Preparation method of Se-coated BSA nano-drug and application of Se-coated BSA nano-drug in acute kidney injury
A technology for acute kidney injury and nano-drugs, which can be used in drug combinations, non-active components of polymer compounds, active components of sulfur/selenium/tellurium, etc. Toxicity, slow progression, prevent assembly
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Preparation and analysis of physicochemical properties of Se@BSA nanomedicine
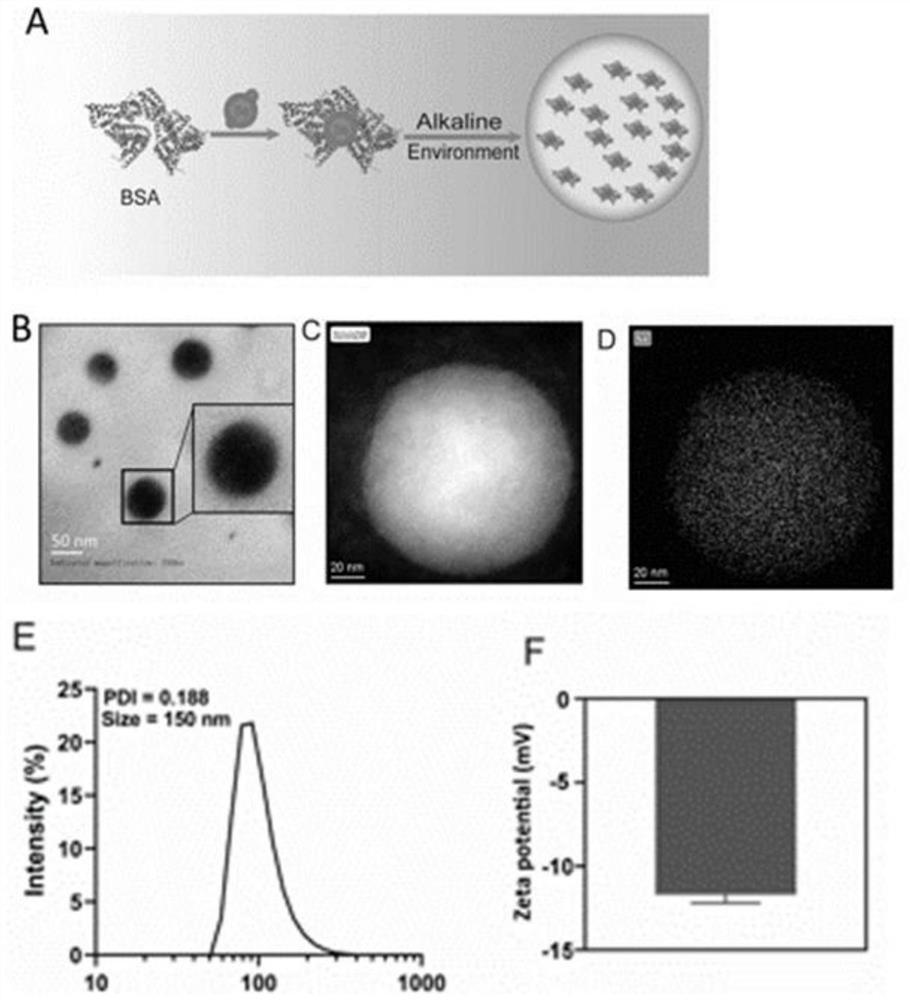
[0027] Dissolve 40mg BSA in 10mL water and stir for 1h, add 10mL 0.05M ascorbic acid solution to react for 0.5h, then add 4mL 0.05M Na 2 SeO 3 The solution was reacted for 1 hour, reacted for 3 hours, adjusted to pH 8, reacted for 10 hours, dialyzed with 14000 dialysis bag for 2 days, and freeze-dried to obtain Se@BSA nanomedicine. The prepared Se@BSA nanomedicine was detected by transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
[0028] The result is as figure 1 As shown in A-F, the Se@BSA nanomedicine is spherical and uniform in size. The particle size of the Se@BAS nanomedicine is about 150nm, and the surface charge is about -12mv.
