Defect type sulfur-indium-zinc microsphere visible-light-induced photocatalyst, and preparation method and application thereof
An indium-zinc-sulfur, defect-type technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as low hydrogen production efficiency, achieve high photocatalytic activity, rich surface active sites, Simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0037] The third embodiment of the present invention provides an application of the defect-type sulfur-indium-zinc microsphere visible light catalyst in photolysis of water to produce hydrogen.
[0038] The fourth embodiment of the present invention provides a method for producing hydrogen by photolysis of water. The above-mentioned defect-type sulfur indium zinc microspheres are added to a system containing water, lactic acid and chloroplatinic acid for light treatment.
[0039] In some examples of this embodiment, the light treatment is to use a 200-400W xenon lamp and a power density of 50-150mW cm -2 Irradiate for 4-6 hours under simulated sunlight conditions.
[0040]In order to enable those skilled in the art to understand the technical solution of the present invention more clearly, the technical solution of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments.
Embodiment 1
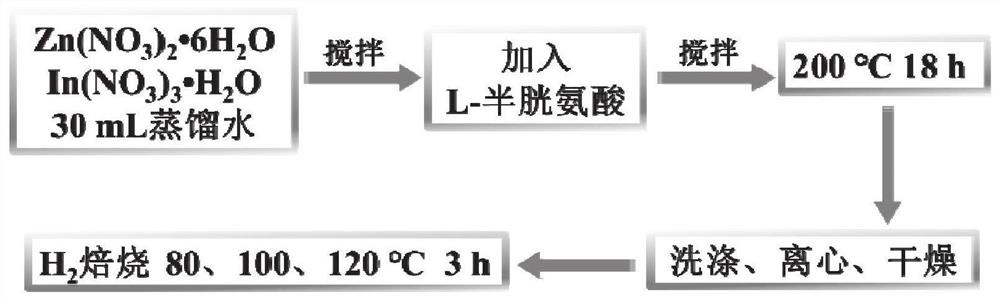
[0042] Weigh 0.074g Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O and 0.15g In(NO 3 ) 3 ·H 2 O stirring (speed is 500r min -1 ) was dissolved in 30 mL of distilled water, and then 0.233 g of L-cysteine was added to continue stirring for 2 h. Hydrothermal reaction at 200°C for 18h. After cooling, the solution was centrifuged (4000r min -1 and centrifuged for 3 min), and the separated precipitate was washed three times with water and ethanol respectively. Vacuum dry in a drying oven at 60°C for 12 hours, and grind the dried powder to obtain ZnIn 2 S 4 Powder material. ZnIn 2 S 4 The powder material is placed in a tube furnace, and hydrogen gas is introduced into the tube furnace, and the flow rate of hydrogen gas is 40mL min -1 , heated up to 80°C at a rate of 2°C / min, fired for 3 hours, and cooled to room temperature to obtain defect-type ZnIn 2 S 4 Powder material.
Embodiment 2
[0044] Weigh 0.074g Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O and 0.15g In(NO 3 ) 3 ·H 2 O stirring (speed is 500r min -1 ) was dissolved in 30 mL of distilled water, and then 0.233 g of L-cysteine was added to continue stirring for 2 h. Hydrothermal reaction at 200°C for 18h. After cooling, the solution was centrifuged (4000r min -1 and centrifuged for 3 min), and the separated precipitate was washed three times with water and ethanol respectively. Vacuum dry in a drying oven at 60°C for 12 hours, and grind the dried powder to obtain ZnIn 2 S 4 Powder material. ZnIn 2 S 4 The powder material is placed in a tube furnace, and hydrogen gas is introduced into the tube furnace, and the flow rate of hydrogen gas is 40mL min -1 , heated at a rate of 2°C / min to 100°C for 3 hours, and cooled to room temperature to obtain defect-type ZnIn 2 S 4 Powder material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com