Nanoscale single exosome separation method
A separation method and nanoscale technology, applied in cell dissociation methods, biochemical equipment and methods, treatment of microorganisms with electricity/wave energy, etc., can solve problems such as low separation efficiency, reduced quality, and low dispersion efficiency, and achieve separation The effect of high yield, convenient method and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
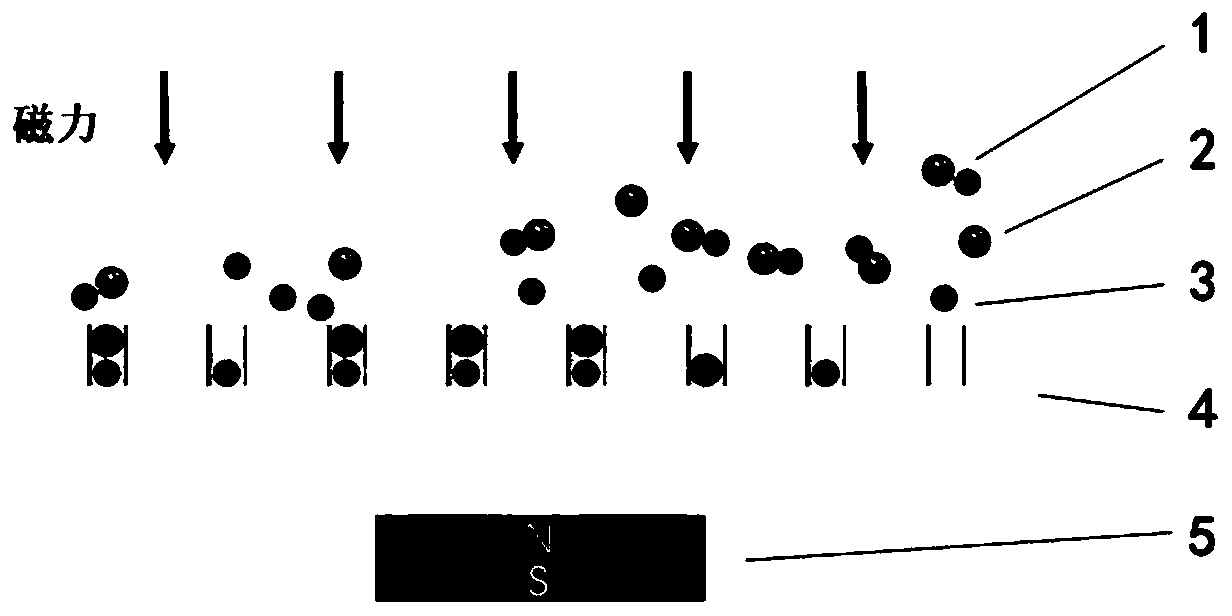
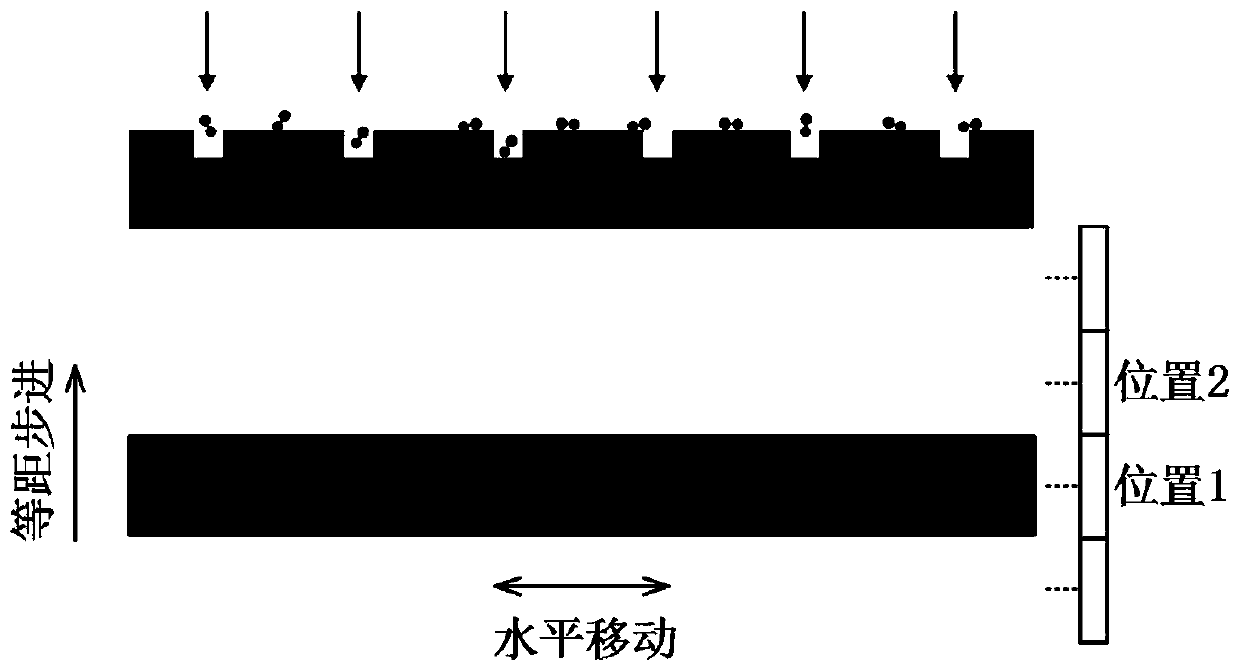
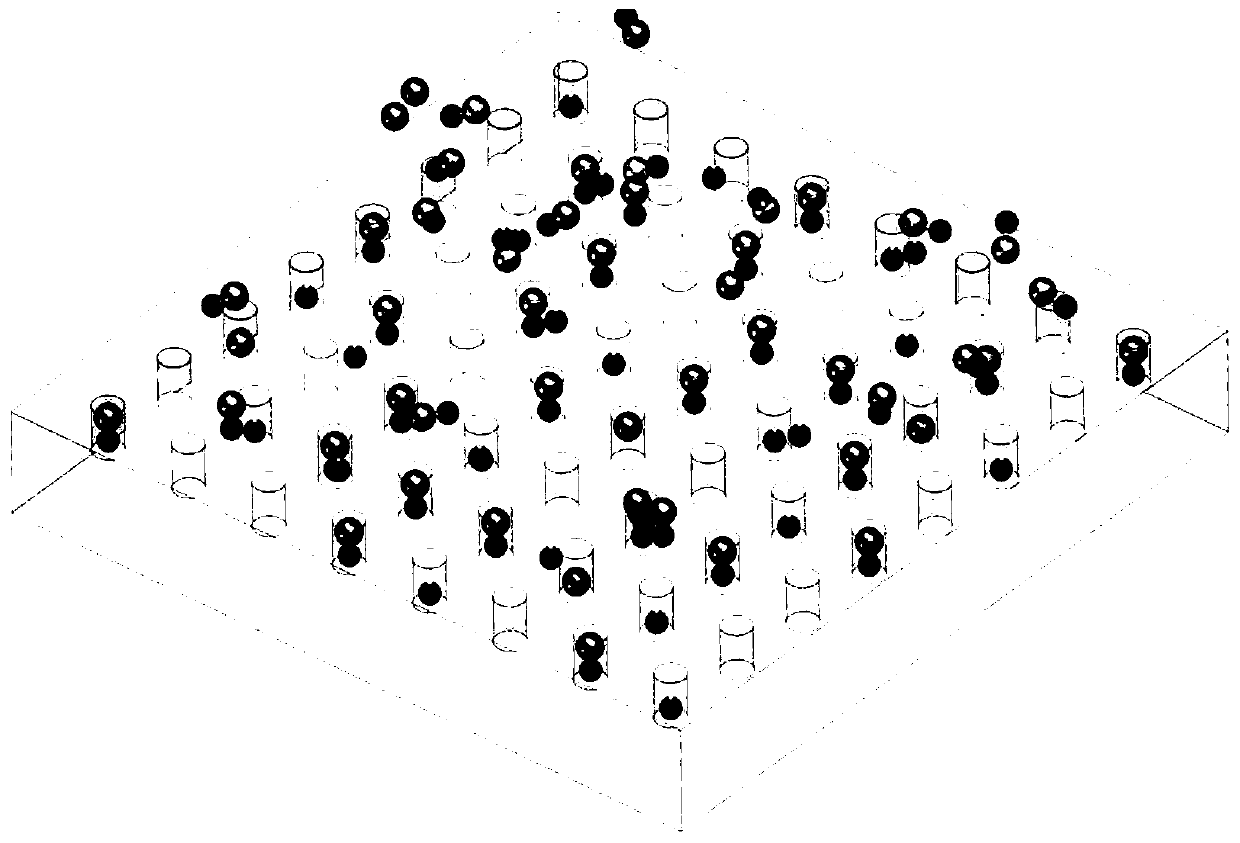
[0066] In this embodiment, the diameter of the nanoholes in the nanohole microarray structure is set to 100±15 nm, and the depth of the nanoholes is set to 250±30 nm. The horizontal and vertical centers of the nano-holes are equally spaced at 2 μm to form a 201×201 lattice square microarray. The number of nano-holes on a single sheet is 40,401, and they are located in the central area of the general-purpose cover glass. The nanohole microarray structure is prepared using the femtosecond laser direct writing equipment of the cooperative research group.
