Method for increasing efficiency of homologous recombination-based gene editing in plant
A technology of gene editing and homologous recombination, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, other methods of inserting foreign genetic materials, genetic engineering, etc., can solve undisclosed problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102] Example 1. Homologous recombination efficiency analysis using anthocyanin labeling
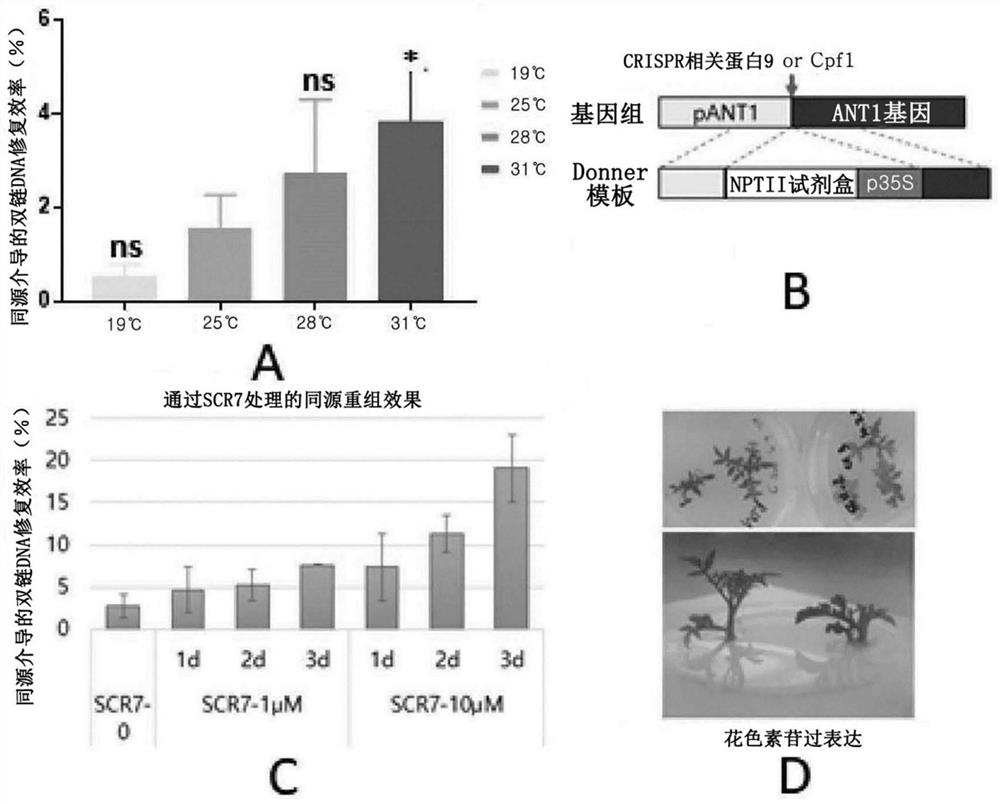
[0103] To investigate the efficiency of homology-mediated double-strand DNA repair-based gene scissors in tomato crops, the 35S promoter was inserted as a transcription factor for regulation of anthocyanin synthesis by homology-mediated double-strand DNA repair. In the upstream promoter position of the transcription start position of the ANT1 gene, and through the overexpression of anthocyanins activated by the ANT1 gene to induce the formation of purple callus.
[0104] When the homology-mediated double-strand DNA repair template (sequence 29) can perform a homology-mediated double-strand DNA repair event by inserting pNos-NPTII-OCSt in the 35S promoter base sequence and its upstream, the acquisition card Namycin resistance. In this case, the upper base sequence having homology is 1043 bp, and the lower base sequence is 592 bp. And, two transcription activator-like effector nuclease ...
Embodiment 2
[0130] Example 2. Increased Homologous Recombination Frequency in Plants by SCR7 Pyrazine Treatment
[0131] Most DNA repair occurs through the non-homologous end-joining pathway, while repair based on homology-mediated double-strand DNA repair occurs in part. According to existing research reports, the efficiency of homology-mediated double-strand DNA repair can be improved in mammals by blocking the non-homologous end-joining pathway. SCR7 pyrazine, an inhibitor of mammalian ligase IV, was reported to increase homology-mediated double-strand DNA repair by approximately 19-fold in mice and 5-fold in human cell lines. According to the viewpoint proposed by Nishizawa-Yokoi et al. (2016, Plant Physiol.170(2):653-666), in plants, ligase IV can play an important role in the non-homologous end joining pathway of rice. However, there have been no reports of the effect of SCR7 pyrazines on homology-mediated double-strand DNA repair in plants. Therefore, the present inventors analyz...
Embodiment 3
[0144] Example 3. The kinetic model of the release of the bean yellow dwarf virus replication replicon
[0145] The inventors found the optimal time point for maximal release of the prototypic yellow dwarf virus replicon in the Agrobacterium-infected tomato cotyledon system. Viral replicons are released in prototypical form from linear triple-helical DNA delivered to the plant nucleus and amplified to hundreds to thousands per cell by rolling circle replication. Information on the kinetics of maximal replicon release can provide information on the optimal period for adapting a small molecule to tissue culture systems. To study the dynamics of replicon release, cotyledons were transformed with Agrobacterium containing the bean yellow dwarf virus vectors pLSL.GFP.R (Cermak et al., 2015), pLSL.R.GGFP and the non-viral vector pAGM4723. Virus prototypes were detected by PCR analysis using specific primers that amplify the junction of two large intergenic regions in genomic DNA iso...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com