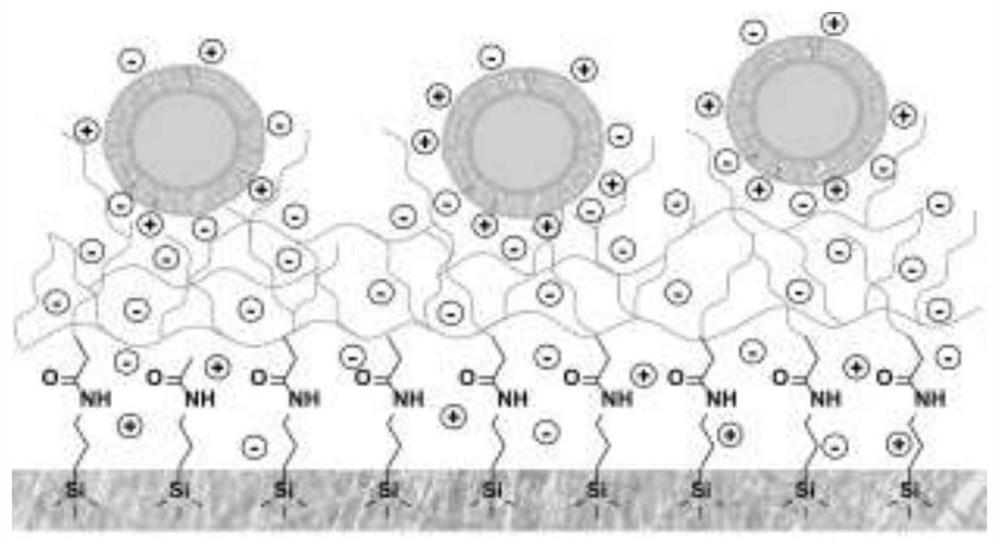
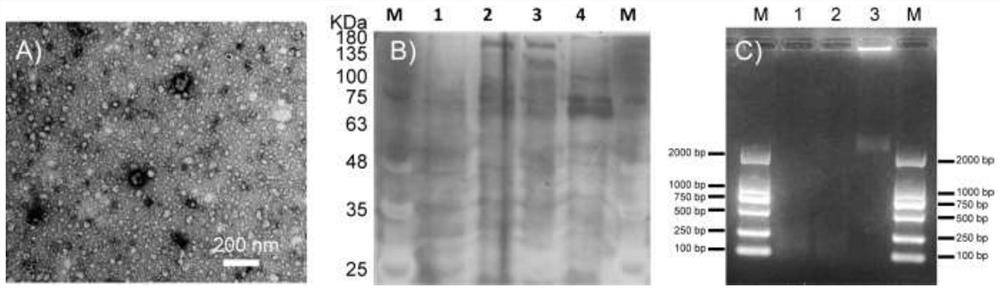
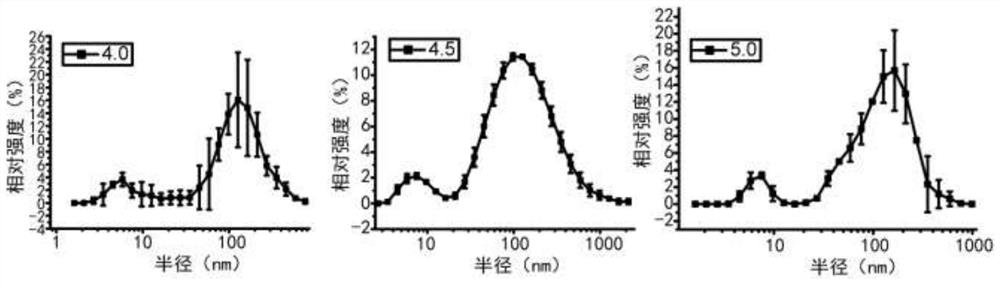
Extracellular vesicle separation and enrichment method based on anionic polymer modified matrix
A separation and enrichment, anion technology, applied in the field of extracellular vesicle separation and enrichment, can solve the problems of small capture capacity, high reagent cost, extracellular vesicle damage, etc., to achieve less free DNA pollution, high purity of the isolated product, Simple effect of separation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1. Sodium alginate modified glass fiber is used for the separation of extracellular vesicles in cell culture medium
[0044] Sodium alginate modified glass fiber spin column is made by fixing sodium alginate to the surface of glass fiber by chemical modification. The first is the activation of the glass fiber surface, using a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid (98%) and hydrogen peroxide in a volume ratio of 7:3 as the activation reagent. Put the filter paper into a glass vessel that has been repeatedly cleaned, put the filter paper into the bottom of the vessel, add concentrated sulfuric acid, then add hydrogen peroxide in proportion under shaking conditions, react at room temperature for 30 minutes, fully wash with deionized water, and then dry. The activated glass fiber was added to the APTES solution with a mass fraction of 1%, reacted at room temperature for 30 minutes, fully washed with deionized water three times, and dried at 80°C for more than 2 hour...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2. Heparin-modified glass fiber for the separation of extracellular vesicles in plasma
[0048] The production of heparin-modified glass fiber spin column uses chemical modification to fix heparin on the surface of glass fiber. The first is the activation of the glass fiber surface, using a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid (98%) and hydrogen peroxide in a volume ratio of 7:3 as the activation reagent. Put the filter paper into a glass vessel that has been repeatedly cleaned, put the filter paper into the bottom of the vessel, add concentrated sulfuric acid, then add hydrogen peroxide in proportion under shaking conditions, react at room temperature for 30 minutes, fully wash with deionized water, and then dry. Add the activated glass fiber into 1% APTES solution, react at room temperature for 30 minutes, wash thoroughly with deionized water three times, and dry at 80°C for more than 2 hours. Mix heparin (10mg / ml) and EDC (0.8mg / ml) at a volume ratio of 1:1...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3. Heparin-modified magnetic beads used for the separation of extracellular vesicles in urine
[0052] The production of heparin-modified magnetic beads uses chemical modification to immobilize heparin on the surface of the magnetic beads. The first is the activation of the surface of the magnetic beads, using a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid (98%) and hydrogen peroxide in a volume ratio of 7:3 as an activation reagent. Put the magnetic beads into a glass vessel that has been repeatedly cleaned, put the filter paper into the bottom of the vessel, add concentrated sulfuric acid, then add hydrogen peroxide in proportion under shaking conditions, react at room temperature for 30 minutes, fully wash with deionized water, and then dry . The activated magnetic beads were added to 1% APTES solution, reacted at room temperature for 30 minutes, fully washed with deionized water three times, and dried at 80°C for more than 2 hours. Mix heparin (10mg / ml) and EDC (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com