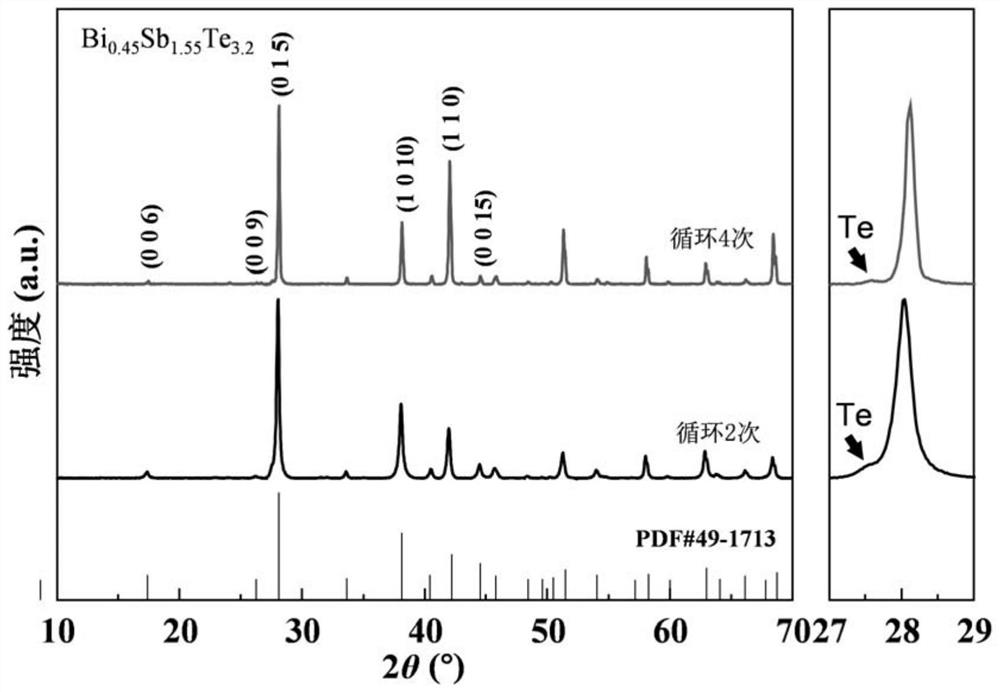
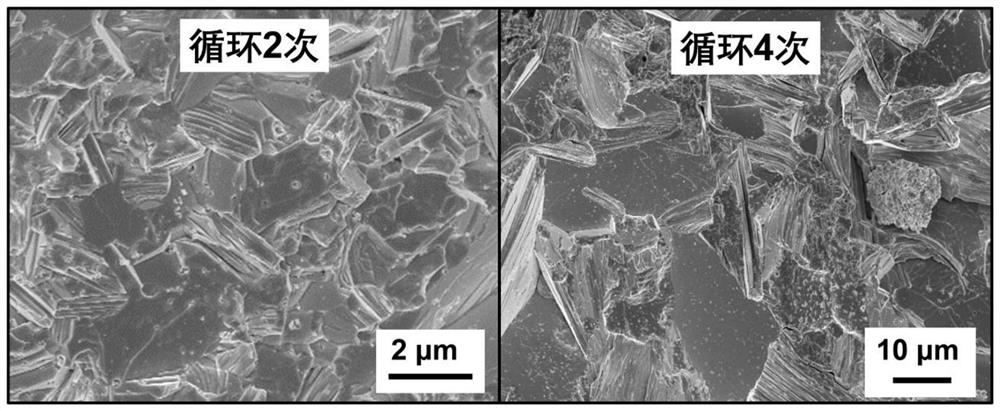
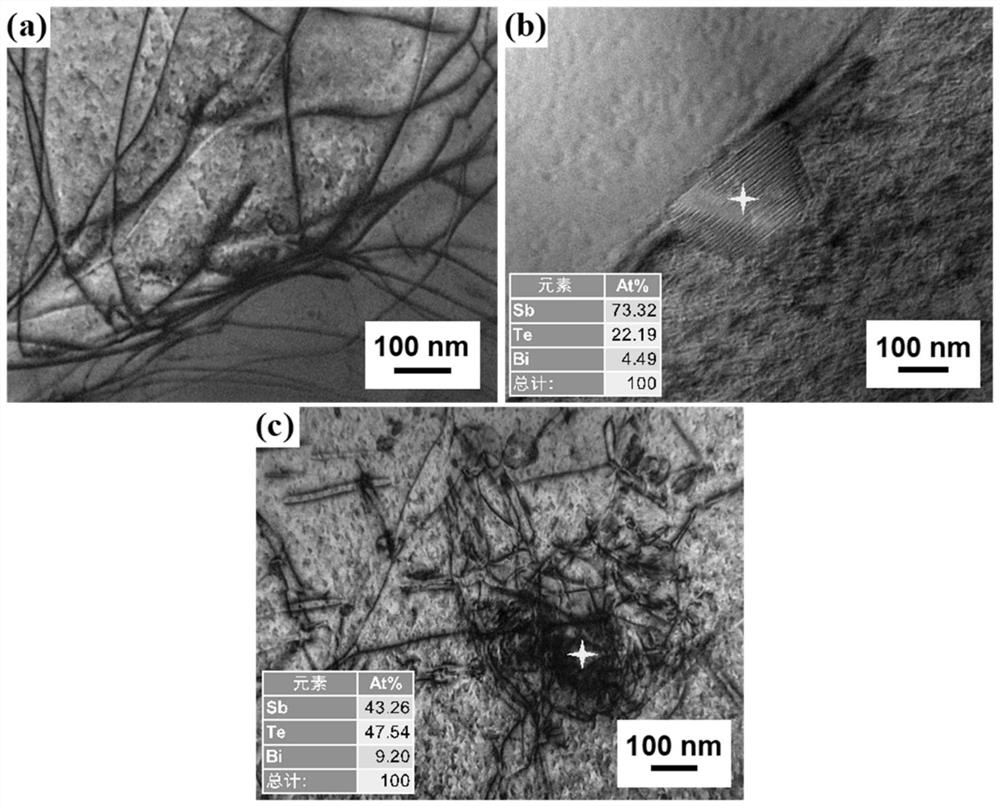
Non-stoichiometric bismuth telluride-based thermoelectric material and preparation method thereof
A non-stoichiometric ratio, bismuth telluride-based technology, applied in the direction of thermoelectric device junction lead-out materials, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the electrical properties of materials, unfavorable carrier transport, poor repeatability, etc., and achieve favorable electron transport , no risk of high temperature, high repetition rate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0040] The preparation method of the non-stoichiometric bismuth telluride-based thermoelectric material proposed by the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0041] (1) According to the chemical composition of the bismuth telluride-based thermoelectric material as claimed in claim 1, take Bi elemental powder, Sb elemental particle and Te elemental powder raw material, put into ball mill jar and pass into protective gas, carry out ball milling process , to get powder;
[0042] (2) Putting the powder obtained in step (1) into a graphite mold, applying pressure in a vacuum to perform cyclic discharge plasma sintering with repeated temperature rise and fall, to obtain a bismuth telluride-based thermoelectric material block.
[0043] In the above preparation method, the purity of the Bi elemental powder and the Sb elemental particles is greater than or equal to 99.99%, and the purity of the Te elemental powder is 99.999%, by mass.
[0044] In the above preparation met...
Embodiment 1
[0065] Bi according to the chemical formula 0.45 Sb 1.55 Te 3.2 (i.e. general formula Bi x Sb 2-x Te 3+y The stoichiometric ratio of x=0.45, y=0.2) takes by weighing 15g of the raw material mixture, specifically 2.0366 grams of Bi elemental powder (purity is 99.99%), Sb elemental particles (purity is 99.99%) 4.0948 grams, Te elemental Powder (99.999% pure) 8.8687 g.
