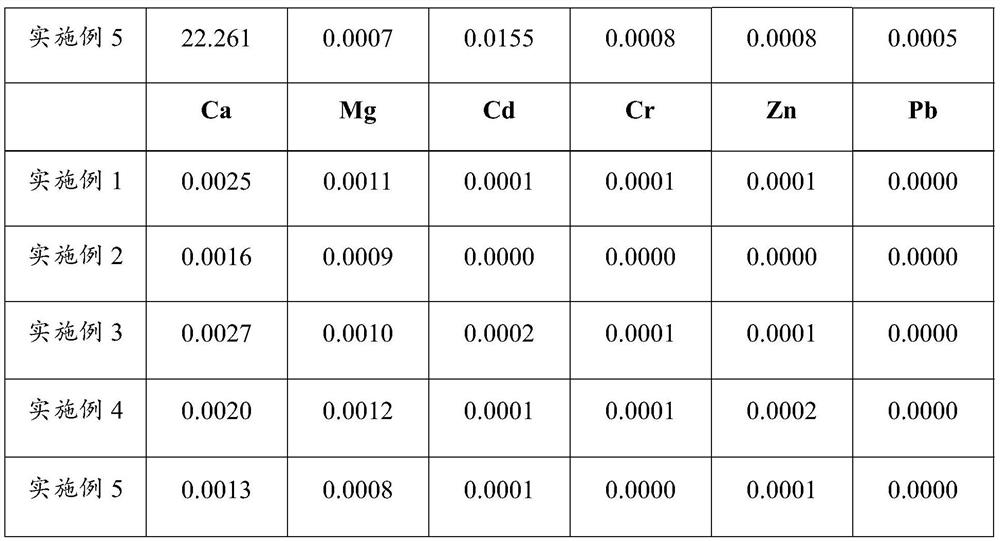
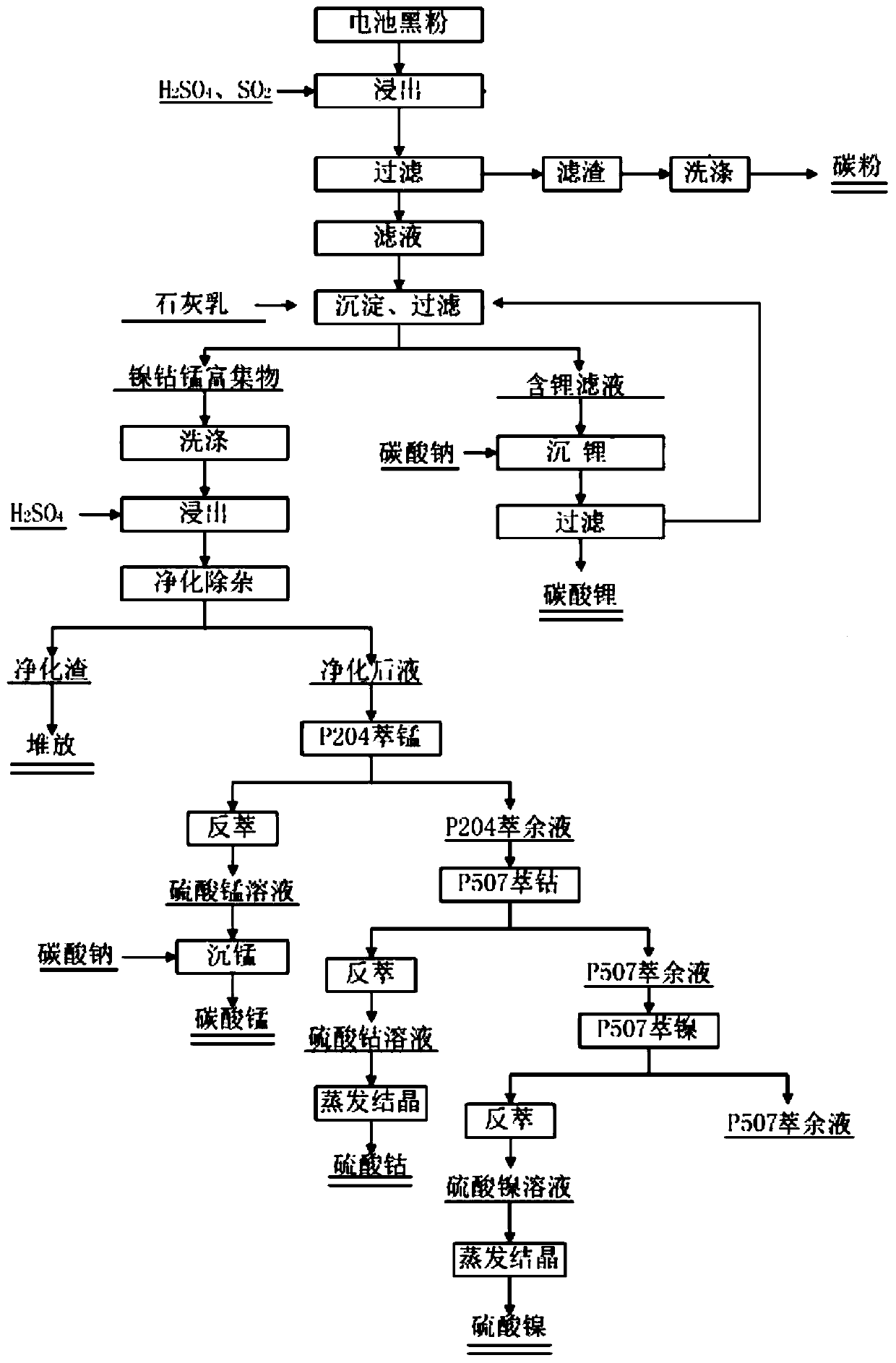
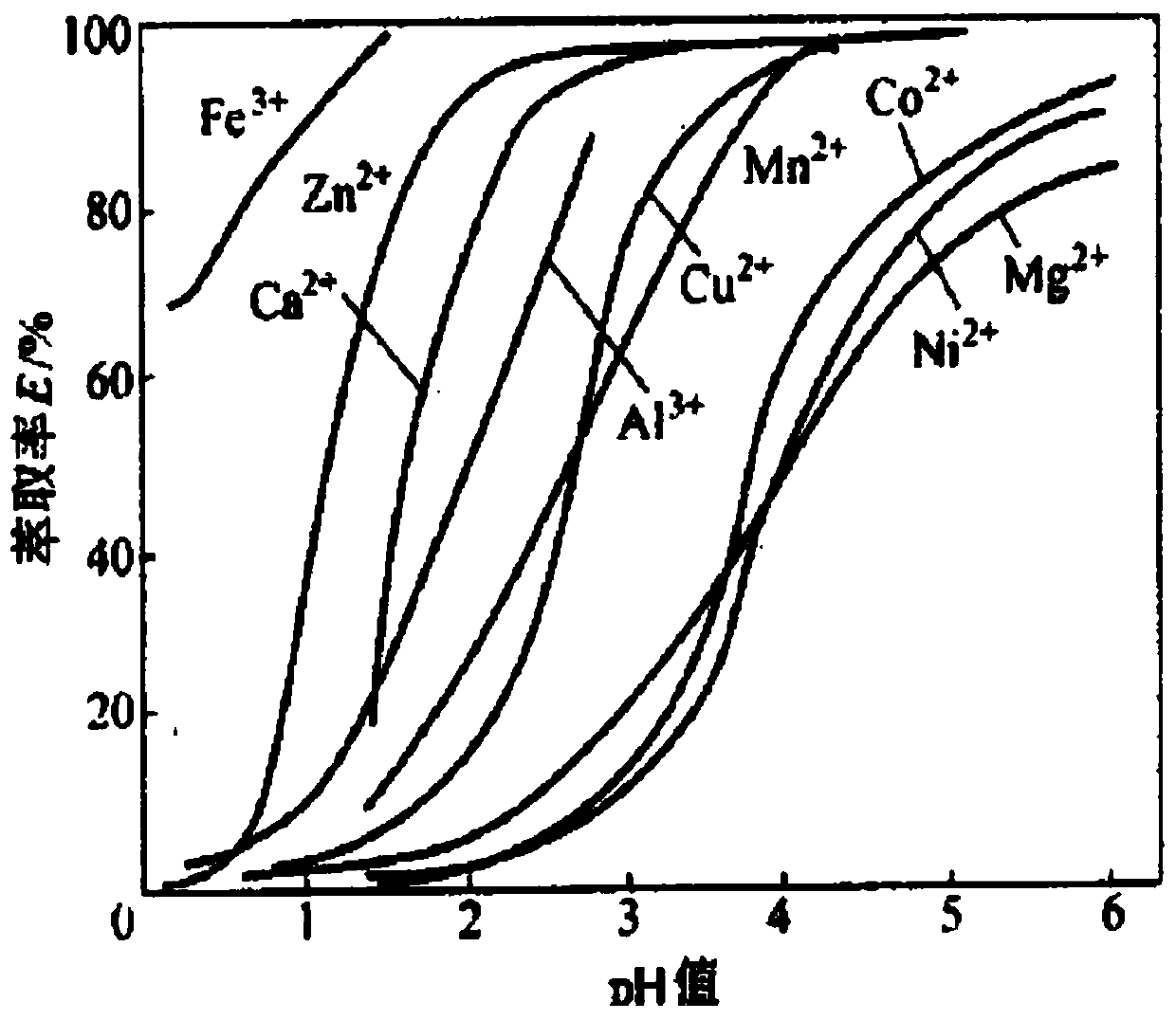
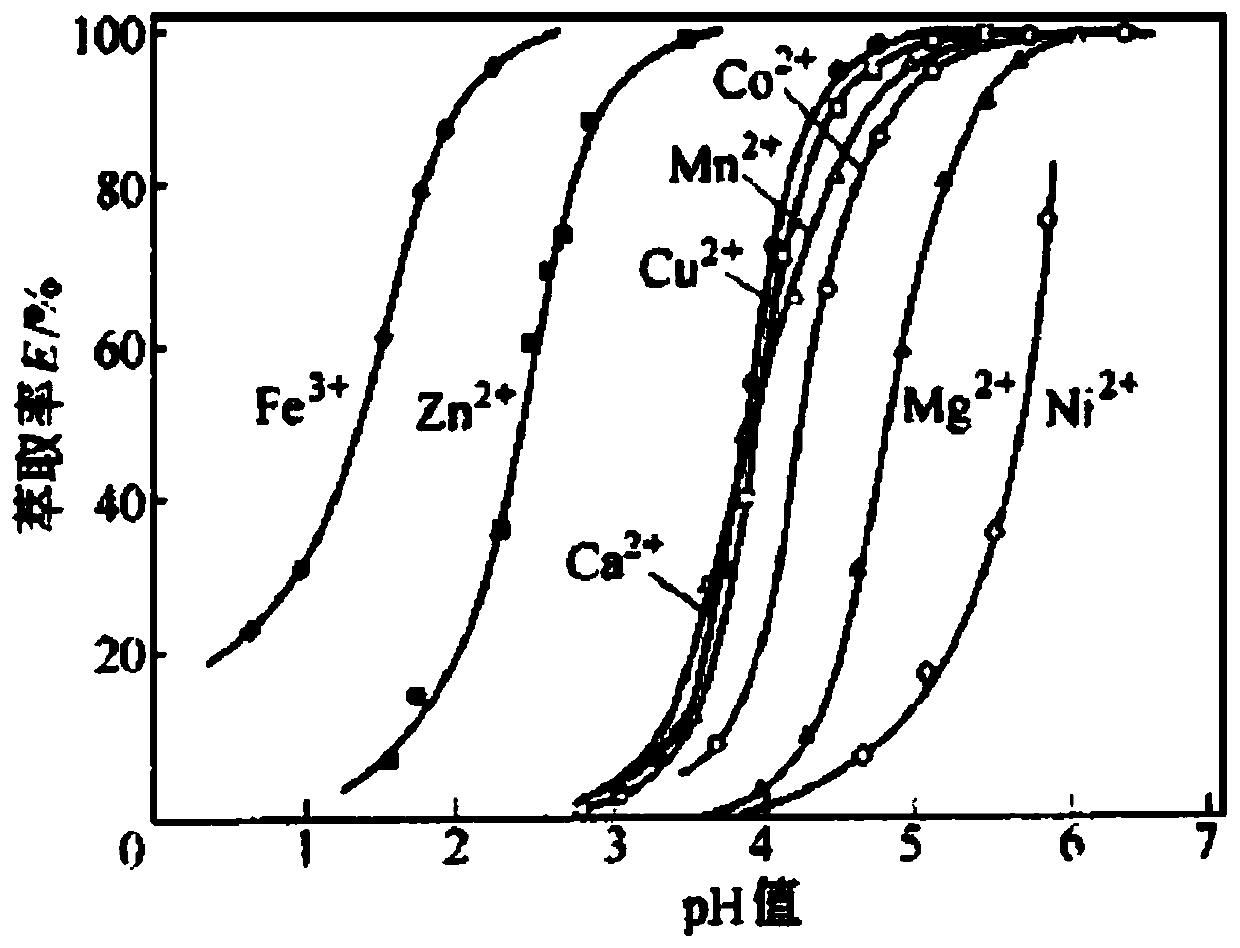
Patents
Literature
892 results about "Nickel sulphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for preparing nickel and cobalt doped lithium manganate by using waste and old lithium ionic cell as raw material
InactiveCN101450815ASimultaneous recyclingShort processManganates/permanganatesManganateManganese oxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide by taking a waste lithium ion battery as a raw material. The method is mainly characterized in that a waste lithium ion battery taking the lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide, lithium nickel cobalt oxide and so on as a battery positive material is selected as the raw material and is pretreated through disassembly, separation, crushing, screening and so on, and then processes such as adhesive removal at high temperature and aluminum removal by sodium hydroxide are adopted to obtain an inactivated positive material containing nickel, cobalt and manganese; then a sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide system is adopted to leach, and P204 is adopted to remove impurities by extraction to obtain pure nickel, cobalt and manganese solution, and proper manganese sulfate, nickel sulfate or cobalt sulfate is blended to ensure that the mol ratio of nickel, cobalt and manganese elements in the solution is 1: 1: 1; and then ammonium carbonate is adopted to adjust the pH value to form a nickel cobalt manganese carbonate precursor, and then a proper amount of lithium carbonate is blended for high temperature sintering to synthesize a lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide battery material. The first discharge capacity of the material is 150 mAh / g, the discharge capacity is still kept more than 130mAh / g after the circulation for 30 times, and the material has good electrochemical performance.
