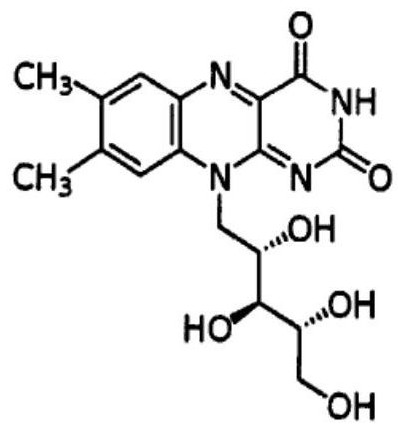
Riboflavin-producing bacillus subtilis and construction method and application thereof
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and riboflavin, which is applied in the field of Bacillus subtilis and its construction, can solve the problems of difficulty in obtaining riboflavin-yielding strains, heavy workload, and the limitation of Bacillus subtilis' ability to increase riboflavin production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1. Obtain riboflavin high-yielding bacterial strain by mutagenesis screening
[0030] With Bacillus subtilis 168 (Bacillus subtilis 168) as the original strain, the B. subtilis 168 strain was subjected to conventional mutagenesis treatment with ultraviolet 15W, 30cm, and 20min, and then mutagenized with nitrosoguanidine under the conditions of 0.4mg / mL, 36°C, 20min. Then, spread on the minimal medium containing 0.2g / L 8-azaguanine (g / L: glucose 20, ammonium sulfate 2, magnesium sulfate 0.4, calcium chloride 0.02, ferrous sulfate 0.02, disodium hydrogen phosphate 1.5, zinc sulfate 0.01, manganese sulfate 0.01, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1.5, agar 18, pH7.0-7.2), culture at 36°C for 24 hours. Afterwards, the strain with the best growth was selected for the next round of mutagenesis, and the concentration of 8-azaguanine in the basic medium was increased. After multiple rounds of mutagenesis screening, the B. subtilis MHZ-1908-1 strain was obtained, which ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Construction of B. subtilis168, Δupp strain by gene seamless editing method
[0033] With Bacillus subtilis B.subtilis168 as the starting strain, the gene scarless editing method used in the present invention is based on the two-step integration mediated by the temperature-sensitive plasmid, through chloramphenicol positive screening and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) reverse screening (Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 98(21):8963-8973. Zhang W, Gao W, Feng J, et al). This screening method needs to delete the upp gene on the genome of the target strain firstly, which encodes uracil phosphoribosyltransferase. When upp and 5-FU exist at the same time, it has a lethal effect on the cells.
[0034] The specific construction process is as follows: using primers upp-1f / 1r, upp-2f / 2r, using the B. subtilis 168 genome as a template, using pfu DNA polymerase to amplify the upstream and downstream homology arms of 888bp and 938bp respectively, and using primers upp...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3: Engineering strain B. subtilis 168, Δupp, purR A148D build
[0036] Using primers purR-1f, purR-1r and purR-2f, purR-2r, and using the B. subtilis 168 genome as a template, use pfu high-fidelity DNA polymerase to amplify to obtain purR A148D Upstream and downstream homology arms; primers purR-1f and purR-2r are used to fuse and amplify the upstream and downstream fragments to obtain purR A148D Fusion fragments (including A148D mutation, complete purR wild-type and mutant nucleotide sequences are shown in SEQ ID No. 1, 2; specific encoded wild-type and mutant protein sequences are shown in SEQ ID No. 7, 8. The fusion fragment and the pKSU plasmid (tool vector) were subjected to SalI and PstI double enzyme digestion respectively, then ligated, and transformed into Trans1 T1 Escherichia coli competent cells. Finally, the recombinant plasmid pKSU-purR was obtained A148D .
[0037] Subsequent transformation and screening methods were the same as in Example 2, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com