In-vitro cell model for simulating revascularization after breast cancer radiotherapy and preparation method and application of in-vitro cell model
A breast cancer cell and cell model technology, which is applied in the field of in vitro cell models for simulating angiogenesis after breast cancer radiotherapy and its preparation, can solve the problem that the influence of blood vessels cannot be reflected, the influence of blood vessels is hindered, and the breast cancer cells and vascular endothelial cells cannot be reflected. Interaction and other problems, to achieve the effect of fast and convenient detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1: Construction of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC-Fluc) stably transfected with fusion genes of firefly luciferase (Fluc) and green fluorescent protein (GFP)
[0041] 1. Recovery of HUVEC cells
[0042] The specific experimental operation of HUVEC cell recovery is as follows:
[0043] 1) Preheat the electric heating constant temperature water tank to 37°C.
[0044] 2) Take out the cryopreservation tube from the liquid nitrogen tank or -80°C ultra-low temperature refrigerator, quickly place it in a 37°C constant temperature water tank, and shake the cryopreservation tube gently to make the cells in it thaw quickly.
[0045] 3) After the cells in the cryopreservation tube are fully thawed, take out the cryopreservation tube and wipe the cryopreservation tube with 75% alcohol cotton ball. Open the cryopreservation tube in the ultra-clean workbench, transfer the cells in it to a 15 ml centrifuge tube, add 5 ml of 10% fetal bovine serum medium, and m...
Embodiment 2
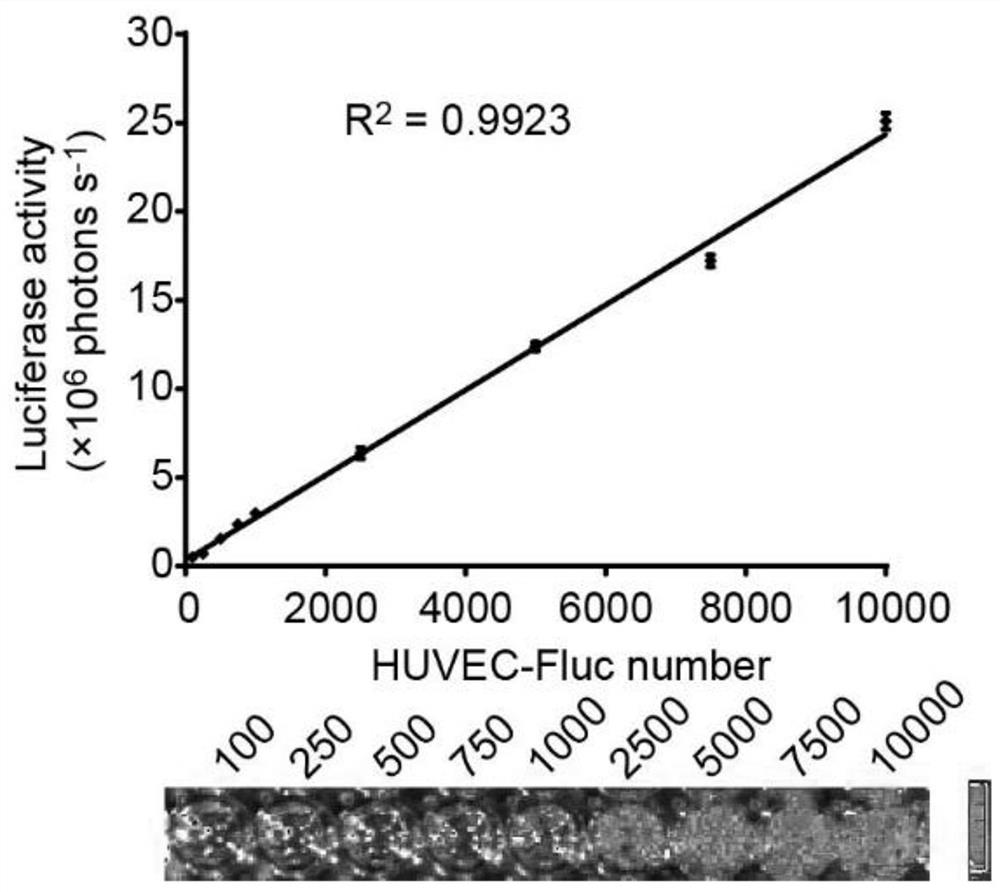
[0106] Example 2: Discussion on the correlation between luciferase activity and cell number in HUVEC-Fluc cells
[0107] In the subsequent in vitro co-culture model, it is hoped that the proliferation of HUVEC-Fluc can be reflected by detecting the activity of HUVEC-Fluc firefly luciferase. Therefore, it is necessary for us to confirm whether there is a positive correlation between firefly luciferase activity and cell number in HUVEC-Fluc. We placed a specified number of HUVEC-Fluc in a 96-well plate, and after the cells adhered to the wall, the luciferase activity of HUVEC-Fluc in the 96-well plate was detected with the help of an in vivo biochemiluminescence imager.
[0108] The specific experimental operation is as follows:
[0109] The well-growing HUVEC-Fluc cells were digested to prepare a single cell suspension. Spread HUVEC-Fluc in 96-well plates at 100, 250, 500, 750, 1000, 2500, 5000, 7500, and 10,000 cells per well, respectively. After the cells were fully adhere...
Embodiment 3
[0113] Example 3: Construction of a cell model for simulating angiogenesis after radiotherapy for breast cancer
[0114] 1. Radiotherapy of breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 using a medical linear accelerator
[0115] The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0116] 1) Cell preparation: X-ray irradiation can be performed on the breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 grown in cell culture dishes of various specifications.
[0117] 2) Place the cells to be irradiated on a piece of transparent plexiglass with a thickness of 15 cm, and cover the cell culture dish with a thin transparent plastic plate to limit the irradiation field of view; the irradiation uses a medical linear accelerator that generates X-rays. The radiation dose rate was 3.6 Gy / min.
[0118] 2. Construction of a cell model for simulating angiogenesis after radiotherapy for breast cancer
[0119] In the present invention, MDA-MB-231 cells and HUVEC-Fluc cells are co-cultured after radiotherapy by a medical li...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com