Detachable and reusable hydrophobic or super-hydrophobic micro-fluidic organ chips
An organ chip and microfluidic technology, which is applied in biochemical instruments, tissue cell/virus culture devices, and stress-stimulated microbial growth methods, etc., can solve problems such as complex procedures, high cost of microfluidic organ chips, and impact on use.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0080] Example 1: A reusable heart chip based on a hydrophobic surface
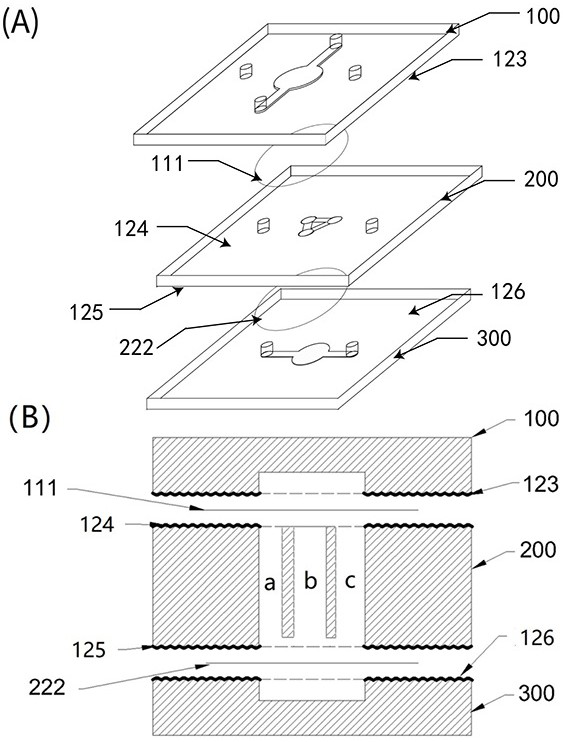
[0081] The heart is the blood-supplying organ of the human body, mainly composed of cardiomyocytes ( Cardiomyocytes ), cardiac fibroblasts ( Fibroblast ), vascular endothelial cells ( Endothelial cells ) and macrophages ( Macrophage ). The heart chip is an in vitro model of the heart, which is used to investigate the toxicity or efficacy of drugs on the heart. In toxicity or efficacy evaluation experiments, it is often necessary to measure the changes of different types of cell proteins and genes. Traditional heart chips often do this for bionic purposes. Several types of cells are mixed cultured, and after administration, it is difficult to separate these different types of cells for gene and protein detection. Therefore, the present invention proposes a heart chip that is especially suitable for proteome and genome detection.
[0082] Such as Image 6 As shown in (A) and (B), the heart chip is ...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Example 2: A reusable liver chip based on a hydrophobic surface
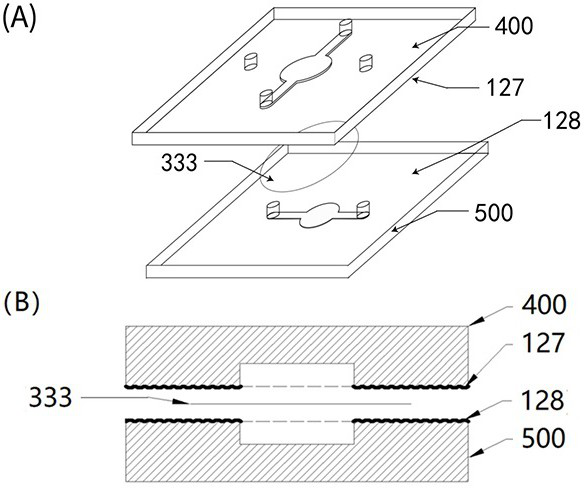
[0086] The liver is the largest metabolic organ in the body, mainly composed of hepatic parenchymal cells ( Hepatocytes ),Fibroblasts( Fibroblasts ), stellate cells ( Stellate cells ), liver vascular endothelial cells ( Endothelial cells ), bile duct epithelial cells ( Biliary epithelial cells ) and Kupffer cells ( Kuppfer Cells )Wait. The liver chip is an in vitro model of the liver, which is used to investigate the metabolism of drugs in the liver and the toxicity of drugs to the liver. In the metabolism and toxicity evaluation experiments, it is necessary to measure the changes of different types of cells at the protein and gene levels. The traditional liver These types of cells are often mixed for bionicity. After administration, it is difficult to separate these types of cells for detection of genes and proteins. Therefore, the present invention proposes a chip that is especially suitable ...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Example 3: A reusable tumor chip based on a hydrophobic surface
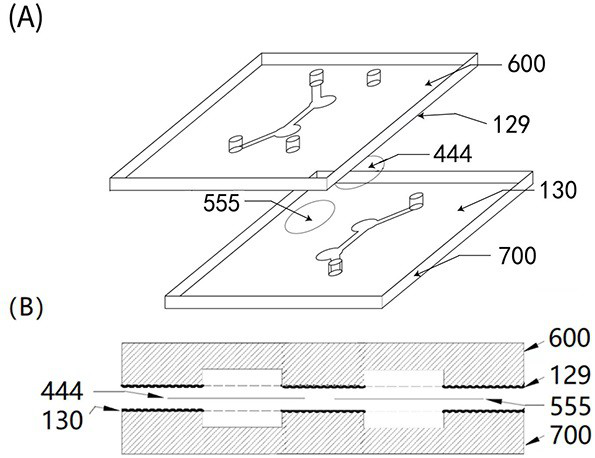
[0091] Tumor is one of the major human diseases, and tumor tissue mainly contains tumor cells ( Cancer cells ),Fibroblasts( Fibroblasts ), vascular endothelial cells ( Endothelial cells ) and immune cells ( Immune cells )Wait. The tumor chip is an in vitro model of tumors, used to investigate the anti-tumor activity of drugs. In drug efficacy evaluation experiments, it is necessary to measure the changes of different types of cells at the protein and gene levels. Traditional tumor chips often use these types of cells for bionic purposes. After administration of mixed culture, it is difficult to separate these different types of cells for gene and protein detection. Therefore, the present invention proposes a tumor chip that is especially suitable for proteome and genome detection.
[0092] The structure of the tumor chip is the same as that of the heart chip in Example 1, but the cells cultured in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com