Ultrahigh-flux single-cell chromatin transposase accessibility sequencing method
A transposase and chromatin technology, applied in the field of single-cell sequencing, can solve the problems of high cost, low contamination rate, low nuclear flux, etc., and achieve the effect of improving flux
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Embodiment 1: microplate preparation
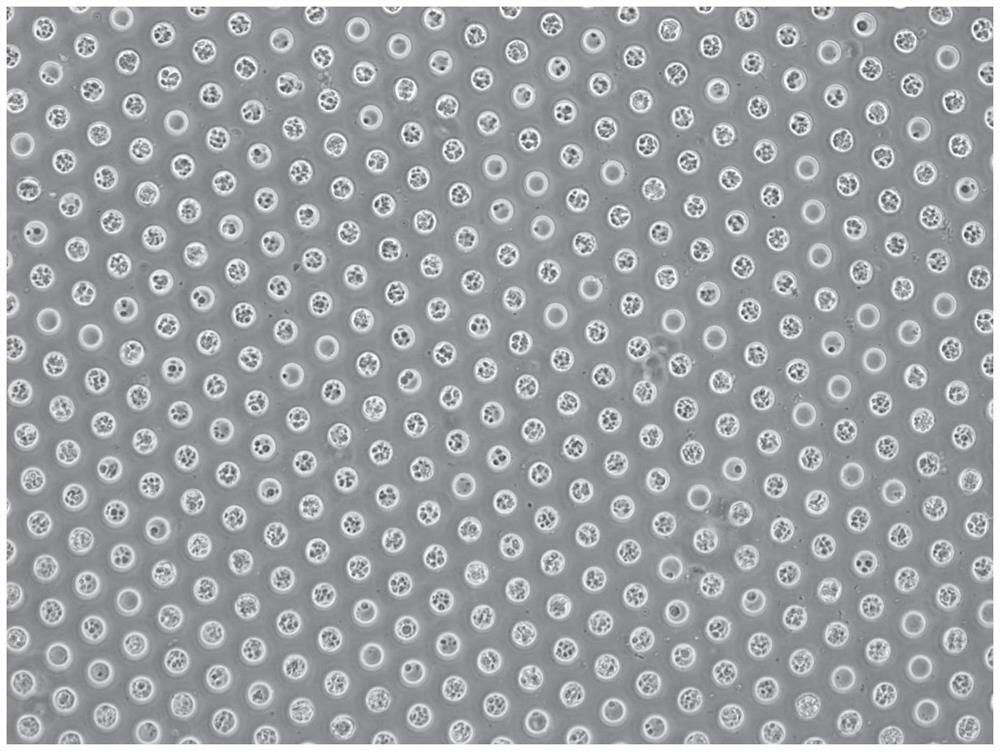
[0061] According to the experimental scale (500,000 human 293T cells and 500,000 mouse 3T3 cells each), design the size of the microwell plate (the size of the well plate is 1.8cm×1.8cm), and etch the microwell on the silicon wafer as the initial mold, and the microwell is a cylinder Body shape, in which the depth of micropores is 60 μm, the diameter of micropores is 50 μm, and the distance between pores is 70 μm. Next pour polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) on the silicon chip, take off PDMS after molding and become the second mold that has microcolumn on the plate, the microporous plate that final experiment uses is that concentration is 5% (mass ratio ) agarose (prepared with enzyme-free water), poured on the PDMS microcolumn plate after hot melting to condense and form, and the agarose plate at this time is a microwell plate with a certain thickness after being peeled off. When saving, add DPBS-EDTA mixture which is harmless to cells...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Example 2: Preparation of molecularly labeled magnetic beads
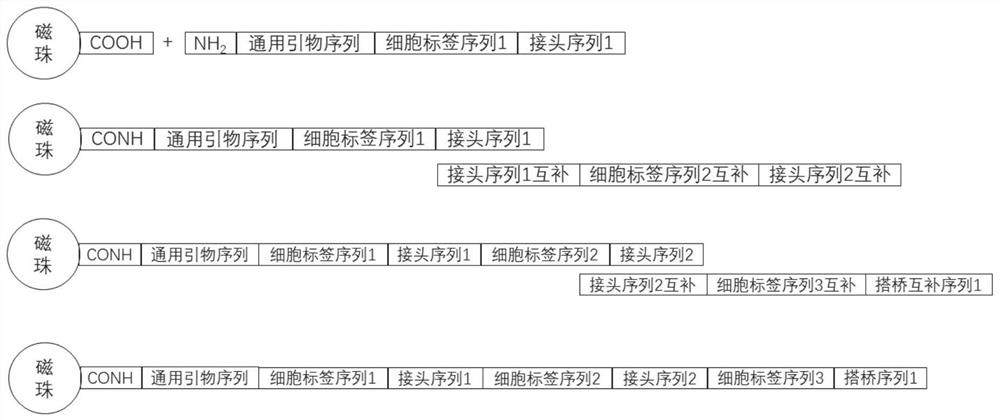
[0063] The magnetic beads were purchased from Suzhou Zhiyi Microsphere Technology Co., Ltd. (Product No. MagCOOH-20190725), the surface was coated with carboxyl groups, and the diameter was 45 μm. The preparation process of molecularly labeled magnetic beads is as follows: figure 1 As shown, there are 5 steps in total:
[0064] (1) Design the molecular marker sequence, divide the molecular marker sequence into three sections, and set a linker sequence between the adjacent two sections for connecting the adjacent two sections through PCR, and the first section starting from 5' includes the universal primer sequence and part of the cell tag sequence, the last segment contains part of the cell tag sequence, the entire molecular tag sequence, and the bridging complementary sequence. Except for the first segment, the rest of the sequences are complementary sequences of the corresponding sequence.
