Method, device and system for rapidly detecting bacterial drug resistance by utilizing nanopores
A nanopore, drug-resistant technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as time-consuming, expensive, and small detection range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
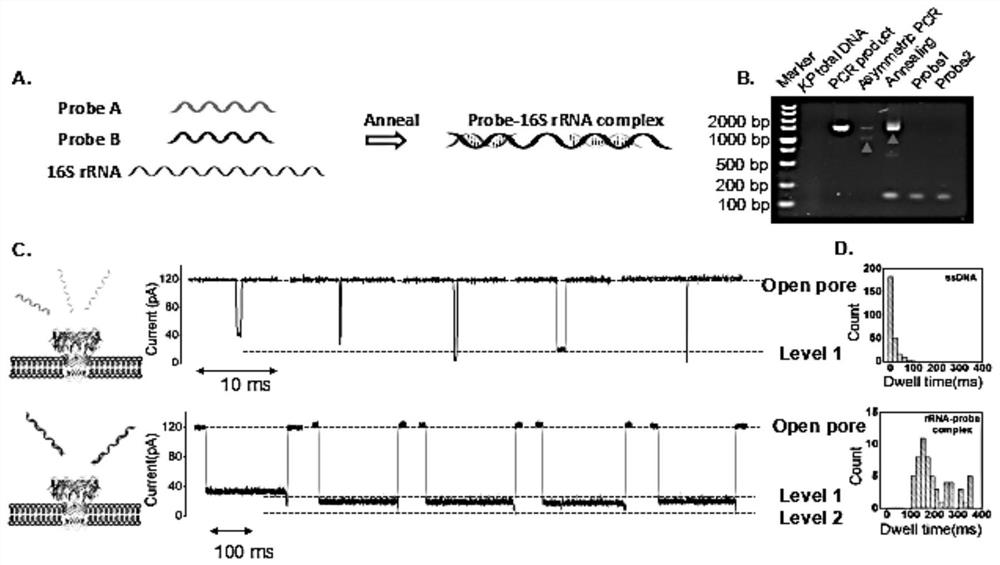
[0070] Example 1 Detection of 16S rRNA-probe complex
[0071] 1. Preparation of Bacterial Extracts
[0072] Two groups of Klebsiella pneumoniae samples from clinical patients were provided by West China Hospital of Sichuan University. Klebsiella pneumoniae samples were cultured to two different concentrations, the first group had a concentration of 0.5 MCF and the second group had a concentration of 4 MCF. At the beginning of the culture, the final concentration of imipenem used in the two groups was 16 mg / L, and the total RNA of Klebsiella pneumoniae was extracted by the TRIZOL method. First, collect 100 µL of the bacterial solution. The supernatant was removed after centrifugation (8000g, 4°C, 2 minutes). Precipitate with lysozyme and incubate at 37 °C for 10 min. Klebsiella pneumoniae were lysed, total RNA was extracted and washed with ethanol. Remove the centrifuge tube cap, dry at room temperature for 5-10min, add DEPC water or dissolve in rnas-free water. Add the R...
Embodiment 2
[0077] The optimization of embodiment two bacterial concentration and standard sample test
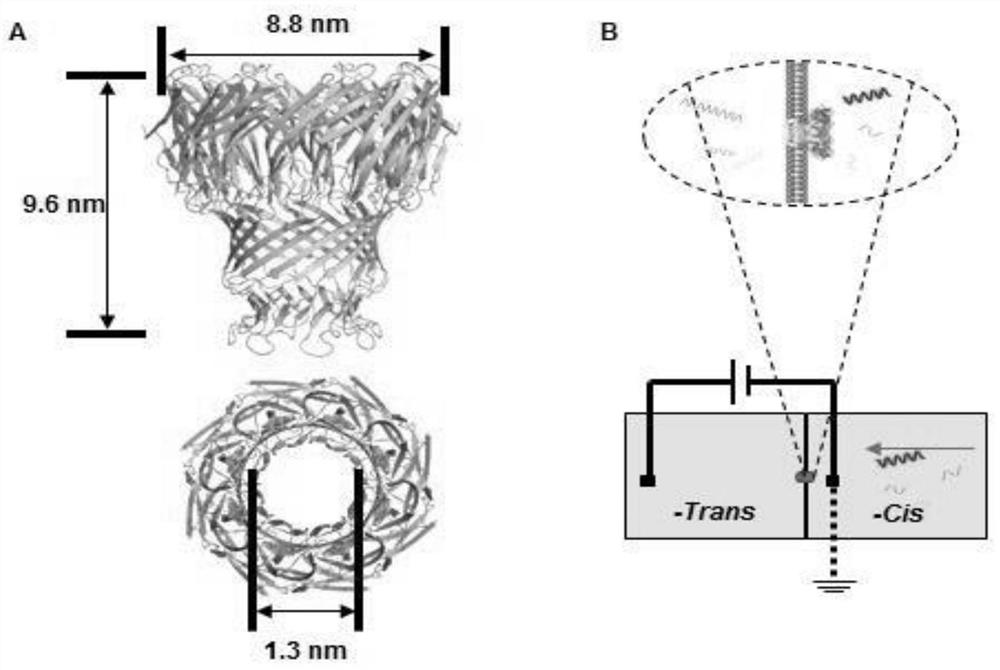
[0078] 1. Expression and purification of MspA nanopore
