Application of saccharomyces cerevisiae in postharvest disease control, storage and preservation of baby Chinese cabbage
A technology for Saccharomyces cerevisiae and baby cabbage, which is applied in the field of postharvest disease control, storage and preservation, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae to achieve the effects of controlling quality decline, slowing the increase in organic acid content and reducing potential harm
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
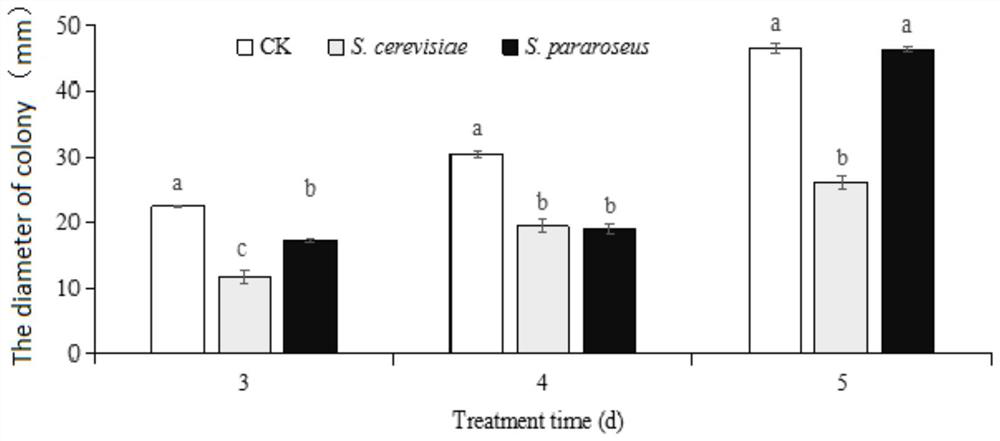
[0035] Inhibitory effects of different yeasts on controlling baby cabbage postharvest diseases in vitro;
[0036] 1. Test plan
[0037] 1. Preparation of Yeast Suspension
[0038] Put 50mL NYDB medium in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, suck 1mL of activated Saccharomyces cerevisiae Y-912 with a pipette gun, and culture it at 28°C and 180rpm for 24 hours to obtain a yeast culture solution, centrifuge it at 7000r / min for 15min, The cells were collected, washed twice with sterile saline, and configured to a size of 1.0×10 8 cells / mL of yeast suspension.
[0039] 2. Preparation of Mold Spore Suspension
[0040] Scrape the Alternaria tenoides spores on the PDA medium, blow and beat repeatedly in sterile saline, shake for 10 minutes, and adjust the concentration to 5.0×10 4 spores / mL of spore suspension.
[0041] 3. The in vitro inhibitory effect of different yeasts on Alternaria adenocarina
[0042] Pour 30mL of PDA medium into a sterile 9cm petri dish, cool and solidify, and punch...
Embodiment 2
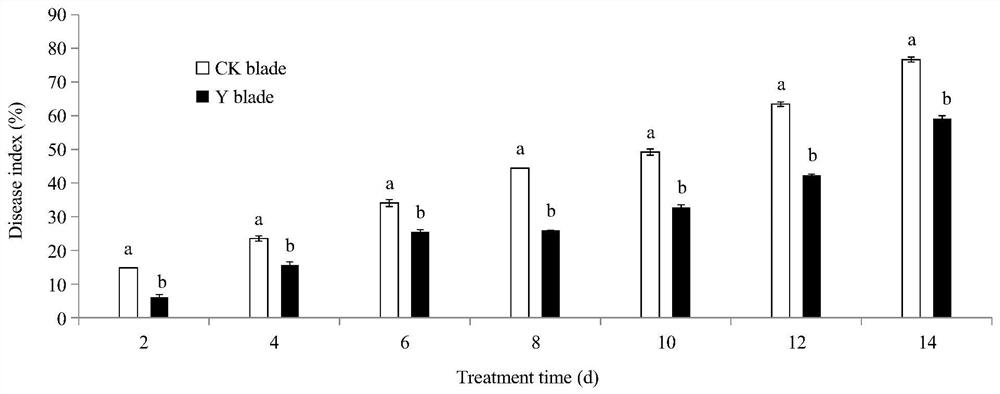
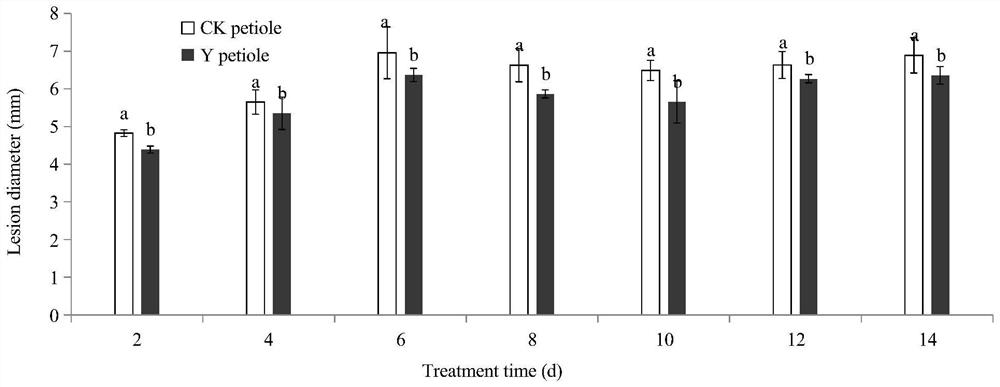
[0046] Saccharomyces cerevisiae Y-912 is used for the purposes of black spot control after harvesting Chinese baby cabbage;
[0047] 1. Test plan
[0048] First of all, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Y-912 of the present invention is used to control postharvest black spot of baby cabbage. The specific steps are: select fresh baby cabbage, remove the outer layer, and select a product with the same size and color, no mechanical damage on the surface, and no damage by diseases and insect pests. Soak the whole leaf with 0.02% sodium hypochlorite solution for 1 min, then rinse it with clean water, and put it in a sterile plastic basket to dry.
[0049] Carry out different treatments at the leaves and petioles of the vegetable leaves: the leaf part of the vegetable leaves is evenly sprayed with 1.0×10 8 cells / mL of the yeast suspension, after 2h, spray the Alternaria tennatus spore suspension (concentration is 1×10 6 spores / mL); the control group was treated with sterile saline inst...
Embodiment 3
[0065] The use of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Y-912 in the storage and preservation of baby cabbage, that is, the effect on postharvest natural decay and quality (Vc, titratable acid, weight loss rate);
[0066] Put the baby cabbage leaves with the same size, no mechanical damage on the surface and no damage from diseases and insect pests in a sterilized plastic basket, and put 1.0×10 8 The yeast suspension of cells / mL is sprayed on the surface of baby cabbage leaves to make it evenly covered; after drying, seal it, store it in a constant temperature incubator (RH 90%, 20°C) and count the baby cabbage rot rate after a certain period of time and disease index, and measured the Vc and titratable acid content of leaves and petioles, as well as the weight loss rate of vegetable leaves. Each treatment was repeated 5 times with 12 vegetable leaves each time.
[0067] The formula for calculating the decay rate is as follows:
[0068] Rot rate = number of rotten leaves / total number of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com