[0067] Dilute the exosome-containing cell culture medium after biological extraction and purification to a concentration of 1×10 NTA quantitative test 7 pieces / ml.
[0068] Choose common and consistent superparamagnetic amino magnetic beads with a diameter of 50nm. The surface contains amino functional groups that can specifically couple with exosome coating proteins. Dilute the magnetic bead sample solution to 1×10 7 ~1×10...
Embodiment 2
[0078] In this embodiment, the diameter of the nanoholes in the nanohole microarray structure is set to 200±15 nm, and the depth of the nanoholes is set to 250±30 nm. The horizontal and vertical centers of the nano-holes are equally spaced at 2 μm to form a 201×201 lattice square microarray. The number of nano-holes on a single sheet is 40,401, and they are located in the central area of the general-purpose cover glass. The nanohole microarray structure is prepared using the femtosecond laser direct writing equipment of the cooperative research group.
[0079] Dilute the exosome-containing cell culture medium after biological extraction and purification to a concentration of 1×10 NTA quantitative test 8 pieces / ml.
[0080] Use common, consistent, superparamagnetic amino beads with a diameter of 100nm, the surface of which contains amino functional groups that can specifically couple with exosome coating proteins, and dilute the magnetic bead sample solution 1×10 8 ~1×10 9...
Embodiment 3
[0090] In this embodiment, the diameter of the nanoholes in the nanohole microarray structure is set to 250±15 nm, and the depth of the nanoholes is set to 300±30 nm. The horizontal and vertical centers of the nano-holes are equally spaced at 2 μm to form a 201×201 lattice square microarray. The number of nano-holes on a single sheet is 40,401, and they are located in the central area of the general-purpose cover glass. The nanohole microarray structure is prepared using the femtosecond laser direct writing equipment of the cooperative research group.
[0091] Dilute the exosome-containing cell culture medium after biological extraction and purification to a concentration of 1×10 NTA quantitative test 9 pieces / ml.
[0092] Choose common and consistent superparamagnetic amino magnetic beads with a diameter of 120nm, the surface of which contains amino functional groups that can specifically couple with exosome coating proteins, and dilute the magnetic bead sample solution to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com