A wearable cloth-based electrochemical sweat sensing device and method
A sensing device and electrochemical technology, applied in the direction of blood characterization devices, electrochemical variables of materials, sensors, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the sensitivity of wearable sensors, the cumbersome manufacturing process of sensors, and the inability to discharge sweat in time, so as to improve sensitivity, The effect of low cost and easy replacement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
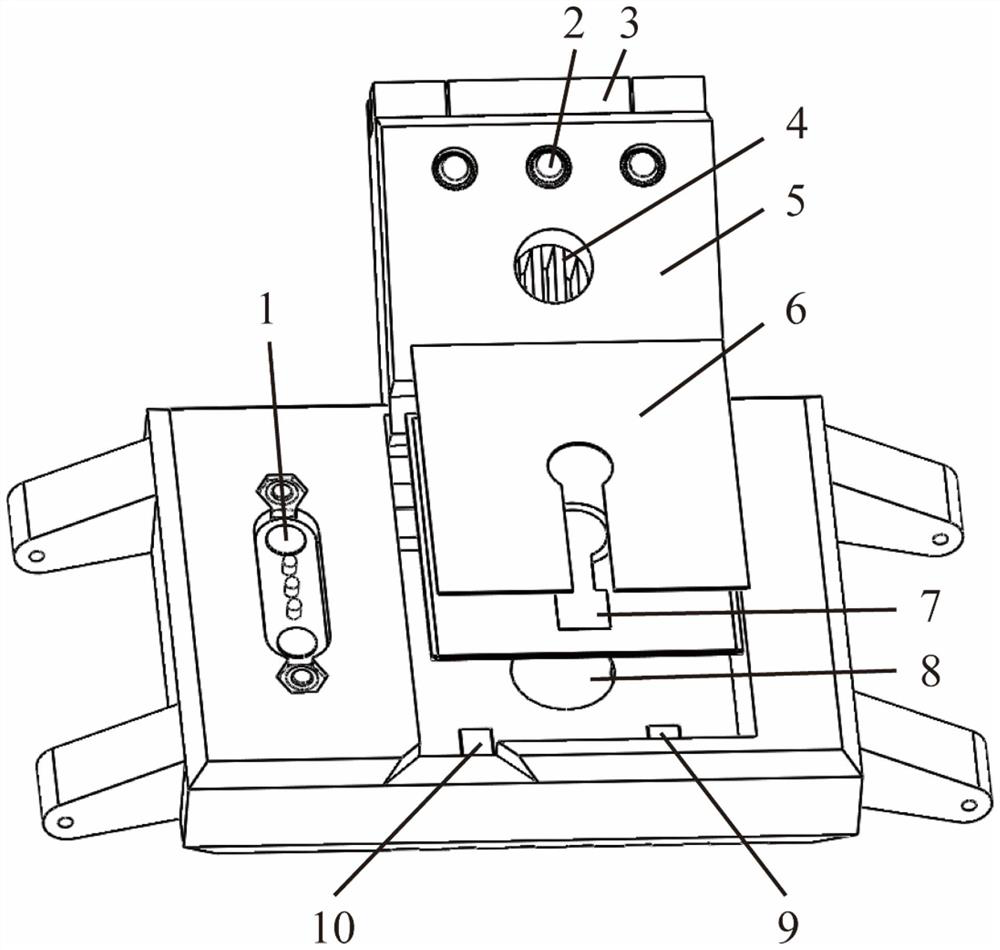
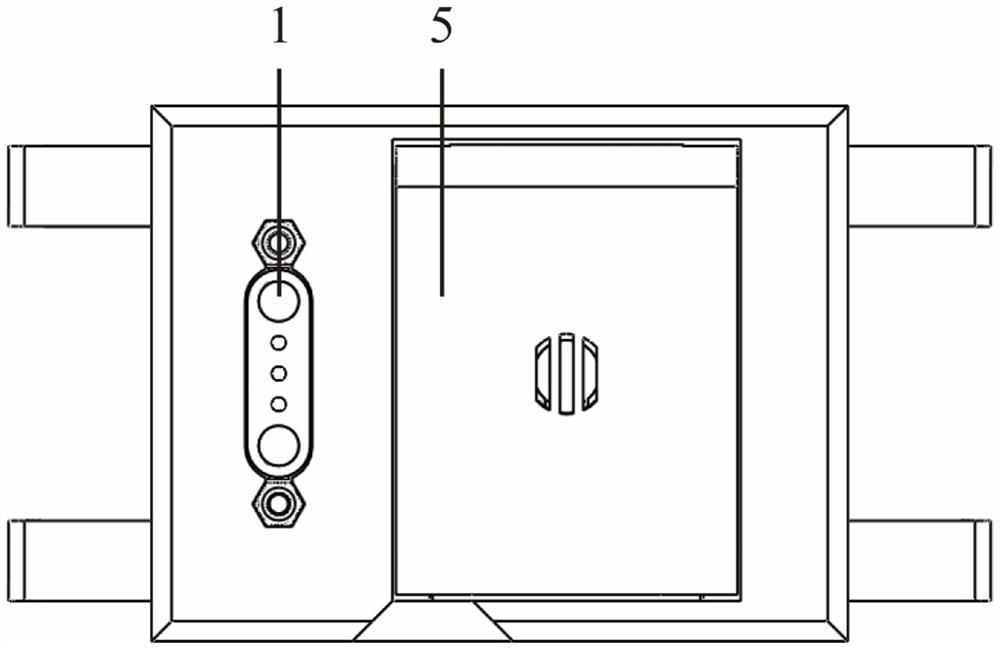
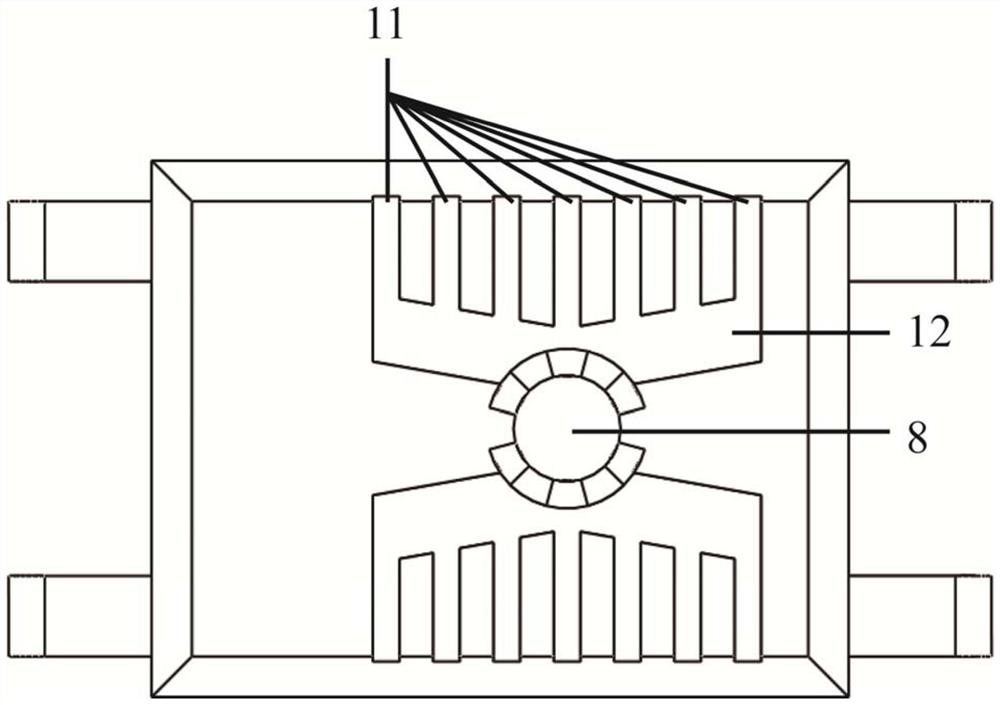
[0040] In this embodiment, a wearable cloth-based electrochemical sweat sensing device, such as Figure 1-3 As shown, it includes a sweat collection layer, a sweat detection layer, a waste liquid collection layer and a fixed pressure sheet layer 5, and the sweat collection layer includes a sweat inlet 11, a sweat collection channel 12, a sweat collection area 8, a sweat drainage channel and a first electrode Contact, the sweat detection layer includes a cloth-based detection chip 7, the cloth-based detection chip includes a cloth-based carrier, an auxiliary unit and a sweat detection unit, the waste liquid collection layer includes a paper-based waste liquid collection sheet 6, the The paper-based waste liquid collection sheet is located above the cloth-based detection chip, and the fixed pressing layer includes a second electrode contact 2 and a magnet 3 for fixing the cloth-based detection chip and the paper-based waste liquid collection sheet. The second electrode contact C...
Embodiment 2
[0051] This embodiment provides a production and detection application process of a cloth-based detection chip as follows:
[0052] Chip preparation: use the Adobe Illustrator CS5 drawing software to design the configuration of the cloth-based three-dimensional three-electrode sweat detection chip, and use the front carbon screen printing technology to make the cloth chip electrode (that is, the three-dimensional three-electrode system, including the working electrode, reference electrode and counter electrode. ), constructing the hydrophobic wax dam of the cloth-based 3D sweat detection chip using the backside wax screen printing technique.
[0053] The unfolded structure of the obtained chip is as follows Figure 4 As shown (referred to as chip A in this embodiment), it includes a single-channel sweat detection chip working electrode 13, a single-channel sweat detection chip reference electrode 14, a hydrophilic region 15, a hydrophobic wax dam 16 and a single-channel sweat ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] This embodiment provides a process for glucose detection using a cloth-based detection chip:
[0059] Electrode modification: The electrode modification process is the same as in Example 2.
[0060] Detection: Prepare glucose standard solutions with concentrations of 0mM, 0.05mM, 0.1mM, 0.2mM, 0.3mM, 0.4mM, 0.5mM, 0.6mM, 0.7mM, 0.8mM, 0.9mM, and 1mM respectively, and set aside. Open the potentiostat program on the computer, select the chronoamperometry as the experimental method, set the scanning voltage to -0.1V, and scan time 100s. The working electrode of the potentiostat is connected to the working electrode of the three-dimensional cloth-based sweat detection chip. The reference electrode clip and the auxiliary electrode clip are respectively connected to the reference electrode and counter electrode of the three-dimensional cloth-based sweat detection chip, and the 0mM glucose standard solution is dripped on the three-dimensional cloth-based sweat detection chip, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com