Tissue-specific meniscus extracellular matrix material as well as preparation method and application thereof
A tissue-specific, meniscus technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of limited application, poor biocompatibility, and ignoring the protection of the overall function of the joint
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
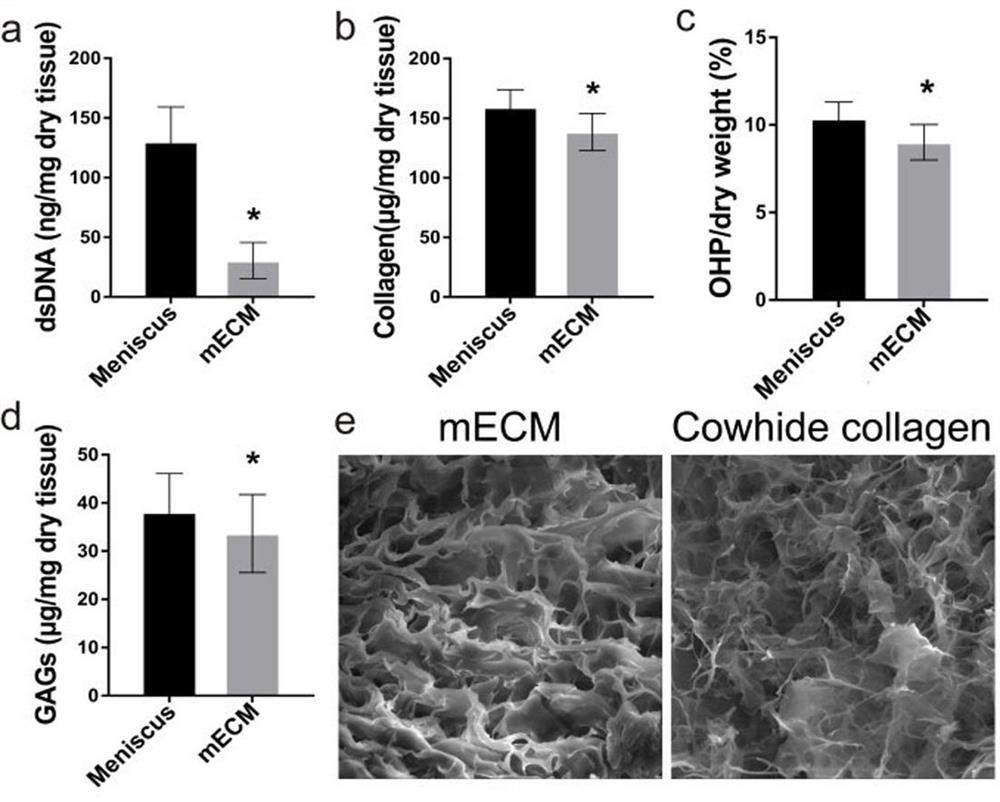
[0035] Example 1. Preparation of mECM.
[0036] 1. Prepare mECM by decellularizing the inner 1 / 3 part of the fresh porcine meniscus, the specific method is as follows:
[0037] (1) Obtain fresh menisci of pigs aged 6-7 months at the slaughterhouse (acquired within 12 hours after slaughter), wash and take the inner 1 / 3 part, and carefully divide it into 5-10 mm in size 3 small pieces of tissue;
[0038] (2) Place the small tissue pieces in an acetic acid solution with a concentration of 0.02mol / L, and soak for 48 hours at 4°C;
[0039] (3) Freeze-dry the tissue pieces at -80°C for 24 hours, then rewarm at room temperature for 4 hours to obtain freeze-dried tissues, and then repeat the above steps to prepare three freeze-dried tissues;
[0040] (4) Grind the freeze-dried tissue into powder, place it in a mixed system of 2% SDS and 10mmol / l tris, stir at 25°C for 24 hours, discard the supernatant, and perform three cycles to obtain a precipitate;
[0041] (5) Treat the precipi...
