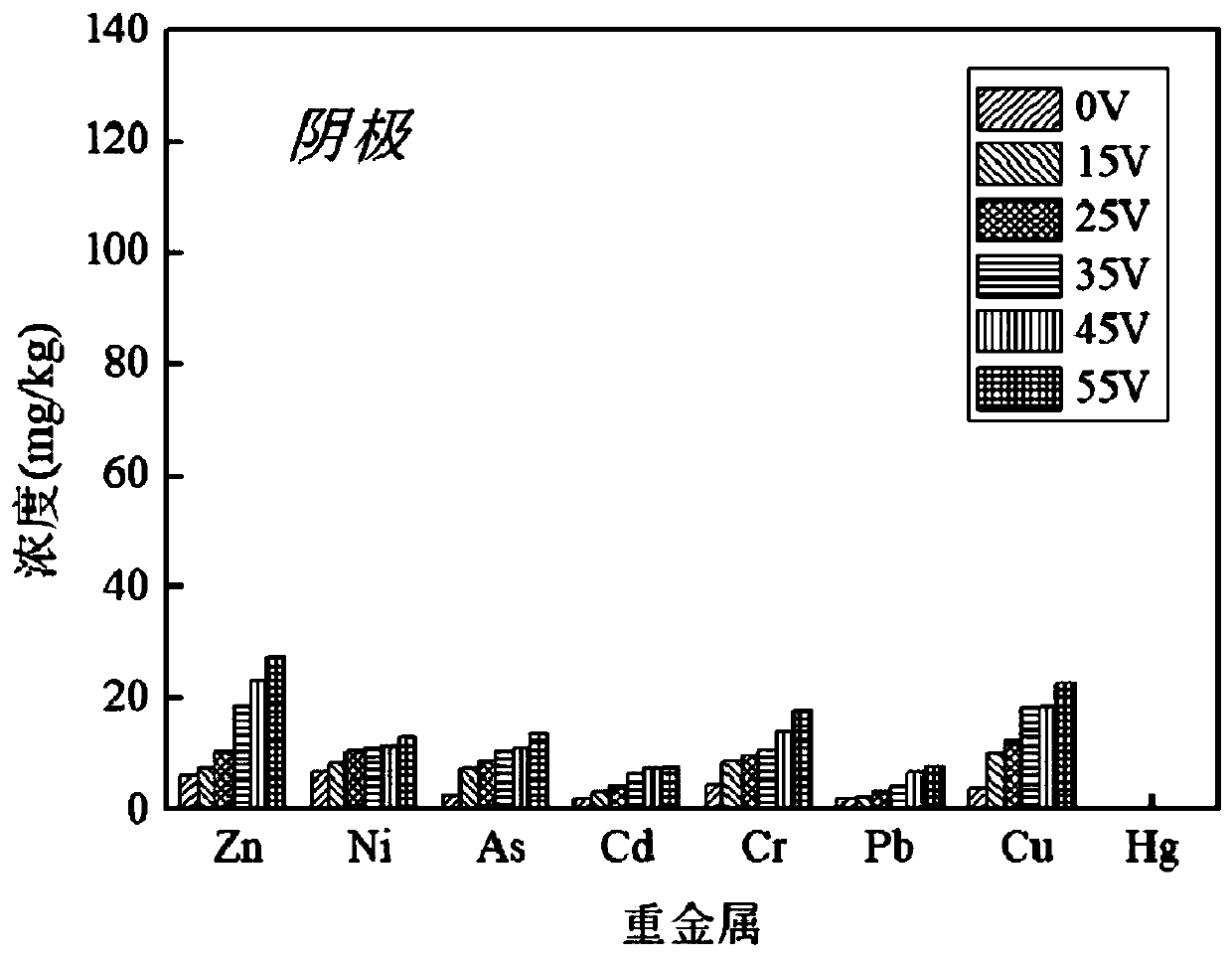
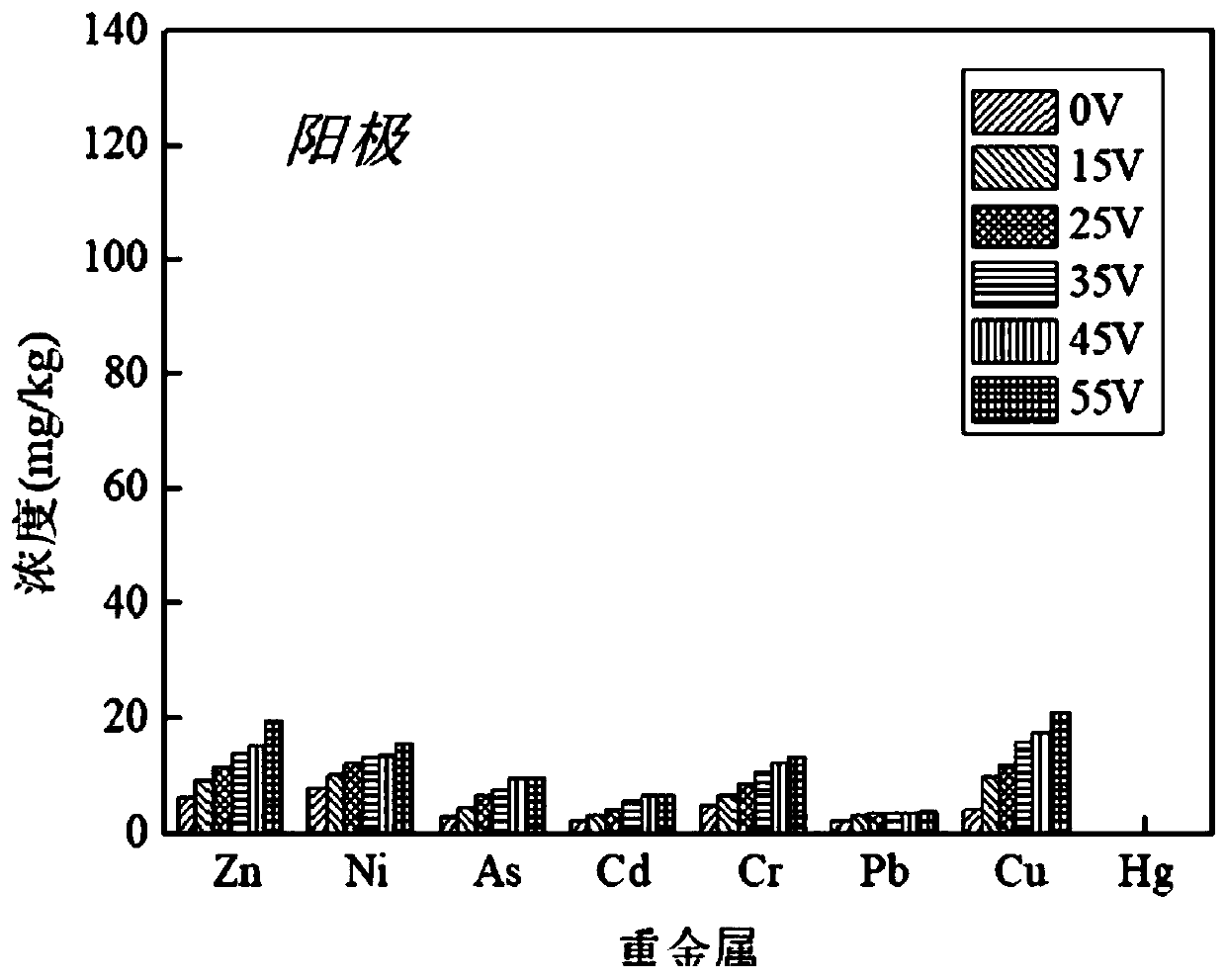
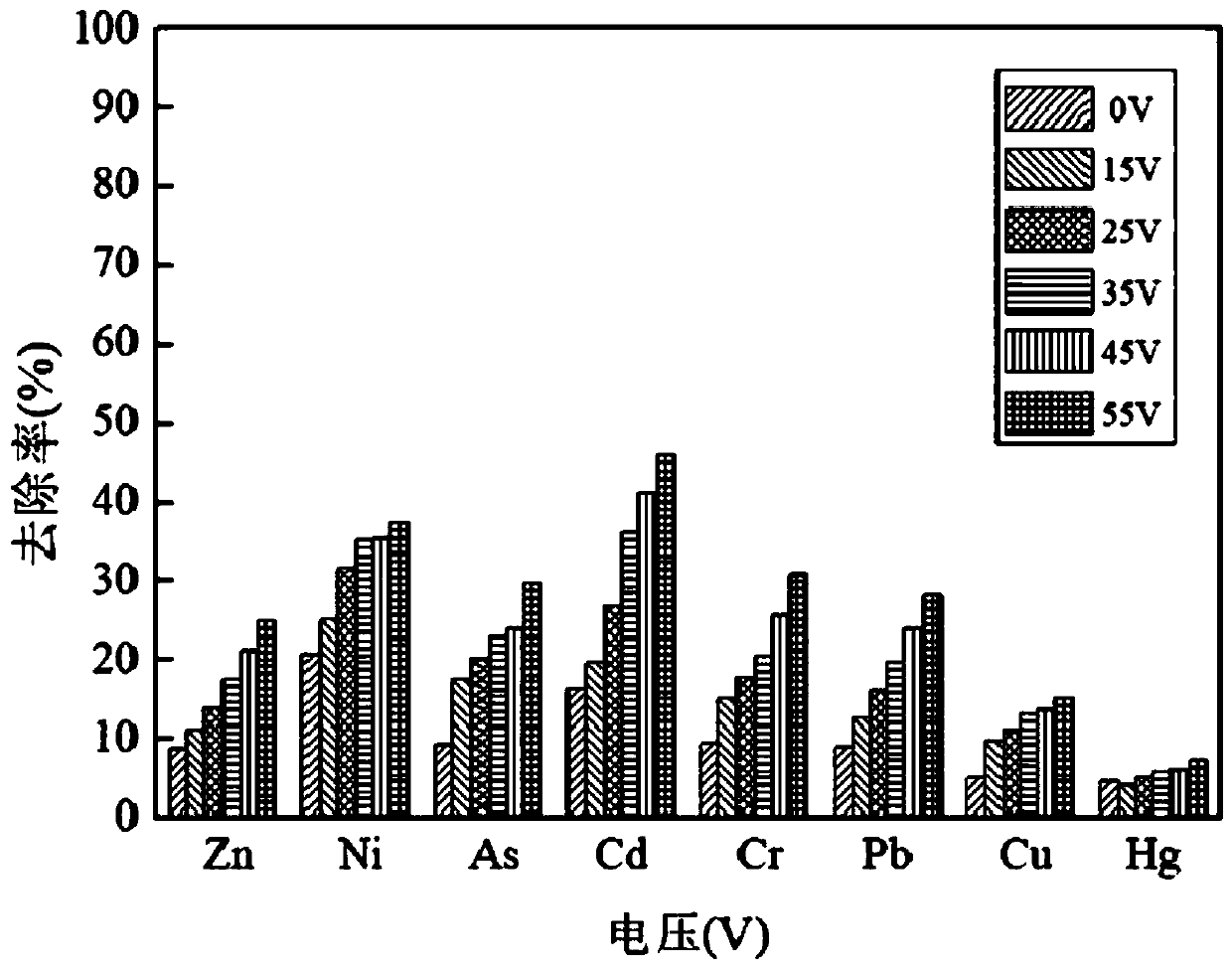
[0027] Take the remaining sludge from a sewage treatment plant, measure the initial content of heavy metals zinc, nickel, arsenic, chromium, cadmium, lead, copper and mercury in the sludge, and use the electroosmotic dehydration device to dehydrate the sludge. The electroosmotic dehydration device Both the cathode and the anode in the electroosmotic dehydration device are made of ruthenium-plated iridium titanium electrodes, so that the electrodes have sufficient strength and corrosion resistance. The voltages loaded on the cathode and anode in the electroosmosis dehydration device are set to 0V, 15V, 25V, 35V, 45V, 55V respectively. , under the pressure of 0.6MPa, press filter for 60min, collect the anion and anode filtrate and mud cake, measure the concentration of each heavy metal ion in the anode and anode filtrate and mud cake, calculate the heavy metal removal rate in the sludge, the heavy metal in the sludge The calculation formula of removal rate is