Cellulase-producing marine bacteria HN B15, microbial preparation thereof and degradation method of natural cellulose
A technology of natural cellulose and marine microorganisms, applied in microorganism-based methods, methods of using microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as low tolerance of enzyme-producing strains, complex ecological structure and instability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] 1. Collect samples
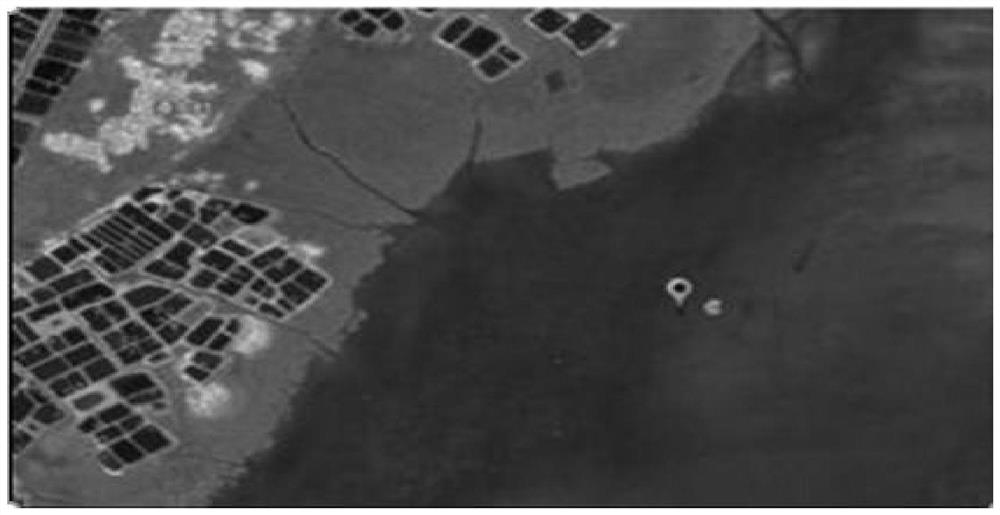
[0042] On December 23, 2018, the seagrass bed ecosystem in the mangrove area of Huiwen Town, Wenchang City (19°28′11.66″N, 110°47′41.22″E)( figure 1 ) to collect sediment mud samples below 3cm near the seagrass bed. The collected mud samples were placed in sterile zipper plastic bags and stored in an ice box at 4°C.
[0043] 2. Separation and purification of microorganisms
[0044] Within 24 hours of collecting the sample, weigh 0.5 g of the mud sample with a sterile spoon and suspend it in a sterile saline solution (0.85% NaCl), stir evenly, and use this as the stock solution to serially dilute the water sample with a sterile saline solution. To obtain dilutions of 1:10, 1:100 and 1:1000, 100 μL of each diluted sample was uniformly spread on 2216E seawater agar medium (0.5% trypsin, 0.1% yeast, 0.01‰ iron phosphate and 1.7% agar ) and cultured in a 30°C incubator for 18 hours. Investigate colony morphology on agar plates, including shape, siz...
Embodiment 2
[0054] 1. Determination of filter paper enzyme activity
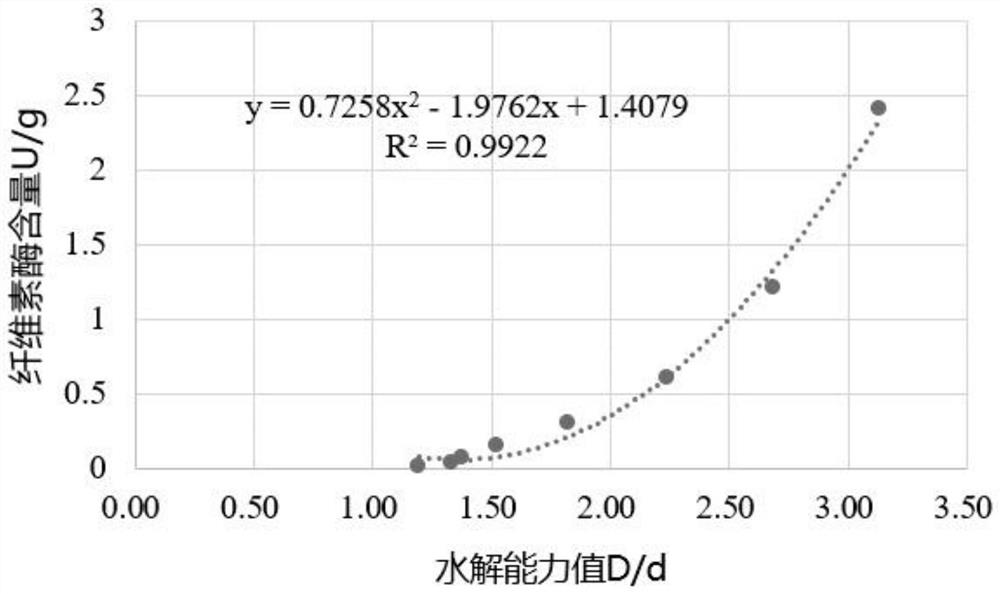
[0055] Take the culture of 2216E liquid grown overnight, centrifuge at 4°C, 5000rpm, 15min; take 0.5mL of the supernatant enzyme solution, add it to 1mL of acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution with a pH of 4.8 and 0.1mol / L, and then add 50± One piece of 0.5mg filter paper (1cm×6cm), insulated at 50°C for 1 hour, (preheated for 5 minutes); add 3mL of DNS chromogenic solution, put it into boiling water for 10 minutes, and cool it under running water at 540nm Measure the absorbance; at the same time, use the inactivated enzyme solution boiled at 100°C for 10 minutes as a control to subtract the background; find out the corresponding glucose content from the glucose standard curve according to the absorbance, and calculate the enzyme activity value according to the grams of glucose produced. Filter paper enzyme activity was calculated according to the following formula:
[0056] X=(W×N×1000) / (T×M)
[0057] X: Enzyme...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com