Owner:GUANGDONG BRUNP RECYCLING TECH +1
Method for preparing nickel/manganese/lithium/cobalt sulfate and tricobalt tetraoxide from battery wastes
ActiveUS20190152797A1Reduce productionHigh puritySolvent extractionCobalt sulfatesManganeseCobalt Sulfate
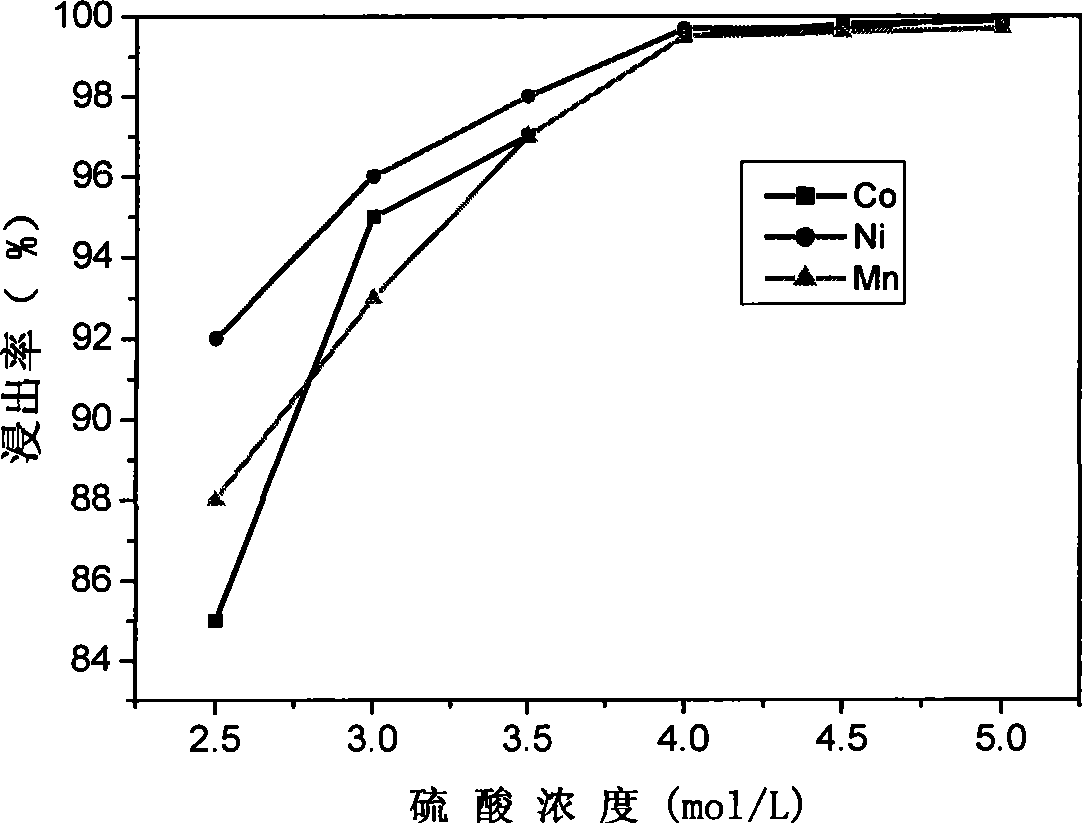
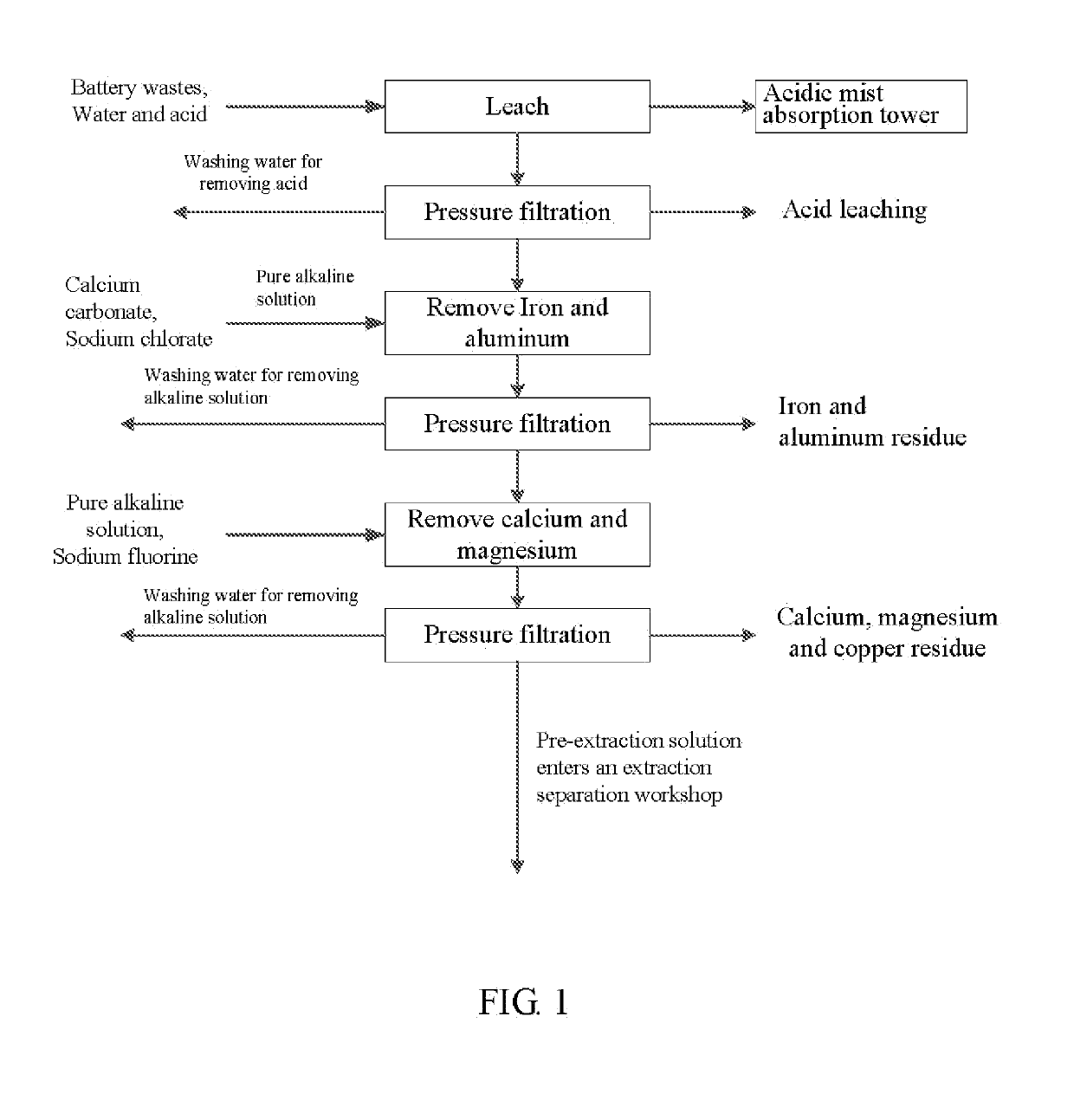
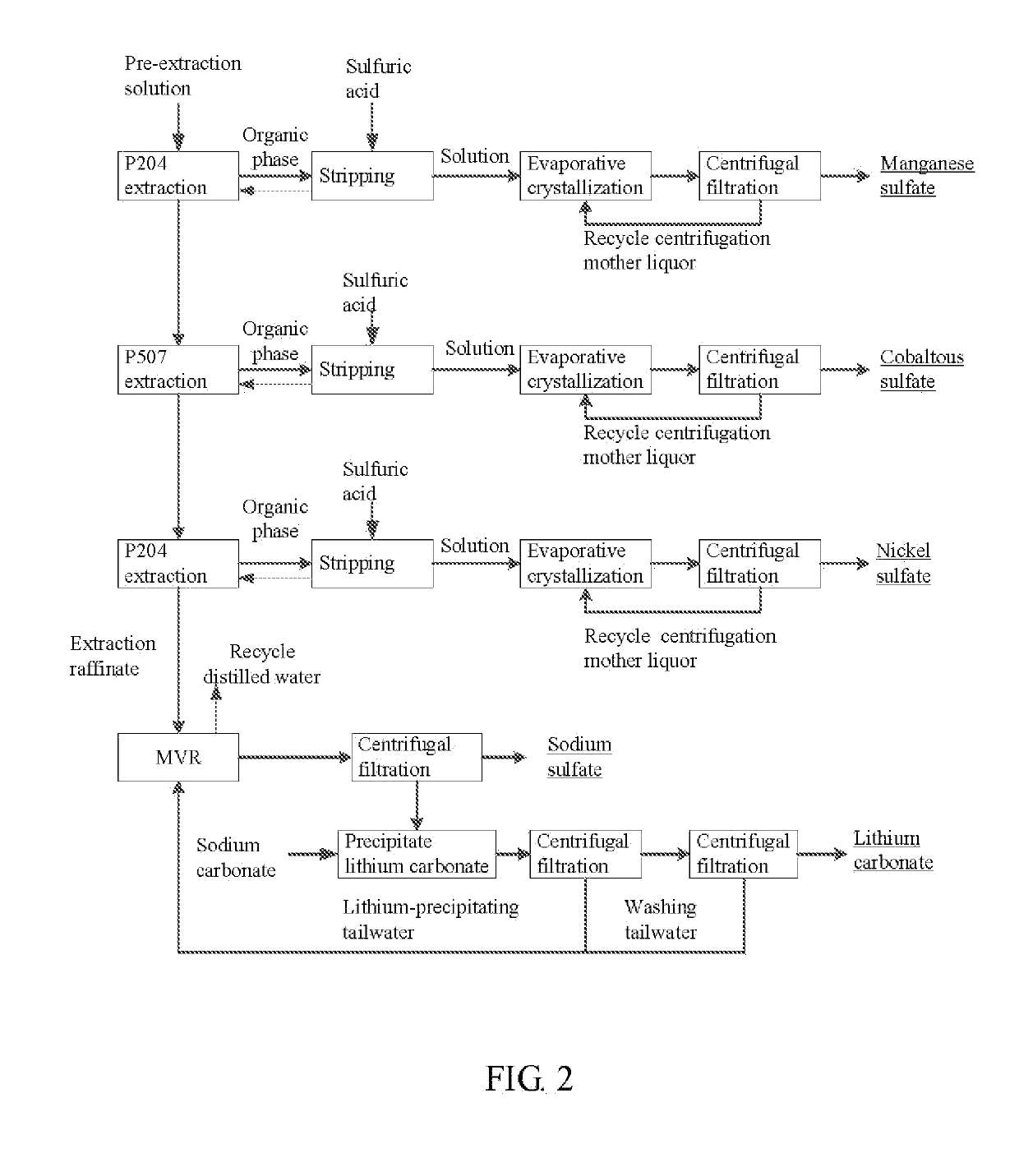
A method for preparing nickel / manganese / lithium / cobalt sulfate and tricobalt tetraoxide from battery wastes adopts the following process: dissolving battery wastes with acid, removing iron and aluminum, removing calcium, magnesium and copper, carrying extraction separation, and carrying out evaporative crystallization to prepare nickel sulfate, manganese sulfate, lithium sulfate, cobalt sulfate or / and tricobalt tetraoxide. By using the method, multiple metal elements, such as nickel, manganese, lithium and cobalt, can be simultaneously recovered from the battery wastes, the recovered products are high in purity and can reach battery grade, battery-grade tricobalt tetraoxide can also be directly produced. The method is simple in process, low in, energy consumption and free in exhaust gas pollution, and can realize zero release of wastewater.