Embodiment 2
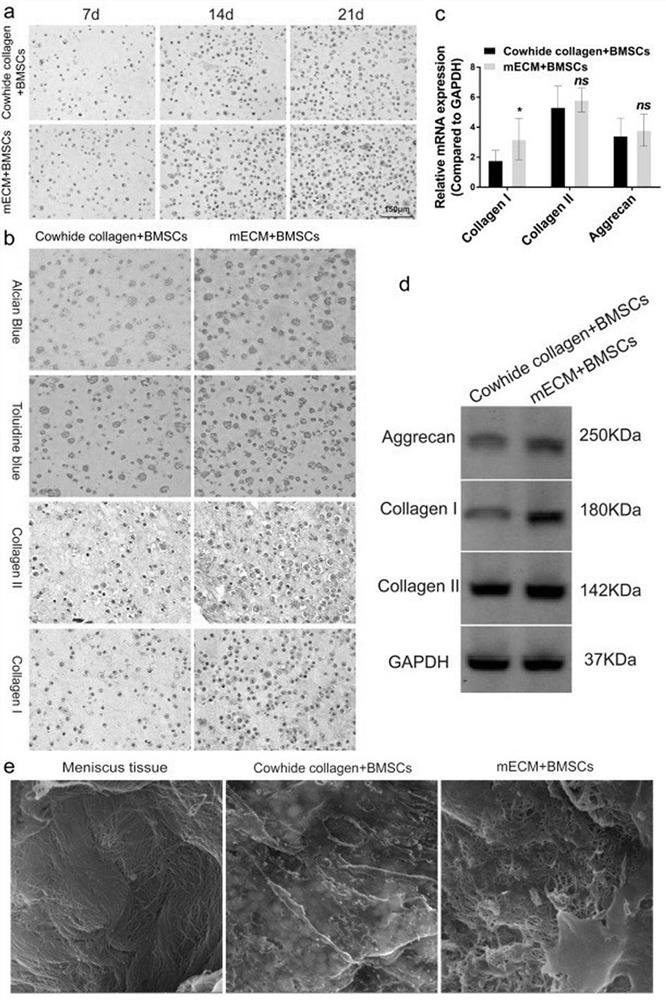
[0057] Example 2. The experiment of mECM promoting the ability of BMSCs to differentiate into fibrocartilage.
[0058] In vitro experiments, this example mixed BMSCs with mECM and conventional cowhide-derived collagen hydrogel (the most commonly used natural scaffold material, Cowhide collagen) for three-dimensional culture, and checked the proliferation of BMSCs in mECM and Cowhidecollagen. Tissue staining, qPCR and Western blotting were used to evaluate the ability of mECM to induce BMSCs to differentiate into fibrocartilage.
[0059] 1. Experimental method:
[0060] (1) Isolation and culture of BMSCs: Three-day-old SD rats were euthanized, soaked in alcohol for two minutes, and the hind limbs of suckling mice were obtained and placed in penicillin and streptomycin solution for two minutes. backbone. Insert a one-mL syringe needle (22-gauge needle) filled with medium into the femoral shaft, flush and collect BMSCs in the femur. BMSCs were cultured in complete medium. The...
Embodiment 3
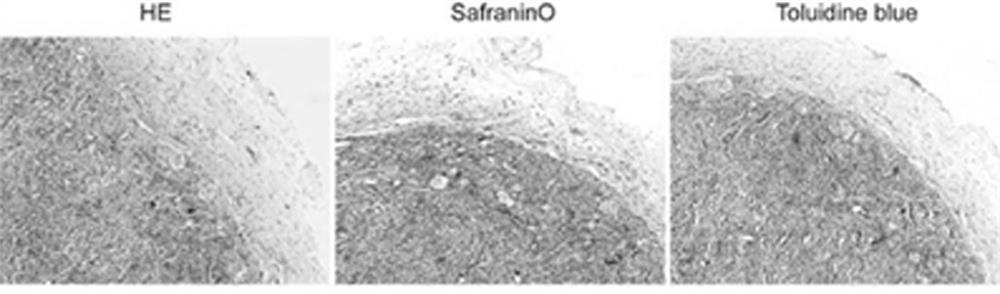
[0072] Example 3. The experiment of rat back mECM promoting the ability of BMSCs to differentiate into cartilage.
[0073] In this example, mECM was combined with BMSCs, cultured three-dimensionally in vitro for one week, transplanted to the back of the rat by microsurgery, and the tissue on the back of the rat was taken out one month later, and the tissue of the tissue was detected by HE, safranin and toluidine blue staining Morphology and chondrogenic differentiation.
[0074] 1. Experimental method:
[0075] (1) Transplantation of the three-dimensional culture complex to the back of rats: refer to the experimental method in Example 2 (2) Perform three-dimensional culture of BMSCs in mECM, and take out the three-dimensional culture complex for use after one week; the back of seven-week-old male rats Skin preparation and disinfection were carried out near the midline, and a longitudinal incision of about 1 cm in length was made along the midline of the back, and the mECM+BMS...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Conductance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com