[0066] Put the weighed mixture into a stainless steel ball milling jar, wherein the mass ratio of stainless steel balls to raw materials is 20:1, and fill the ball milling jar with argon-hydrogen mixed gas as a protective gas, wherein the hydrogen volume content is 5%, and the argon The gas volume content is 95%, and ball milled at a speed of 450 r / min for 6 hours in a planetary ball mill (QM-3SP2, Nanjing University Instrument Factory).
[0067] Put the above-prepared powder into a graphite mold, put it into a spark plasma sintering furnace (SPS) after compaction, and raise it to 420 ° C in 7 minutes in th...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Bi according to the chemical formula 0.45 Sb 1.55 Te 3.2 (i.e. general formula (1) Bi x Sb 2-x Te 3+yThe stoichiometric ratio of x=0.45, y=0.2) takes by weighing 15g of the raw material mixture, specifically 2.0366 grams of Bi elemental powder (purity is 99.99%), Sb elemental particles (purity is 99.99%) 4.0948 grams, Te elemental Powder (99.999% pure) 8.8687 g.
[0072] Put the weighed mixture into a stainless steel ball milling jar, wherein the mass ratio of stainless steel balls to raw materials is 20:1, and fill the ball milling jar with argon-hydrogen mixed gas as a protective gas, wherein the hydrogen volume content is 5%, and the argon The gas volume content is 95%, and ball milled at a speed of 450 r / min for 6 hours in a planetary ball mill (QM-3SP2, Nanjing University Instrument Factory).
[0073] Put the above-prepared powder into a graphite mold, put it into a spark plasma sintering furnace (SPS) after compaction, and raise it to 420 ° C in 7 minutes in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com