Owner:HUNAN JINYUAN NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
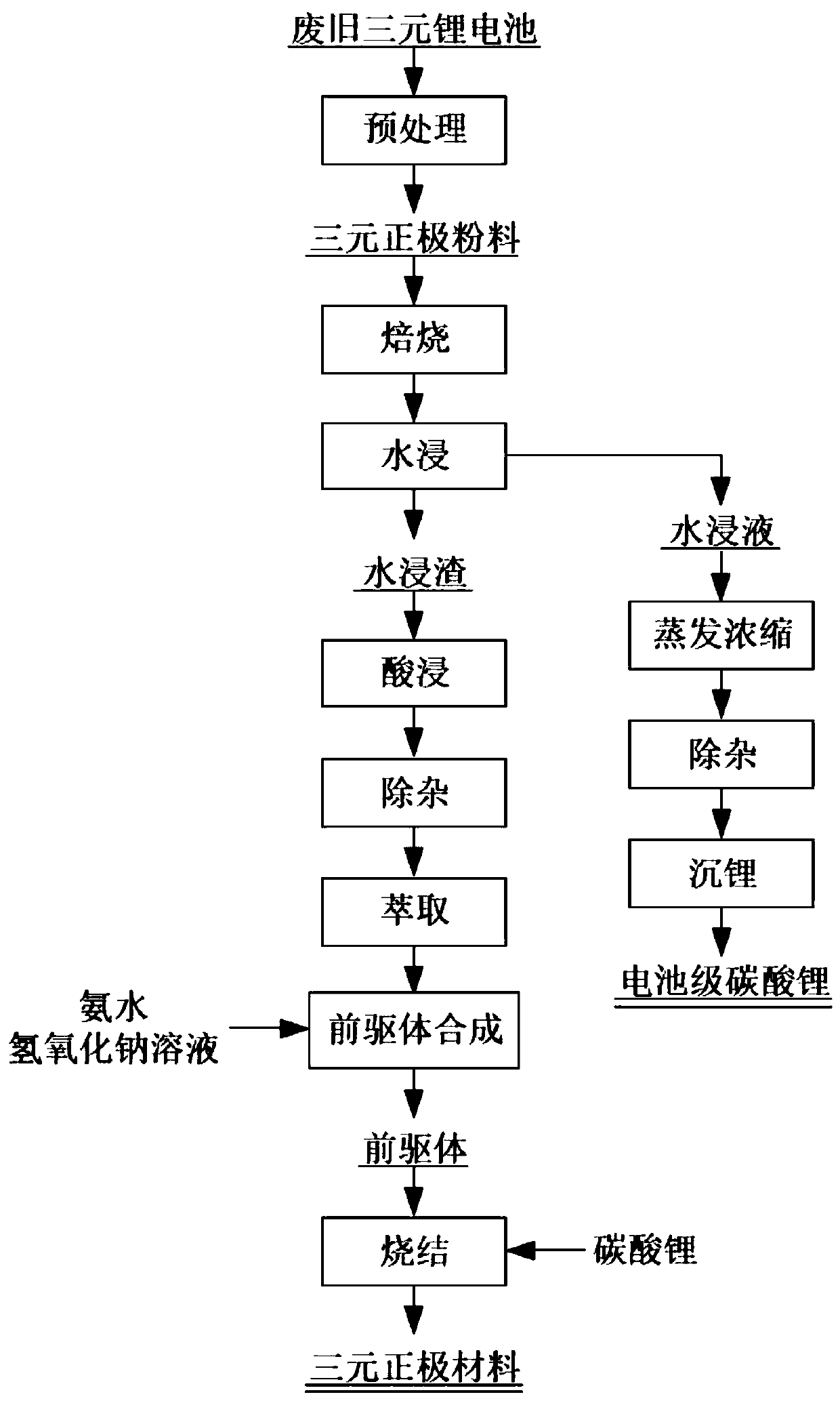
Method for preparing ternary positive electrode material through recovering waste ternary lithium battery
ActiveCN111206148AHigh recovery rateReduce recycling costsCell electrodesWaste accumulators reclaimingManganese sulphatePregnant leach solution
The invention provides a method for preparing a ternary positive electrode material through recovering a waste ternary lithium battery. The method comprises the following steps of 1) mixing pretreatednickel cobalt lithium manganate waste positive electrode powder with sulfate, and roasting to obtain a roasted product; 2) immersing the roasted product in water to obtain water immersion liquid andwater immersion slag; wherein the water immersion liquid contains lithium salt; 3) reacting the water immersion slag with an acid solution and hydrogen peroxide to obtain a nickel-cobalt-manganese leaching