Method for producing titanium dioxide through low-temperature chlorination of titanium-rich material
A technology of titanium dioxide and titanium-rich materials, applied in the fields of metallurgy and chemical industry, can solve problems such as difficult to effectively control furnace temperature, increase production costs, and increase heat release, so as to avoid loss of flow, improve utilization efficiency, and reduce chlorination reaction temperature Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
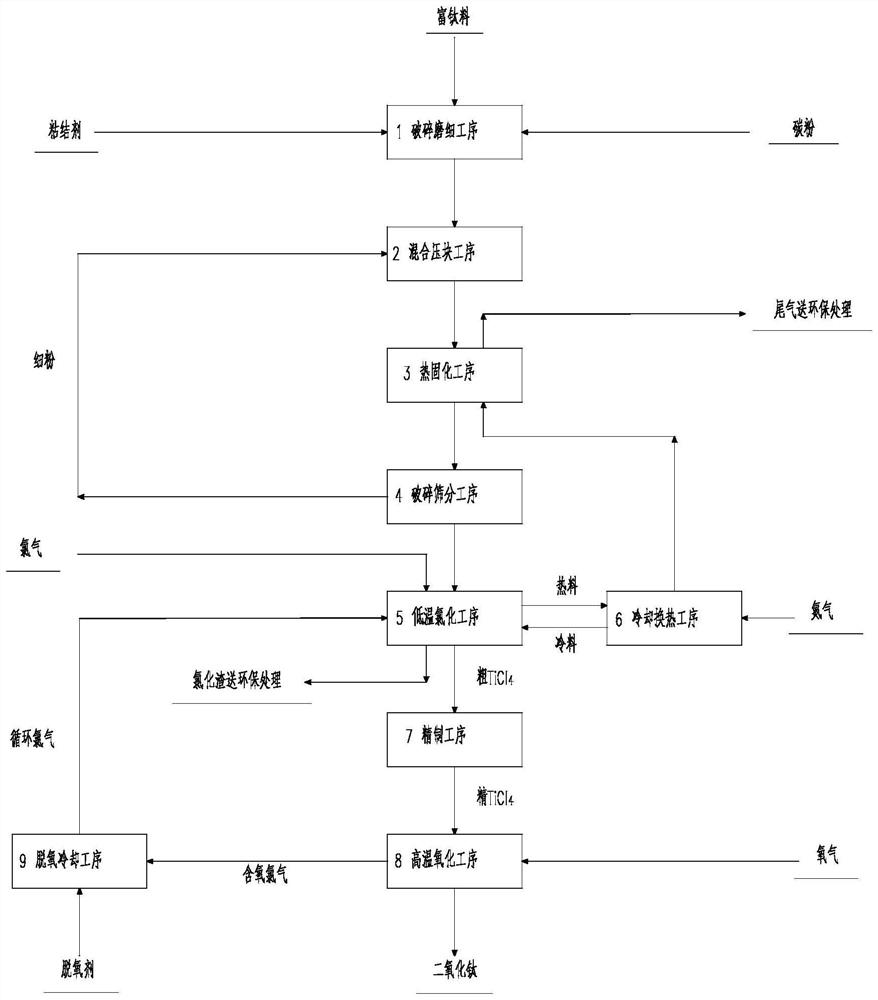
[0043] combine figure 1 A method for producing titanium dioxide by low-temperature chlorination of titanium-rich materials used in this embodiment includes crushing and grinding process 1, mixing and briquetting process 2, thermal curing process 3, crushing and screening process 4, low-temperature chlorination process 5, Cooling and heat exchange process 6, refining process 7, high temperature oxidation process 8 and deoxidation cooling process 9, the method is carried out according to the following steps:
[0044] 1) In the crushing and grinding process 1, the titanium-rich material is mixed with carbon powder and a binder to be crushed and ground to obtain fine ore powder;
[0045] 2) In the mixing and briquetting process 2, the fine ore powder is uniformly mixed with the fine powder from the crushing and screening process 4, and then pressed into a pressed block;
[0046] 3) In the thermal curing process 3, the pressed block material is exchanged with the hot nitrogen gas ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] This embodiment adopts a method for producing titanium dioxide by low-temperature chlorination of a titanium-rich material described in Example 1. The titanium-rich material is direct reduction of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate and melted titanium slag, containing 40% TiO 2 , 5% CaO, 13% MgO. In the crushing and grinding step 1, carbon powder refers to activated carbon, and the binder refers to phenolic resin. In the crushing and grinding step 1, the added mass of carbon powder is 10% of the mass of titanium-rich material, and the added mass of binder is 1% of the mass of titanium-rich material. In the crushing and grinding step 1, the average particle size of the ground mixed fine mineral powder is controlled to be 0.1 μm. In the mixed briquetting process 2, the fine mineral powder is formed by pressing, wherein the pressure is 0.3 MPa. In the thermal curing step 3, the temperature of the hot nitrogen gas is 400°C, and the curing temperature is 100°C. In th...
Embodiment 3
[0056] This embodiment adopts the method for producing titanium dioxide by low-temperature chlorination of a titanium-rich material described in Example 1. The titanium-rich material is artificial rutile containing 98% TiO 2. In the crushing and grinding step 1, carbon powder refers to metallurgical coke, and the binder refers to sucrose. In the crushing and grinding process 1, the mass of carbon powder added is 50% of the mass of titanium-rich material, and the mass of binder added is 10% of the mass of titanium-rich material. In the crushing and grinding step 1, the average particle size of the ground mixed fine mineral powder is controlled to be 50 μm. In the mixed briquetting process 2, the fine mineral powder is formed by pressing, wherein the pressure is 20 MPa. In the thermal curing step 3, the temperature of the hot nitrogen gas is 680°C, and the curing temperature is 650°C. In the crushing and screening step 4, the average sieving particle size of the chlorinated r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com