A strain of anti-phage aspartase variant production bacteria and its selection method and application
An aspartase and anti-bacteriophage technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of prolonged fermentation period, loss, and reduced fermentation enzyme production, so as to solve the problems of susceptibility to bacteriophage infection, good genetic stability, and improve economic benefits Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] The source of the strain: the aspartase variant producing strain pL181, which can produce enzymes and catalyze the ammoniation of acrylic acid to produce β-alanine.
[0030] The aspartase variant producing strain pL181 corresponds to the aspartase variant AHB032, which is described in the following patent: Wu Bian et al. Aspartase variants and their preparation methods and applications [P].ZL201710659654. 9. The aspartase variant is modified on the basis of the wild-type aspartase to improve its catalytic activity for promoting the hydrogenation of acrylic acid to generate β-alanine.
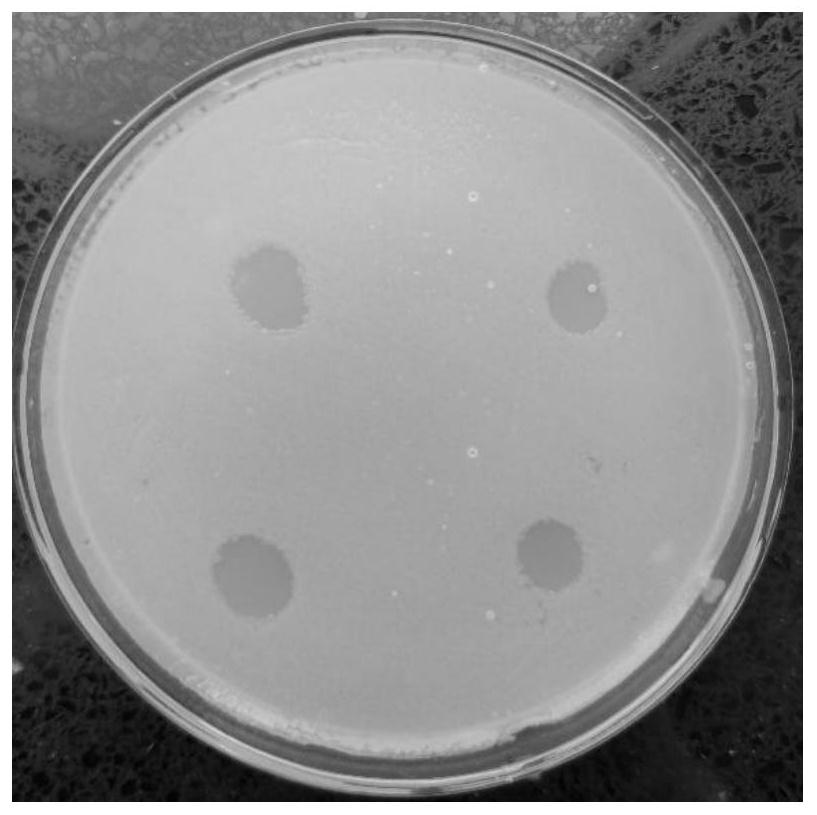
[0031] Separation and purification of bacteriophage by double-layer plate method: take 10ml of aspartase variant production bacteria pL181 fermentation broth contaminated by phage in the workshop, centrifuge at 8000rpm for 15min, take the supernatant and filter it through a 0.22μm sterile microporous membrane to sterilize. Take 100μl of the filtrate and mix it with 300μl of pL181 bacteria...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Starting strain: aspartase variant producer pL181.
[0035] Phage: Escherichia coli phage CGMCC NO.17999, isolated through Example 1.
[0036] Medium: LB medium (yeast powder 5.0g / L, peptone 10.0g / L, sodium chloride 10.0g / L, pH 7.0-7.2, solid medium plus agar 2%).
[0037] Continuous spontaneous breeding method: Pick a single colony of pL181 from a fresh plate and insert it into LB liquid medium (3ml / 10ml test tube), culture overnight at 37°C and 200rpm for 16-18h, and insert 0.1ml of titer to 10 10pfu / ml of phage lysate, and detect the initial OD value. After continuing to culture with shaking for 6-24 hours, check the OD value again, select a diluted LB plate with a smaller decrease in OD value, and place it in a 37°C incubator for overnight culture. Pick a single colony from the plate and repeat the above operation for 10 consecutive times.
Embodiment 3
[0039] Starting strain: the strain obtained by screening in Example 2.
[0040] Low-energy ion implantation mutagenesis method: Take out the fresh plate of the bacterial strain, add 15ml of sterile water, scrape and wash the bacteria and transfer them into a 250ml conical flask with glass beads, add sterile water to the conical flask to make a bacterial suspension, Adjust the bacterial concentration at 10 8 pieces / ml. Take 200 μl of the above-mentioned bacterial suspension and evenly spread it on a sterile blank LB culture dish, air-dry it in a sterile state, inject the energy at 20keV, and inject the dose at 10×10 14 , 15×10 14 , 20×10 14 ions / cm 2 , the target chamber vacuum is 10 -3 pa, injected in a 5s pulse, with an interval of 15s for nitrogen ion implantation, after the ion injection was completed, the petri dish was eluted with 1ml sterile physiological saline under aseptic conditions, and 10 4 、10 5 、10 6 The diluted samples were spread on the LB plate medium ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com