Method for analyzing chlorophyll and degradation product components thereof in tea leaves
A technology of degradation products and analysis methods, which is applied in analysis materials, material separation, measurement devices, etc., can solve the problems of complex pretreatment, low sensitivity, long time consumption, etc., and achieve simple and rapid pretreatment, high detection coverage, and analysis system. full effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] 1) Extraction of chlorophyll and its degradation products in the tea to be tested
[0041] ① After the tea sample to be tested is ground, pass through a 30-mesh sieve and set aside;
[0042]②Weigh about 20.0mg±0.1mg of tea powder into a centrifuge tube, add 300μL methanol solution containing internal standard compound, and vortex for 30s. The internal standard compound is lysophosphatidylcholine LPC19:0, the concentration is 2.00 μg / mL; phosphatidylcholine PC38:0, the concentration is 1.33 μg / mL;
[0043] ③ Add 1mL MTBE, vortex for 30min;
[0044] ④Add 300μL ultrapure water and vortex for 30s;
[0045] ⑤ After standing for 10 minutes, centrifuge at high speed (10000rpm*10min) to make layers;
[0046] ⑥ Take 600 μL of the upper layer and 250 μL of the lower layer, transfer to a new centrifuge tube, concentrate and dry by low-temperature centrifugation, and set aside.
[0047] 2) LC-MS analysis of chlorophyll and its degradation products in the tea to be tested
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: Chlorophyll degradation pathway analysis in green tea
[0058] (1) Get a green tea sample and analyze it according to the method in Example 1. Three copies of each tea sample were taken for testing as technical replicates.
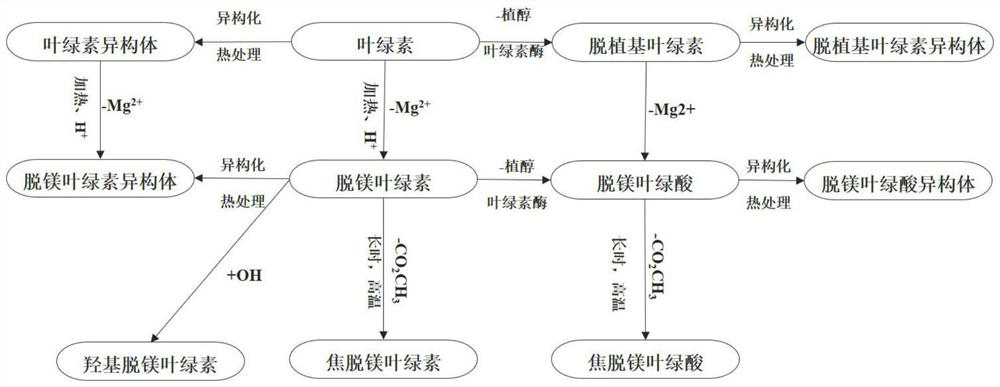
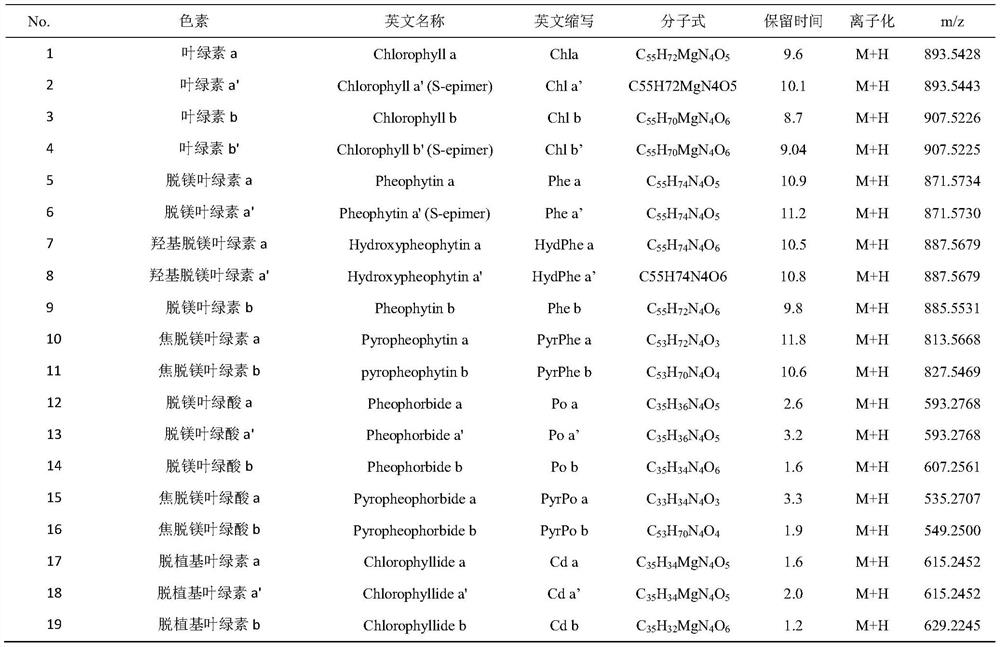
[0059] (2) Analysis of chlorophyll degradation pathways in green tea: the results showed that all 19 chlorophylls and their degradation products involved in the present invention could be detected in green tea samples, covering enzymatic and non-enzymatic degradation products of different properties. Path analysis shows that ( figure 1 ), green tea processing involves the following reactions: ① Isomerization: Chlorophyll a and b are converted into their respective isomers a' and b'. ②Enzyme-catalyzed explantation reaction: under the action of chlorophyllase, a hydrolysis reaction occurs to generate water-soluble explantation chlorophyll. ③ Demagnesium degradation reaction: Under acidic or heating conditions, the Mg on the porphyrin rin...
