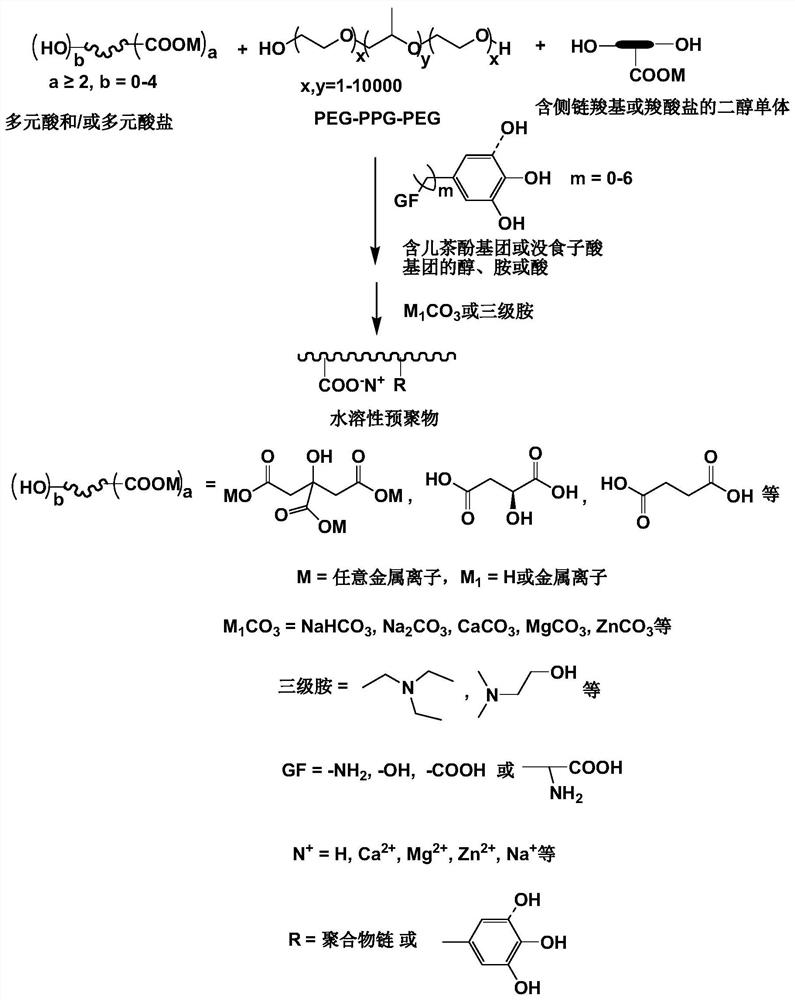
Degradable temperature-sensitive adhesive, preparation method and application thereof
An adhesive and temperature-sensitive technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve the problems of insufficient applicability and the lack of temperature sensitivity of the adhesive, and achieve good biocompatibility, good stress-strain performance, and good elasticity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] This embodiment provides a degradable temperature-sensitive adhesive, the preparation method of which comprises the following steps:
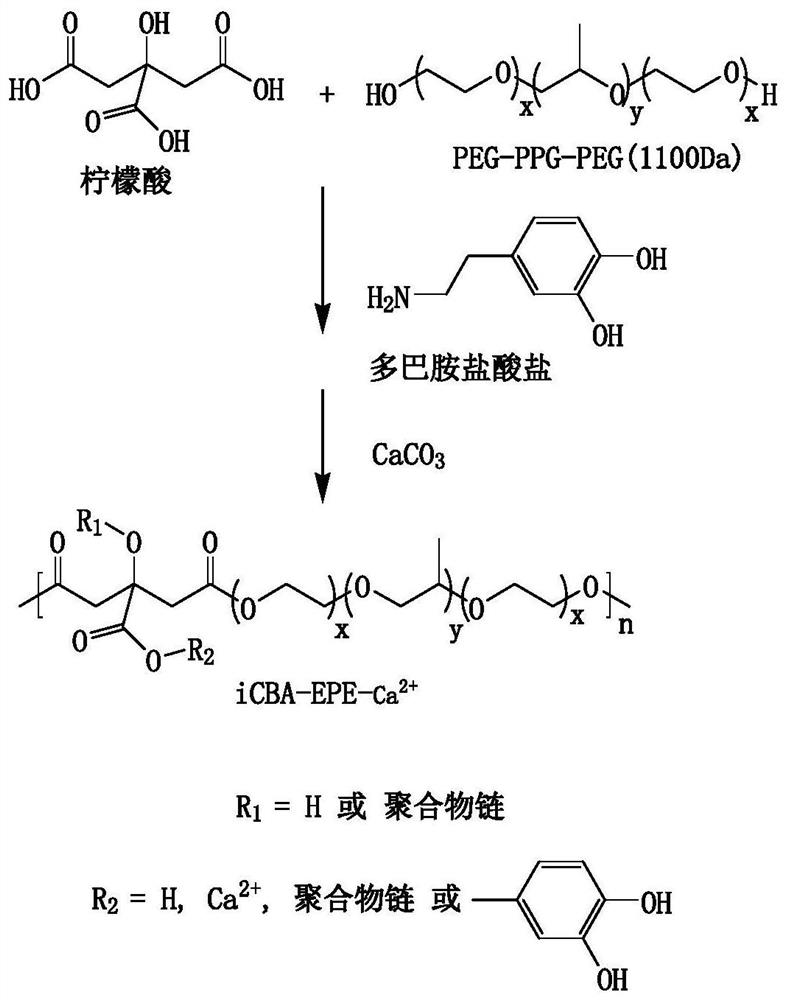
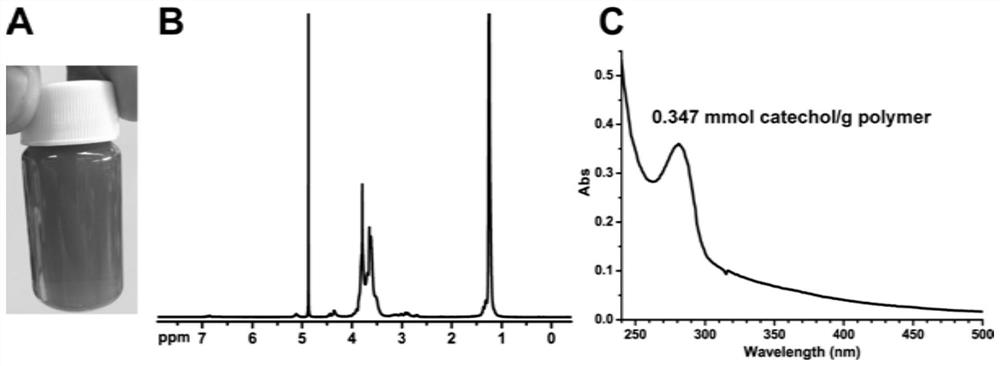
[0064] (1) Take 11.528g citric acid, 55g PEG-PPG-PEG (EPE, molecular weight 1100Da), 2.844g dopamine hydrochloride, place in a single-mouthed round-bottomed glass flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer of appropriate size, and place in a 160°C oil Under the bath, citric acid and dopamine hydrochloride are dissolved in EPE to obtain a uniform reaction mixture (a small amount of deionized water can be added to help dissolve, and 0~0.5g stannous isooctanoate or sulfuric acid can also be added as a catalyst); then the oil The temperature of the bath is lowered to 140°C, and the reaction mixture is continuously stirred under vacuum conditions (rotating speed 600rpm). During the polymerization process, the rotating speed is gradually reduced according to the viscosity of the polymer until the viscosity of the reaction system increases to the po...
Embodiment 2
[0072] This example provides a degradable temperature-sensitive adhesive, its preparation method and raw materials are similar to Example 1, the only difference is that 20g of calcium carbonate in Example 1 is replaced by 21g of magnesium carbonate, the obtained water-soluble pre The polymer is iCMBA-EPE-Mg 2+ .
