8, 9-dihydrocannabidiol as well as synthesis method and application thereof
A technology for cannabidiol and synthesis method, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, active ingredients of hydroxyl compounds, organic compounds/hydrides/coordination complex catalysts, etc., and can solve the problem of large amount of catalysts and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
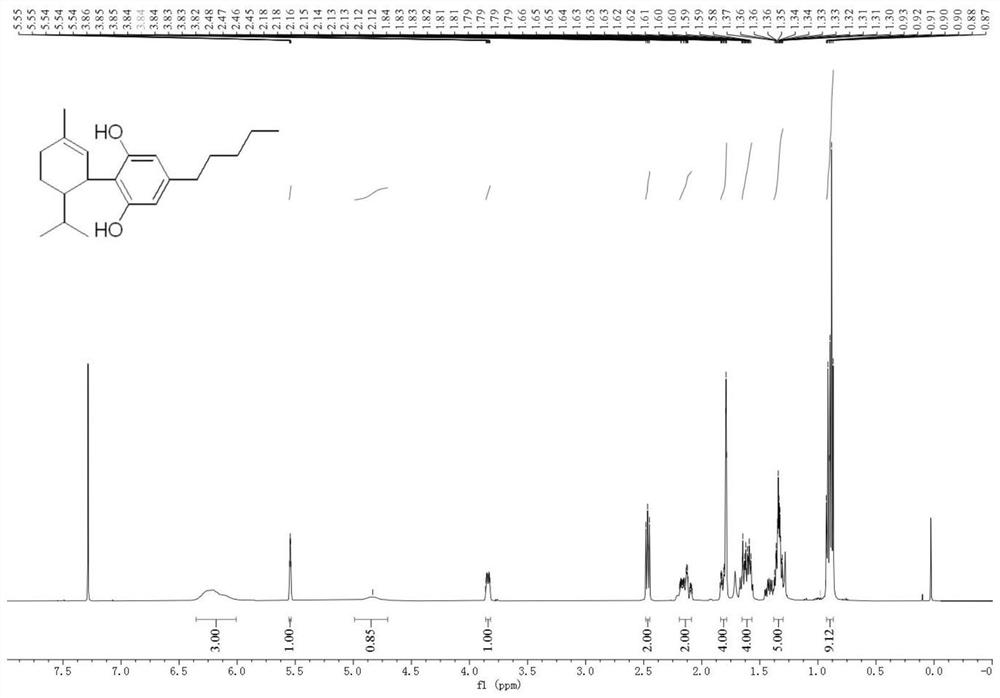
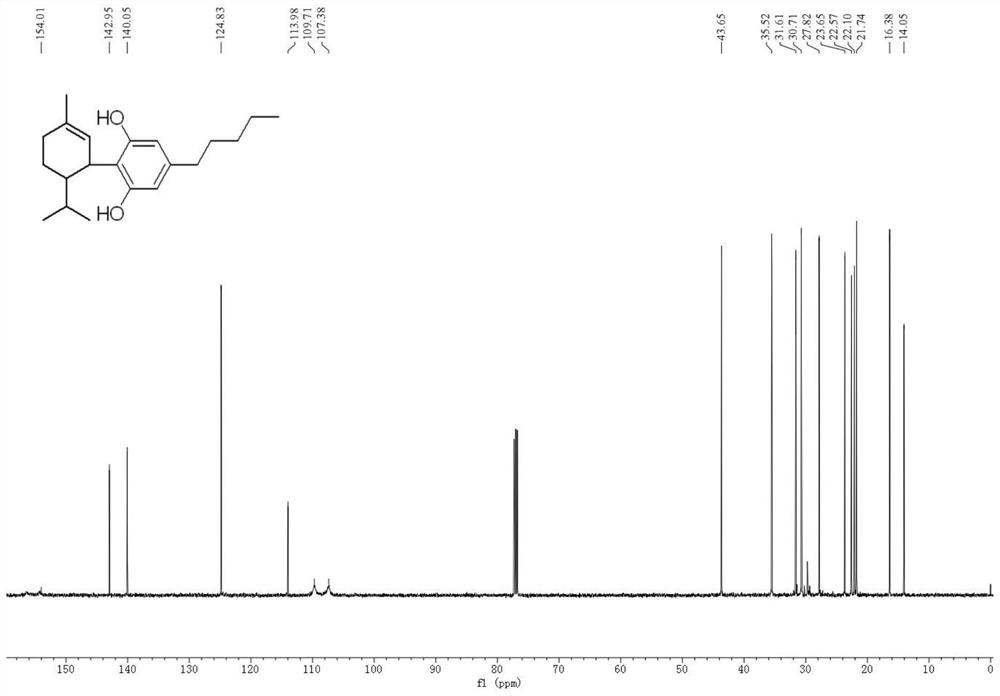
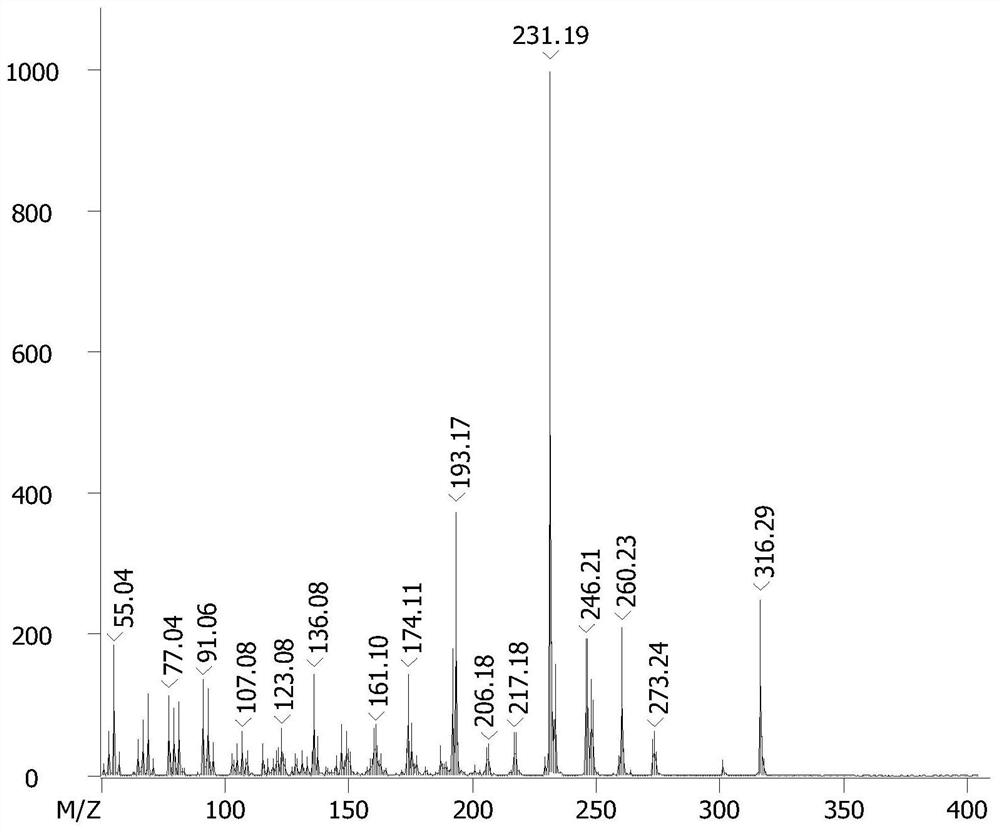
[0041] Olivetol (18g, 0.1mol) and α-phellandrene (17g, 0.125mol) were dissolved in toluene (10mL), ferric chloride (0.162g, 1mmol) was added, and the mixture was heated at room temperature (25°C) The reaction was stirred, monitored by TLC and HPLC, until the yield of 8,9-dihydrocannabidiol no longer increased, filtered, and the resulting filtrate was washed with saturated brine (3×50mL), and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure, the crude product Separation by silica gel column chromatography, and elution with a mixture of petroleum ether and ethyl acetate (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 40:1), followed by TLC elution detection. The eluate from the silica gel column containing the target product was collected and concentrated to obtain 8,9-dihydrocannabidiol (28.44 g, yield 90%) as a dark yellow oil. The specific proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum and carbon nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of the obtained H2CBD are shown in figure 1 with figure...
Embodiment 2-8
[0043] Embodiment 2-8, comparative example 1-2: the impact of catalyst on yield
