Gene editing microneedle for treating inflammatory skin diseases and application thereof
An inflammatory skin disease, gene editing technology, applied in skin diseases, microneedling, gene therapy, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in reaching the epidermis and dermis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1: Preparation of gene-edited microneedle patch
[0024] This embodiment includes the following raw materials by mass percentage:
[0025] Needle tip matrix: collagen tripeptide 10%, sodium hyaluronate (molecular weight 34kDa) 10%, the rest is water.
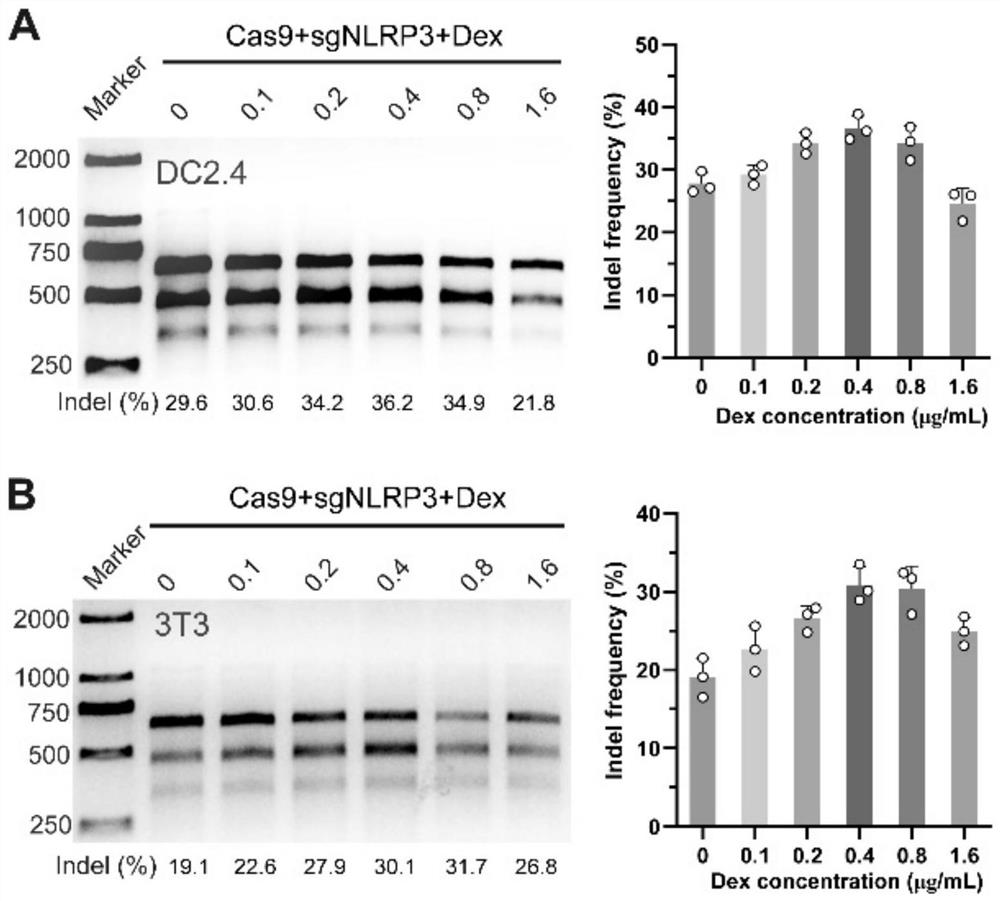
[0026] In addition, every 10 mL of sodium hyaluronate + collagen tripeptide solution in the microneedle tip matrix contains 60 μg of dexamethasone, 20 μg of Cas9 protein, and 5 μg of sgRNA.
[0027] Base matrix: collagen tripeptide 10%, sodium hyaluronate (molecular weight 34kDa) 10%, the rest is water.
[0028] The preparation method of this embodiment:
[0029] 1. According to the prescription ratio, take 1g sodium hyaluronate (molecular weight 34kDa) and 1g collagen tripeptide and disperse in 10mL water, stir until fully dissolved, add the dexamethasone nanocomposite wrapped in degradable polymer carrier in the prescription ratio PLGA / Dex and degradable cationic carrier wrap the gene editing ribonucleoprotei...