[0073] The adhesive obtained in this example (marked as TSBA-2) is liquid at room temperature and cured at about 37° C. to obtain a cross-linked adhesive.
[0074] Use rats or rabbits to construct a large bone defect model, mix a certain amount of hydroxyapatite (HA) into TSBA-2 (liquid at room temperature) at room temperature, and inject it into the bone defect site, TSBA-2 / HA As the temperature rises at the bone defect site, it gradually transforms into a uniform composite hydrogel to fill the bone defect. It shows that the magnesium ions in the adhesive can promote bone repair, Fe 3+ It can provide certain antibacterial activity.
Embodiment 3
[0076] This embodiment provides a degradable temperature-sensitive adhesive, the preparation method of which comprises the following steps:
[0077] (1) Take 8.070g of citric acid, 3.854g of citric acid monosodium salt, 55g of PEG-PPG-PEG (EPE, molecular weight 1100Da), 2.844g of dopamine hydrochloride, and place them in a single-port round bottom equipped with a magnetic stir bar of appropriate size In a glass flask, dissolve citric acid, monosodium citric acid and dopamine hydrochloride in EPE in an oil bath at 160°C to obtain a uniform reaction mixture (a small amount of deionized water can be added to help dissolve, and 0-0.5 g stannous octoate or sulfuric acid as a catalyst); then the temperature of the oil bath is lowered to 140°C, and the reaction mixture is continuously stirred (rotating speed 600rpm) under vacuum conditions, and the rotating speed is gradually reduced according to the viscosity of the polymer during the polymerization process until the reaction The vi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com