[0044] The synthesis methods of Examples 2-8 and Comparative Examples 1-2 are similar to those of Example 1, except that the catalysts used are different. The Lewis acid catalysts used in each embodiment and comparative examples and the corresponding yields are shown in Table 1.
[0045] The catalyst that table 1 embodiment 1-10 adopts and corresponding yield
[0046] catalyst Yield (%) Example 1 Ferric chloride 90 Example 2 Boron trifluoride monohydrate 53 Example 3 Boron trifluoride diethyl ether 53 Example 4 Ferric chloride hexahydrate 50 Example 5 Aluminum trichloride 54 Example 6 Copper Chloride Dihydrate 38 Example 7 ferric bromide 41 Example 8 tin chloride 33 Comparative example 1 nickel chloride Trace (<5)
[0047] As can be seen from the results in Table 1, the synthetic method of the present invention n...
Embodiment 9
[0048] Embodiment 9: the influence of the consumption of catalyst iron trichloride on yield
[0049] The synthetic method of Example 9 and the synthetic method of Comparative Example 3 are similar to that of Example 1, except that the amount of catalyst is different. The amount of catalyst used in each embodiment and the corresponding yield are shown in Table 2.
[0050] Table 2 embodiment 1, the catalyst consumption that 9 and comparative example 3 adopt and corresponding yield
[0051] Ferric chloride dosage (wt%) Yield (%) Example 9 0.45 65 Example 1 0.9 90 Comparative example 3 4.5 89
[0052] As can be seen from the results in Table 2, along with the increase of ferric chloride consumption, the yield also increases thereupon; when the consumption of ferric chloride was 0.9%, the yield reached the highest 90%; The consumption of iron, the product yield can not continue to increase; And the consumption of ferric trichloride exceeds 4...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com