Embodiment 2
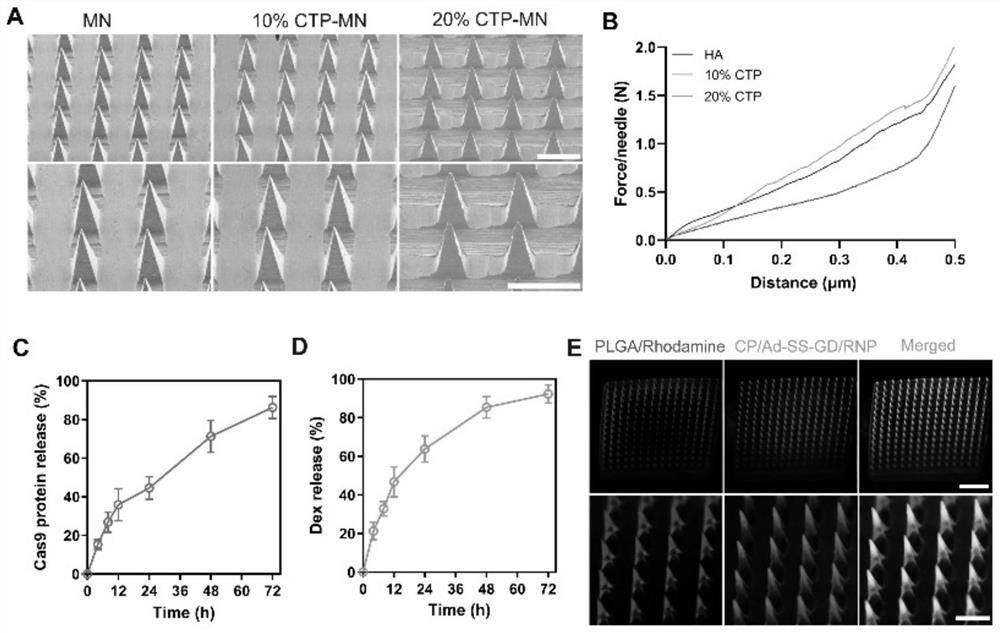
[0031] Example 2: Characterization of gene-edited microneedle patches
[0032] The specific operation method is as follows: use a scanning electron microscope to observe the morphology of microneedles with different percentages of collagen tripeptides. Place the microneedles containing different percentages of collagen tripeptides on the texture analyzer with the needle point facing up, and the probe of the texture analyzer moves down at a speed of 1mm / s, and the mechanical strength is reflected by measuring the curve of displacement and force.
[0033] In order to investigate the dissolution of the microneedle in the skin, the double-loaded microneedle patch was applied to the back skin of the mouse for 0, 1, 3 and 5 minutes, then removed, and then the remaining microneedle patch was taken out and photographed with a scanning electron microscope.
[0034] In order to evaluate the drug release behavior of the microneedles in vitro, the double-loaded microneedle patch was first...
Embodiment 3
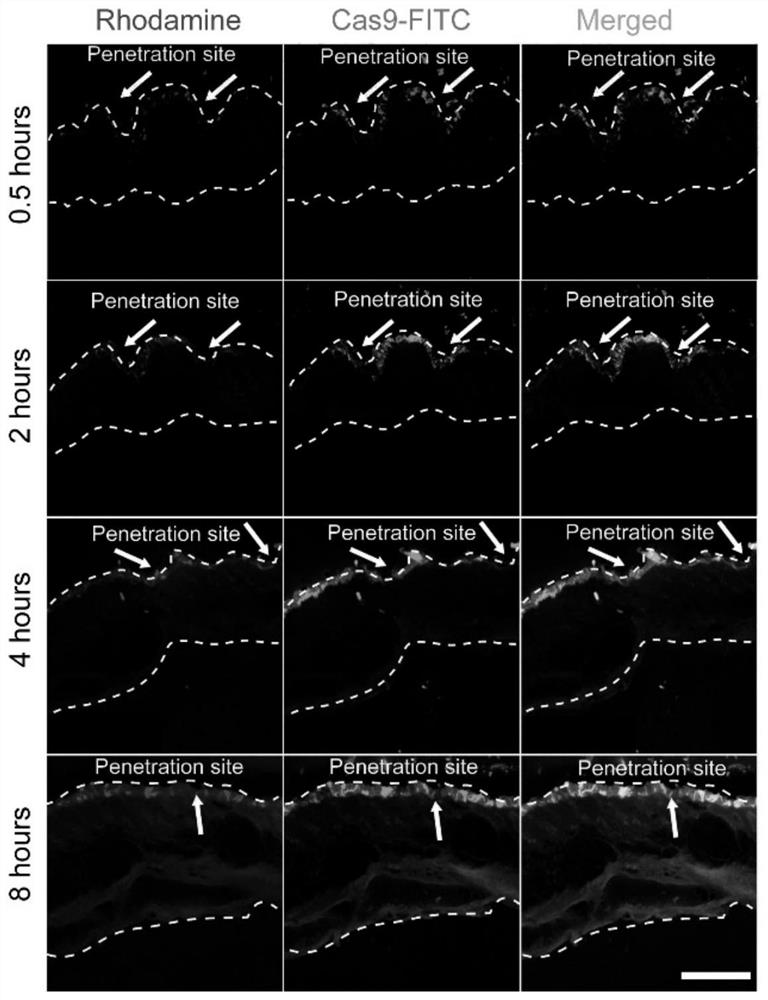
[0036] Example 3: Drug distribution after the gene-edited microneedle patch pierces the skin
[0037] In order to study the degradation behavior of microneedles in vivo, a double-loaded microneedle patch loaded with PLGA / rhodamine B and CP / Ad-SS-GD / Cas9protein-FITC was prepared, and then the double-loaded microneedle patch was applied to the back of the mouse The back skin tissue was separated from the skin at different times for frozen embedding, and then the tissue was placed in a frozen section for sectioning, and the fluorescence distribution was observed under a laser confocal microscope
[0038] Experimental results: if figure 2 As shown, the microneedle patch can be successfully penetrated into the mouse skin with a depth of about 300 μm. After piercing into the mouse skin, the tip of the microneedle can quickly absorb the liquid in the skin tissue and dissolve rapidly. At the same time, rhodamine and Cas9-FITC Released in large quantities, distributed in the epidermi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com