Embodiment 3
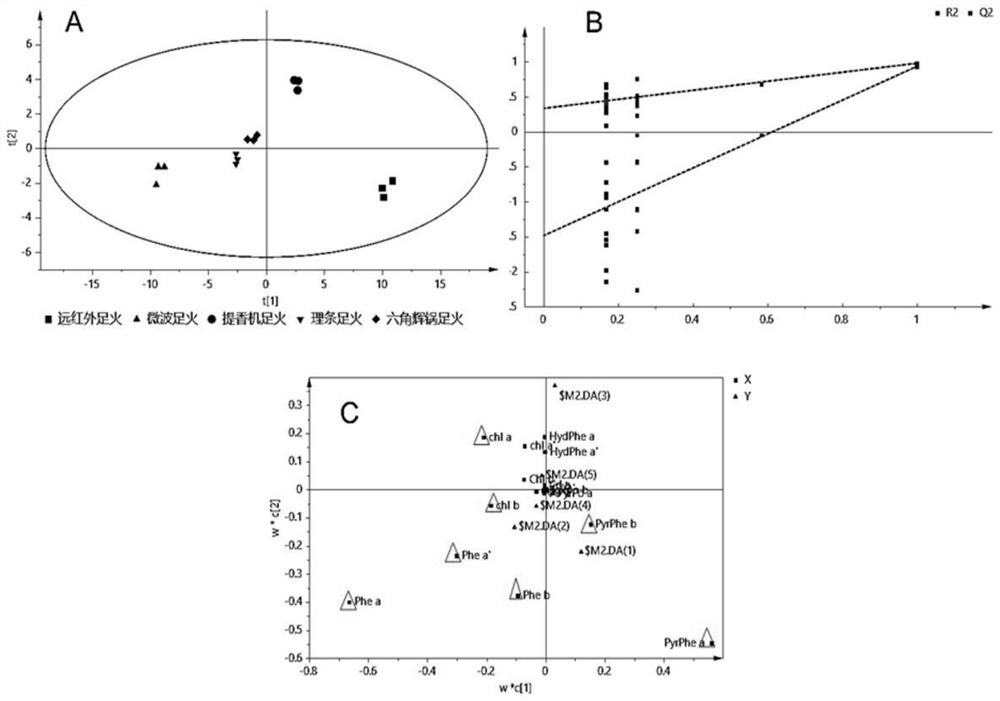
[0060] Example 3: Comparative analysis of chlorophyll and its degradation products in green tea under different foot fire methods
[0061] (1) Making green tea: spread naturally (indoor temperature 25-28°C, relative humidity 70%-80%, wait until the moisture content drops to about 70%) → drum-type finishing (leaf throwing amount 150kg / h, 260°C, 75s )→cooling (1h)→kneading (30kg leaves, rotating speed 50-52r / min, lightly kneading for 30min)→hair drying (110°C, 20min, until the moisture content drops to about 20%). Then use five different foot fire methods (far-infrared foot fire, microwave foot fire, aroma machine foot fire, strip machine foot fire and hexagonal hui pot foot fire) to carry out foot fire drying to obtain green tea.
[0062] (2) The green tea made by different foot fire methods is analyzed according to the method in Example 1. Three copies of each tea sample were taken for testing as technical replicates.
[0063] (3) Orthogonal partial least squares discriminan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com