Method for separating hesperidin, neohesperidin, naringin and synephrine from immature bitter oranges
A technology of neohesperidin and hesperidin, applied in the fields of naringin and synephrine, neohesperidin, and extraction of hesperidin, which can solve the problems of low yield, complicated operation, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
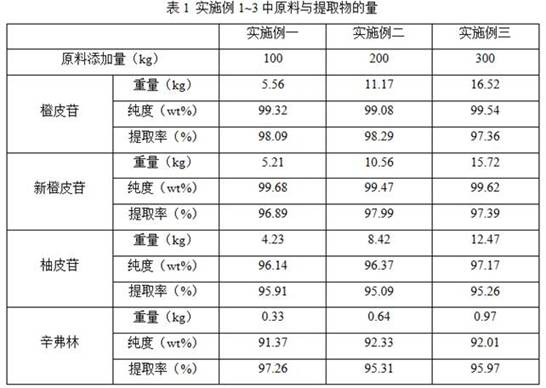
[0044] (1) Heating extraction: take 100 kg of Fructus Aurantii, crush, pass through a 20-mesh sieve, add 3000L of water in 3 times, stir and extract for 1 hour at 85℃ each time, cool, pass through a fine filter membrane, collect the extract and extract separately Slag
[0045] (2) Separation of hesperidin: The extract residue obtained in step (1) was extracted with 1500L sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 0.5wt% at 30°C for 1.5h, centrifuged and filtered, the filtrate was adjusted to pH value with hydrochloric acid 2. After standing for crystallization at room temperature, the precipitated crystals are filtered under reduced pressure and vacuum dried to obtain 5.56 kg of hesperidin product with a purity of 99.32wt% and an extraction rate of 98.09%;
[0046] (3) Separation of neohesperidin: pass the extract obtained in step (1) through D101 macroporous adsorption resin, and collect the effluent for later use; the macroporous adsorption resin is desorbed with 2BV ethan...
Embodiment 2
[0050] (1) Heating extraction: take 200kg of Citrus aurantium, crush, pass through a 30-mesh sieve, add 8000L water in 4 times, stir and extract at 90℃ for 1.5h each time, cool, pass through a fine filter membrane, collect the extract and Extract residue
[0051] (2) Separation of hesperidin: the extract residue obtained in step (1) was extracted with a 4000L potassium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 1.0 wt% at 35°C for 2.5 hours, centrifuged and filtered, and the filtrate was adjusted to pH value with hydrochloric acid 4. After standing for crystallization at room temperature, the precipitated crystals are filtered under reduced pressure and vacuum dried to obtain 11.17kg of hesperidin product with a purity of 99.08wt% and an extraction rate of 98.29%;
[0052] (3) Separation of new hesperidin: pass the extract obtained in step (1) through D101 macroporous adsorption resin, and collect the effluent for later use; the macroporous adsorption resin is desorbed with 2.5BV o...
Embodiment 3
[0056] (1) Heating extraction: Take 300kg of Fructus Aurantii, crush, pass through 40 mesh sieve, add 12000L of water in 4 times, stir and extract 2h each time at 92℃, cool, pass through fine filter membrane, collect extract and extract separately Slag
[0057] (2) Separation of hesperidin: The extract residue obtained in step (1) was stirred and extracted with 7500L saturated lime aqueous solution at 45°C for 4h, centrifuged and filtered, the filtrate was adjusted to pH 6 with hydrochloric acid, and then left to stand at room temperature for crystallization , The precipitated crystals were filtered under reduced pressure and vacuum dried to obtain 16.52 kg of hesperidin product with a purity of 99.54wt% and an extraction rate of 97.36%;
[0058] (3) Separation of neohesperidin: pass the extract obtained in step (1) through D101 macroporous adsorption resin, and collect the effluent for use; the macroporous adsorption resin is desorbed with 3BV 75% ethanol by volume to obtain desor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com