Embodiment 2
[0030] The role of Se@BSA nanomedicine in ischemia / reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury
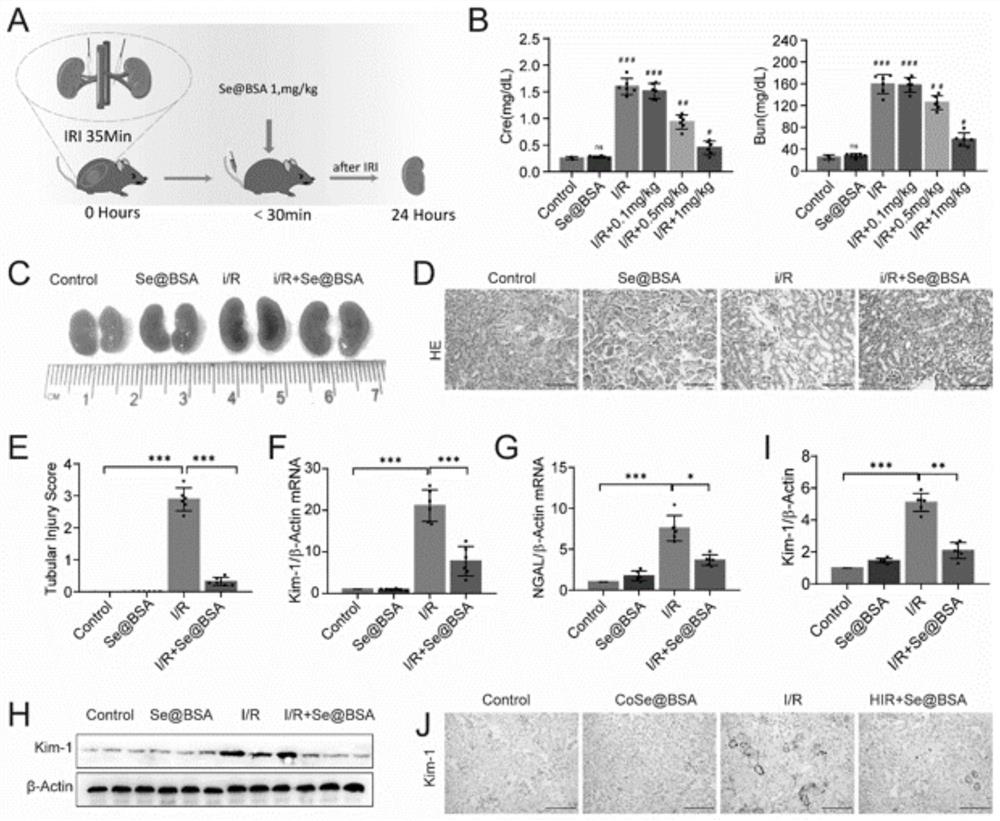
[0031] A total of 40 C57BL / 6 mice with a body weight of 20-22 g (Beijing HFK Biotechnology Company) were selected, and the mice were randomly (n=10) divided into four groups: sham operation, sham operation+Se@BAS, I / R and I / R+Se@BAS.
[0032] Such as figure 2 As shown in the schematic diagram of the ischemia / reperfusion operation in middle A, the bilateral kidneys of mice in the I / R group were clipped for 35 minutes; in the I / R+Se@BAS group, different doses (0, 0.1 , 0.5, 1mg / kg) of Se@BAS nanospheres; in the sham operation group, the same dose of PBS was injected; in the sham operation+Se@BAS (1mg / kg) group, the same dose of PBS and Se@BSA nanospheres were injected . Serum samples were collected and stored at -80°C, using creatinine (CRE) detection kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bio, C011-2-1) and urea nitrogen (BUN) kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Biology, C013-2-1) Detect CRE and BUN. The resul...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Safety evaluation of Se@BSA nanomedicine
[0050] (1) Distribution of Se@BSA nanomedicine in mice
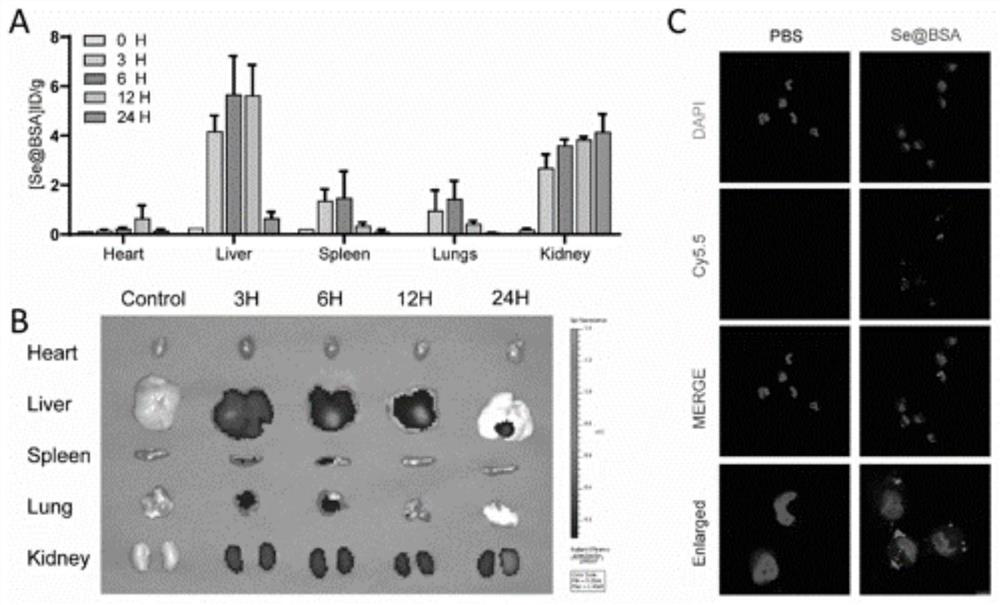
[0051] The mice were injected with Se@BSA (1mg / kg), and the mice were detected by in vivo imaging at 3, 6, 12h, and 24h. After 24h, the heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney tissues were taken, and selenium was determined by ICP-MS content. The result is as image 3 As shown in A and B, ICP-MS results show that the content of Se@BSA nanospheres in various organs increases with time, mainly enriched in liver and kidney; mouse imaging results show that Se@BSA nanospheres in The biodistribution in mice was time-dependent. Se@BSA was mainly concentrated in the liver and kidney, peaked at 6 hours after injection, and mainly concentrated in the kidney at 24 hours. The selenium content in the organs decreased significantly, but the Se concentration in the kidney increased at 24 hours, which was similar to the ICP-MS results, indicating that Se@BSA had partial kidney targetin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface charge | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com