Method for producing battery-grade nickel sulfate by taking ferro-nickel alloy as raw material
A nickel-iron alloy and battery-level technology, which is applied in the preparation of nickel sulfate and nickel compounds, etc., can solve the problems of increased production costs, harsh working environment, and difficult disposal, and achieve the goal of reducing usage, reducing production costs, and improving recovery efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
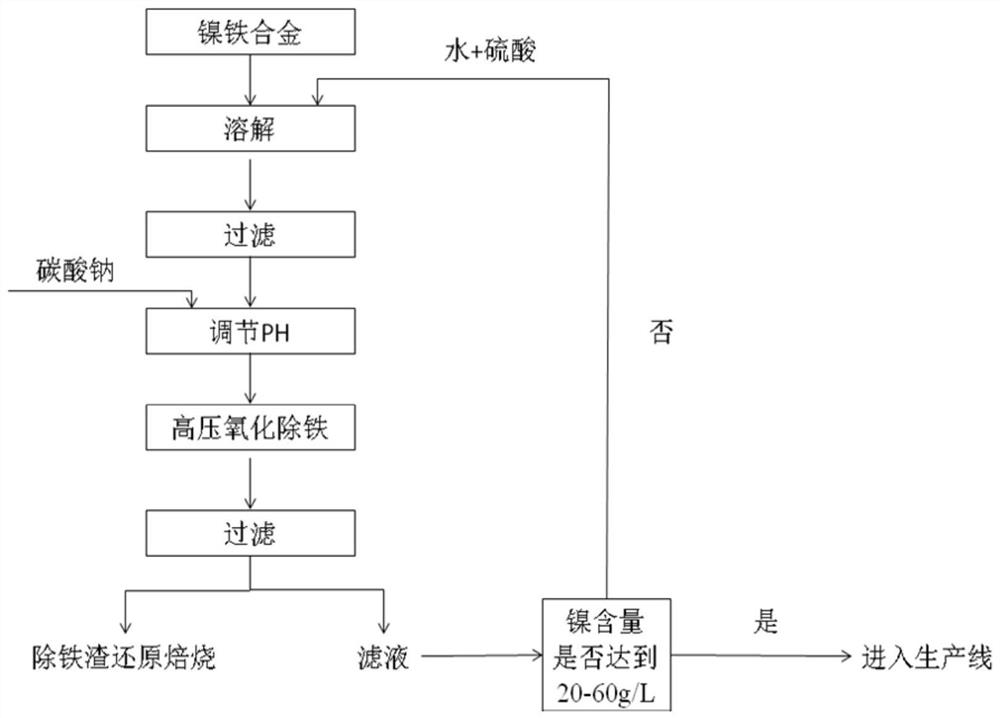
[0031] according to figure 1 The process flow chart shown, the detailed steps are as follows:
[0032] a. Add 500g of water to 1kg of nickel-iron alloy, then add sulfuric acid to make the sulfuric acid concentration 1.0mol / L, heat to 70°C under normal pressure and let it dissolve. + The reaction ends when the concentration is lower than 0.5mol / L;
[0033] B, filter the immersion solution obtained in step a, remove a small amount of slag and undissolved nickel-iron alloy;
[0034] c, the filtrate obtained in step b is adjusted to pH 2 with soda ash;
[0035] d. Stir the solution obtained in step c for 30 minutes, pour it into an autoclave, set the temperature at 110°C, oxygen pressure at 0.3MPa, and react for 2 hours;
[0036] e. The product obtained in step d is filtered, the filter residue is reduced and roasted, and the filtrate is used for circulation and standing for dissolution.
[0037] f. Carry out reduction roasting at 400° C. for the filter residue (i.e. iron remo...
Embodiment 2
[0040] according to figure 1 The process flow chart shown, the detailed steps are as follows:
[0041] a. Add 5000g of water to 1kg of nickel-iron alloy, then add sulfuric acid to make the sulfuric acid concentration 3.0mol / L, heat to 110°C under normal pressure and let it dissolve. + The reaction ends when the concentration is lower than 0.5mol / L;
[0042] B, filter the immersion solution obtained in step a, remove slag and ferronickel;
[0043] c, the filtrate obtained in step b is adjusted to pH 5 with soda ash;
[0044] d. Stir the solution obtained in step c for 30 minutes, pour it into an autoclave, set the temperature at 250°C, and the oxygen pressure at 0.8MPa, and react for 6 hours;
[0045] e. The product obtained in step d is filtered, the filter residue is reduced and roasted, and the filtrate is used for circulation and standing for dissolution.
[0046] f. Carry out reduction roasting at 700° C. for the filter residue (i.e. iron removal slag) obtained in step...
Embodiment 3
[0049] according to figure 1The process flow chart shown, the detailed steps are as follows:
[0050] a. Add 2500g of water to 1kg of nickel-iron alloy, then add sulfuric acid to make the sulfuric acid concentration 2.0mol / L, heat to 90°C under normal pressure and let it dissolve. + The reaction ends when the concentration is lower than 0.5mol / L;
[0051] B, filter the immersion solution obtained in step a, remove a small amount of slag and undissolved nickel-iron alloy;
[0052] c, adjusting the pH of the filtrate obtained in step b to 3.5 with soda ash;
[0053] d. Stir the solution obtained in step c for 30 minutes, pour it into an autoclave, set the temperature at 180°C, oxygen pressure at 0.55MPa, and react for 3.5 hours;
[0054] e. The product obtained in step d is filtered, the filter residue is reduced and roasted, and the filtrate is used for circulation and standing for dissolution.
[0055] f. Carry out reduction roasting at 550° C. for the filter residue obtai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com