[0079] The gene of the MspA nanopore was cloned into the pET-28b plasmid, and the pET-28b plasmid carrying the MspA gene was transferred into the competent cells of the engineering bacteria BL21 Escherichia coli. At a temperature of 37°C, the successfully transferred Escherichia coli was cultured with LB medium, and kanamycin was added to 50 μg / ml. When the optical density (600nm) was close to 0.8, 0.8mM IPTG was added into the LB (lysogenic fermentation broth) medium, and the induction temperature was 15°C. After 12 hours of induction, E. coli were collected by centrifugation. The supernatant was collected after crushing E. coli with an ultrasonic generator, and further purified with an anion exchange column (Q-Sepharose) and molecular sieves (Superdex200 16 / 90). Purified proteins were analyzed by 10% SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Example 3 Double-blind test of MspA nanopore detection of clinical samples
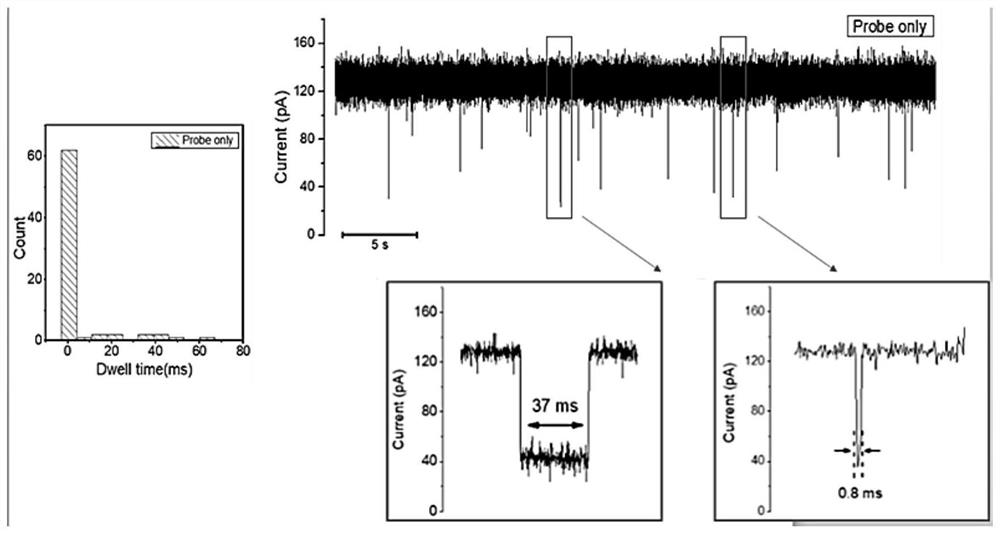
[0088] Bacteria in blood samples from 20 patients with Klebsiella pneumoniae infection provided by West China Hospital were cultured, total RNA was extracted and used for double-blind experiments. Each sample was assayed at least three times with the MspA nanopore. After analysis, the number of 16S rRNA probe signals with a blocking rate of 0.6 to 0.8 and a residence time of 100 ms to 400 ms was collected and compared with the target signal translocation frequency threshold fthreshold.
[0089] Among the 20 samples, as shown in Table 1, 9 of them are above the threshold (0.1 min -1 ) and was judged to be carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. As shown in Table 2, the other 11 samples are below the threshold of 0.1 min -1 , these clinical samples were determined to be carbapenem-sensitive Klebsiella pneumoniae samples ( Figure 5 in A). Compared with assay results obtained from standar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com