Dissolution regeneration and stable dispersion system of monomolecular cellulose
A technology of dissolution regeneration and dispersion system, which is applied in the preparation of sulfonate and organic chemistry, etc. It can solve the problems of cellulose molecular macromolecular chain damage, high dissolution temperature, and long temperature for dissolving cellulose.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
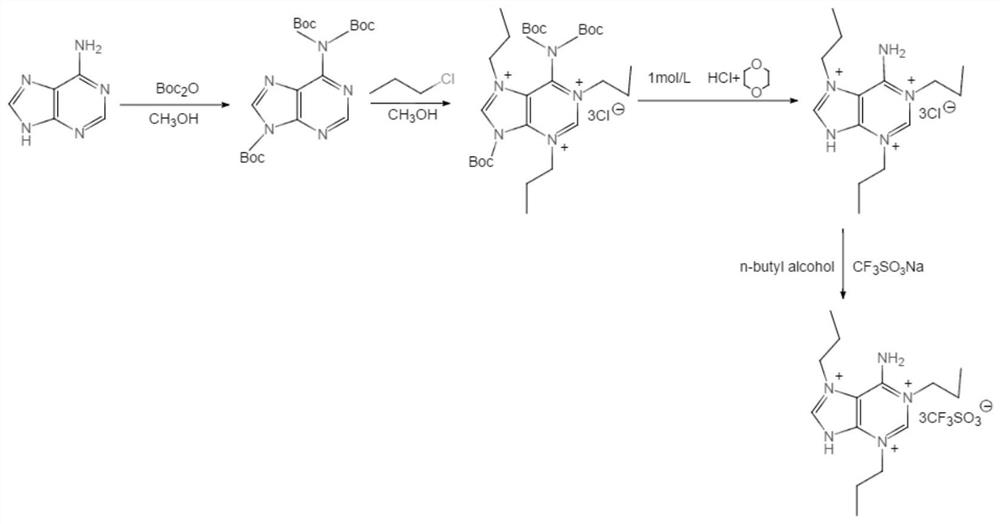
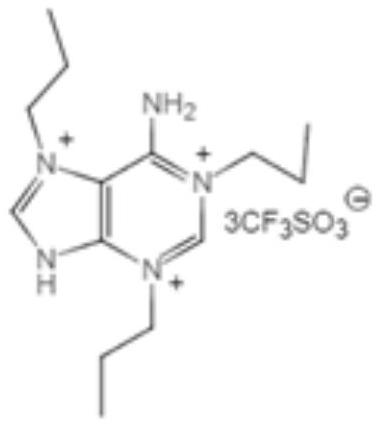
[0025] Synthesis of novel adenine ionic liquids:
[0026] Add 0.8mol of adenine to a 500mL single-necked round bottom flask, and then add 200mL of methanol and 2.4mol of tert-butoxycarbonic anhydride Boc 2 O was heated to reflux in a constant temperature oil bath at 45°C and stirred for 1 h. Then 2.45mol of 1-chloropropane was added, heated to reflux and stirred in a constant temperature oil bath at 40°C for 25h. After the reaction was completed, the solvent methanol was removed by heating and rotary evaporation. Add 2mL of 1mol / L HCl / dioxane, heat and stir in a constant temperature oil bath at 60°C for 1h to remove Boc, and remove HCl / dioxane and isobutene and CO produced by Boc by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure. 2 . Add 1.5g NaHCO 3 The remaining HCl was removed. The white solid in the lower layer was washed three times with ethyl propionate, then rotary evaporated under reduced pressure at 40°C, and then placed in a vacuum oven for 9 hours at 60°C to obtain ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Ionic liquid recovery:
[0038] When preparing regenerated monomolecular cellulose, the mixed solution of ionic liquid and water was obtained. Firstly, it was subjected to vacuum rotary evaporation at 90°C, and then the aqueous solution of ionic liquid was frozen into a solid state in a refrigerator, and then put into a freeze dryer. Freeze-dry at ℃ for 24 hours, and remove the final remaining small amount of distilled water. Wait for the temperature to slowly rise to room temperature in a desiccator to obtain a pure ionic liquid.
[0039] Application of monomolecular cellulose as water retaining agent:
[0040] Prepare 775.0g of gypsum powder, add 0.80g of monomolecular cellulose, and then add 240.3g of water and stir evenly to make mortar. After adding gypsum mortar to the Buchner funnel with a mass of 847.0g, the total mass is 1208.5g, and the total mass of the funnel after suction filtration is 1200.0g. The calculated water retention rate of monomolecular cellulo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com