as follows: R=(C 0 ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Take the remaining sludge of a sewage treatment plant, measure the initial heavy metal zinc, nickel, arsenic, chromium, cadmium, lead, copper and mercury content in the sludge, and then add sodium sulfate to the sludge to be 0g / gTSS, 0.02g / gTSS, 0.04g / gTSS, 0.07g / gTSS, 0.11g / gTSS, 0.15g / gTSS, where TSS is the concentration of total suspended solids in the sludge, at a speed of 300r / min, the stirring time is 30min, and the electroosmotic dehydration is set The bipolar voltage in the device is 55V, and under the condition of 0.6MPa, press filter for 60min, collect the anode and cathode filtrate and mud cake, measure the concentration of heavy metal ions in the anode and cathode filtrate and mud cake, and calculate the heavy metal removal in the sludge Rate.
[0033] Such as Figure 4 and 5 As shown, with the increase of the concentration of sodium sulfate added to the sludge, the heavy metal content in the filtrate of the cathode and anode both showed a trend of first ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Take the remaining sludge of a sewage treatment plant, measure the initial heavy metal zinc, nickel, arsenic, chromium, cadmium, lead, copper and mercury content in the sludge, and then add citric acid to the sludge at 0g / gTSS, 0.02g / gTSS, 0.04g / gTSS, 0.07g / gTSS, 0.11g / gTSS, 0.15g / gTSS, where TSS is the concentration of total suspended solids in the sludge, at a speed of 300r / min, the stirring time is 30min, and the electroosmotic dehydration is set The bipolar voltage in the device is 55V. Under the condition of pressure of 0.6MPa, press filter for 60min, collect the anode and cathode filtrate and mud cake, measure the concentration of each heavy metal ion in the anode and cathode filtrate and mud cake, and calculate the sludge heavy metal removal rate.
[0037] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the content of heavy metals in cathodic filtrate increases first and then tends to be stable with the increase of citric acid dosage. When the dosage is 0.11g / gTSS, Zn, Ni, As, Cd, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com