A method for enriching n-glycopeptides or n-sugar chains
A sugar chain and enrichment technology, applied in the field of enriching N-glycopeptides or N-glycosides, can solve the problems of complex operation steps, time-consuming and high technical requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
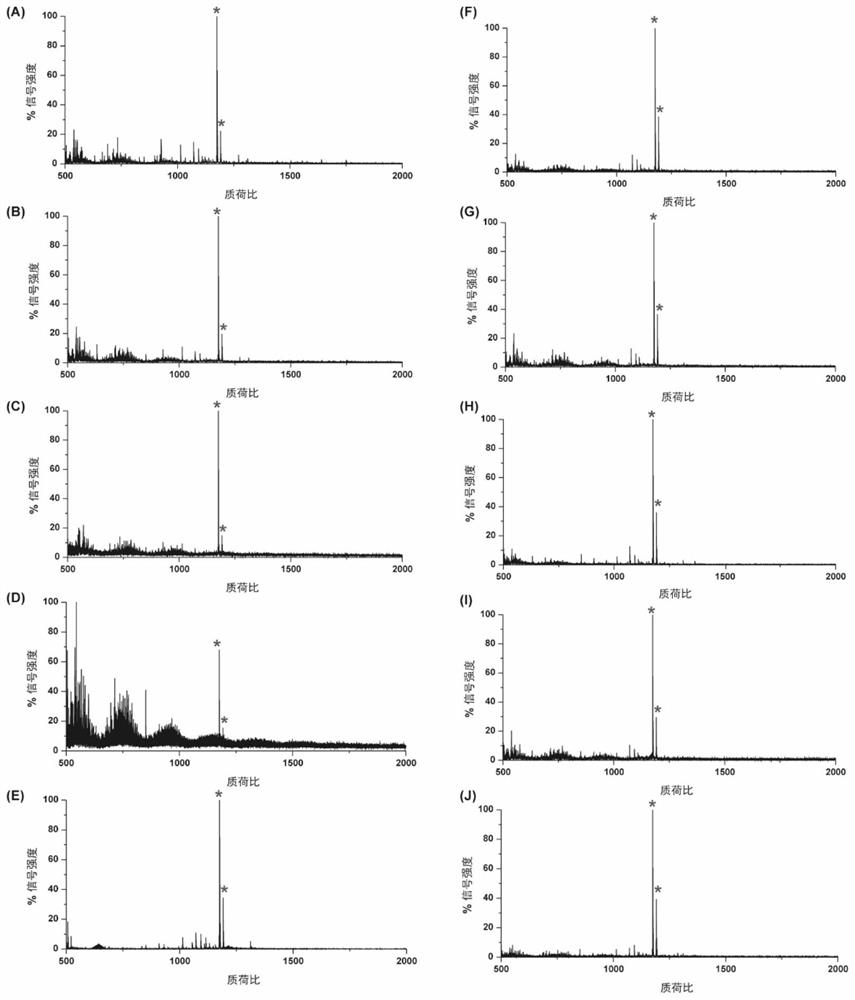
[0044] The enrichment of embodiment 1N-glycopeptide
[0045] Bacterial cellulose pieces were cut into 1 cm × 1 cm pieces to obtain BC pieces, which were washed 3 times with distilled water, and then, BC pieces were freeze-dried and stored at 4 °C for further use.
[0046] Proteins were diluted in 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate (ABC) buffer at a concentration of 2 μg / μL and denatured in a 100° C. water bath for 5 min. Proteins were then reduced with 10 mM DTT for 1 h at 37°C, followed by alkylation with 25 mM IAA for 0.5 h at 37°C. Then trypsin was added to the solution at an enzyme:protein ratio of 1:50 (w / w), incubated overnight at 37°C, and then boiled at 100°C for 5min to terminate the enzymatic hydrolysis reaction. Digested peptides were dried by vacuum centrifugation and stored at -20°C for later use.
[0047] To obtain a mixture of sugar chains from the peptide, the lyophilized peptide from the last step was dissolved in 50 mM ABC, and the peptide N- Glycosidase F release...