solution; 4) removing impurities from the nickel-cobalt-manganese leaching solution, then extracting cobalt, manganese and nickel, and saponifying and reversely extracting obtained organic phaseto obtain a nickel sulfate solution, a cobalt sulfate solution and a manganese sulfate solution; and 5) co-precipitating the nickel sulfate solution, the cobalt sulfate solution and the manganese sulfate solution with a sodium hydroxide solution and ammonia water, mixing obtained precursor with lithium carbonate, sintering, and screening iron to obtain the ternary positive electrode material. According to the method, lithium is extracted firstly, so that the influence of a lithium element on subsequent nickel-cobalt-manganese extraction is reduced, the impurity content in the ternary positiveelectrode material is reduced, and the recovery rate of nickel-cobalt-manganese is greatly improved; and meanwhile the recovery rate of the lithium can be improved.
Owner:NINGBO RONBAY LITHIUM BATTERY MATERIAL CO LTD
Polypeptide-ammonium polyphosphate trace element liquid chelated fertilizer and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a polypeptide-ammonium polyphosphate trace element liquid chelated fertilizer and a preparation method of the liquid chelated fertilizer. The polypeptide-ammonium polyphosphate trace element liquid chelated fertilizer comprises the components by weight percent: 5-25% of urea, 5-15% of ammonium polyphosphate, 5-25% of potassium nitrate, 0.2-3% of potassium silicate, 0.8-5% of potassium chloride, 0.008-0.1% of polyaspartic acid, 0.8-5% of ammonium sulfate, 0.8-5% of ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) calcium, 0.2-3% of EDTA magnesium, 0.02-1.5% of EDTA boron, 0.005-0.1% of EDTA zinc, 0.005-0.1% of EDTA iron, 0.005-0.05% of EDTA copper, 0.005-0.05% of EDTA manganese, 0.001-0.01% of nickel sulfate, 0.001-0.01% of ammonium molybdate, 0.0008-0.01% of cobaltous sulfate, 0.008-0.1% of polyacrylamide and the balance of water. The polypeptide-ammonium polyphosphate trace element liquid chelated fertilizer disclosed by the invention is simple in technology, scientific in proportion, balanced in fertilization, low in cost and good in effect.