[0065] (2) T...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Example 3: Preparation of Specific Molecular Tag Transposase Embedding Complex
[0074] Tn5 transposase naked enzyme was purchased from Nanjing Novizan Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The transposase and embedding buffer were provided by (Vazyme) Tn5 Transposome (S111) kit produced by Nanjing Novizan Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0075] (1) The embedded nucleic acid sequence is shown in Table 2 below.
[0076] Table 2
[0077]
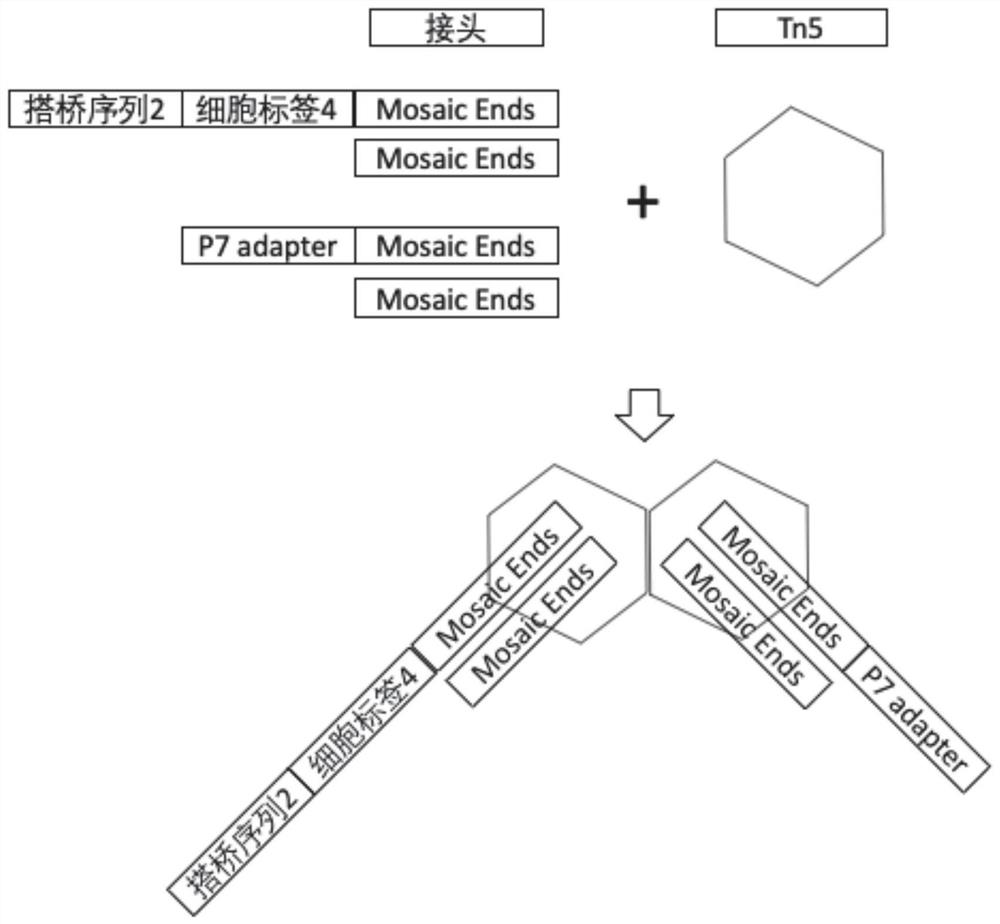
[0078]Among them, the specific molecular tag 10×N contained in the specific tag fragment is the core sequence of the cell tag sequence, and the core sequence corresponding to each Tn5 complex is different. choices, so a 10×N sequence can have 4 10 options. N represents any one of A / T / C / G, which is randomly synthesized.
[0079] (2) Annealing of 96 oligonucleotide sequences with specific molecular tags (P7 adapter fragment + Mosaic Ends fragment annealing to obtain a universal sequence, namely figure 2 The P7 Adapter-Mosaic Ends / Mosaic Ends in the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com