Embodiment 2
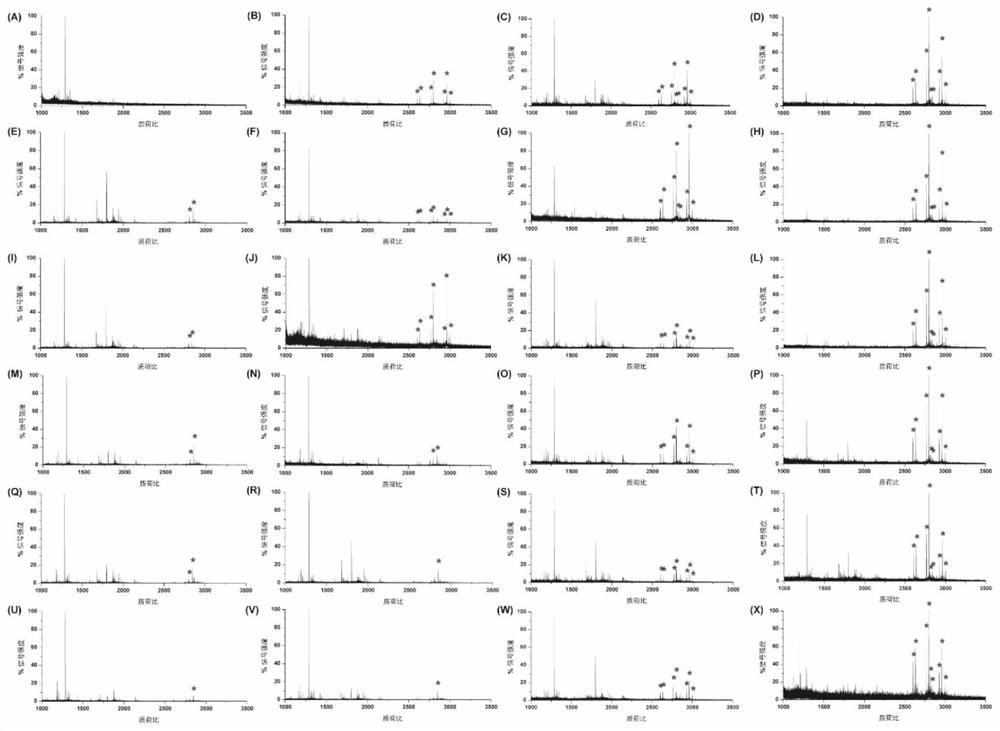
[0049] Example 2 Enrichment of N-sugar chains
[0050] Bacterial cellulose pieces were cut into 1 cm × 1 cm pieces to obtain BC pieces, which were washed 3 times with distilled water, and then, BC pieces were freeze-dried and stored at 4 °C for further use.
[0051] Proteins were diluted in 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate (ABC) buffer at a concentration of 2 μg / μL and denatured in a 100° C. water bath for 5 min. Proteins were then reduced with 10 mM DTT for 1 h at 37°C, followed by alkylation with 25 mM IAA for 0.5 h at 37°C. Then trypsin was added to the solution at an enzyme:protein ratio of 1:50 (w / w), incubated overnight at 37°C, and then boiled at 100°C for 5min to terminate the enzymatic hydrolysis reaction. Digested peptides were dried by vacuum centrifugation and stored at -20°C for later use.
[0052] To obtain the glycan mixture from the peptide, the lyophilized peptide in the last step was dissolved in 50 mM ABC, and the glycan peptide was added at an enzyme:protein ra...
Embodiment 3
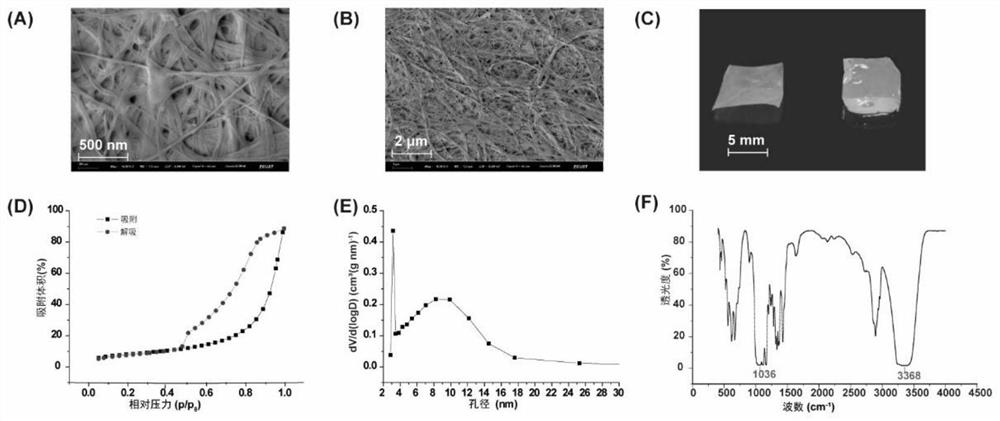
[0054] Example 3 Characterization of bacterial cellulose
[0055] Bacterial cellulose is composed of sugar chains with β-1,4-glycosidic bonds and has an interconnected 3D porous network structure. The morphology of bacterial cellulose was observed by SEM. Such as image 3 As shown in A and 3B, bacterial cellulose has a nanoscale fiber structure. The interconnected 3D porous network structure provides high specific surface area, strong flexibility and high tensile strength. Bacterial cellulose has a remarkable water absorption capacity. Bacterial cellulose forms solid sheets after drying, while the solution swells like a gel after absorption ( image 3 C). Significant water capacity was evaluated by mass change before and after water absorption. Bacterial cellulose can absorb 80 times its own weight in water.
[0056] The nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherm further proved the porous structure of bacterial cellulose ( image 3 D). The hysteresis loop representing th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com