Owner:张朝晖
Method for performing electroless nickel plating on surface of aluminum nitride ceramic
ActiveCN101962760AHigh bonding strengthImprove high temperature resistanceLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectroless nickelSodium acetate
The invention provides a method for performing electroless nickel plating on the surface of aluminum nitride ceramic, belonging to the ceramic thin-film metallization field. The method comprises the following specific steps: 1) polishing the surface of aluminum nitride with a machinery; coarsening the aluminum nitride substrate with mixed acid or alkali, completely cleaning away the residual acid or alkali; 3) sensitizing the coarsened substrate in stannous chloride solution, activating in palladium chloride solution or performing activation without palladium; 4) weighting a certain amount of nickel sulphate, sodium hypophosphite, sodium citrate, sodium acetate, lactic acid, thiourea and sodium dodecyl sulfate in sequence to prepare a chemical plating solution; and 5) adjusting the pH value of the solution to 4.0-6.0 with acid or alkali, heating the solution to 70-95 DEG C, and placing the prepared substrate in the solution to perform electroless nickel plating. The invention is characterized in that the electroless nickel plating can be performed on the surface of the aluminum nitride ceramic substrate which is difficult to plate; and a certain amount of surfactant is added so that the plating becomes denser and smoother, the binding force between the plating and the substrate is increased, and the solderability of the plating is better.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Chemical nickel-plating method for carbon fiber
InactiveCN102086517ALow costEasy to operateLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingFiberCarbon fibers
The invention discloses a chemical nickel-plating method for carbon fiber, which is designed for overcoming the disadvantages of high cost, a large number of process steps and poor operability existing in the prior art. In the method, a chemical plating process is adopted; and a pre-treatment is performed on a raw material and chemical plating solution is prepared before the chemical plating. The pre-treatment process comprises the steps of: calcining by using a muffle furnace to remove glue; soaking in solution of absolute ethanol to remove oil; performing surface roughening and activating treatment by using solution of sodium hydroxide and solution of silver ammonia; sensitizing by using a sensitizer, namely stannous chloride; and performing surface reduction by using solution of sodium hypophosphite. The chemical plating solution consists of nickel sulfate hexahydrate, sodium hypophosphite, sodium pyrophosphate and sodium citrate. The chemical nickel-plating on the carbon fiber is finished by placing a pre-treatment product of the chemical plating into the chemical plating solution, and reacting, standing, filtering and drying under a chemical plating condition. The method has the characteristics that: the product has a uniform surface, a compact plating layer and uniform particles.
Owner:沈阳临德陶瓷研发有限公司
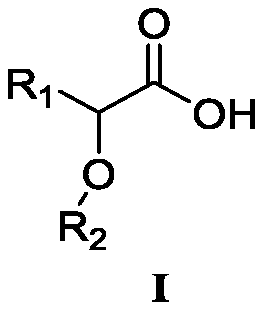
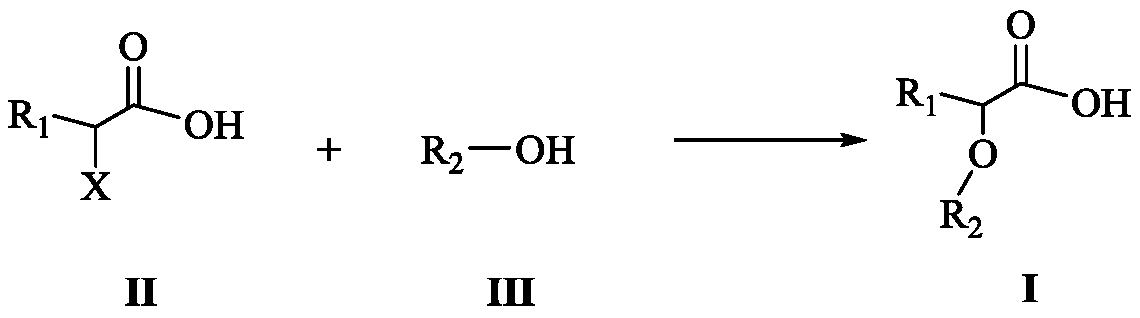
Carboxylic acid compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111592459AHigh separation factorHigh load rateOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationCarboxylic acidAqueous solubility
The invention discloses a carboxylic acid compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof. When the carboxylic acid compound is applied to extraction separation of metal ions, the separation coefficient is high, the reverse extraction acidity is low, the load rate is high, and the reverse extraction rate is high. The carboxylic acid compound serving as an extraction agent is highin stability and low in water solubility, so that the extraction process is stable, the environmental pollution can be reduced, and the cost is reduced. The carboxylic acid compound disclosed by the invention is low in cost, has a great application prospect and can be used for various systems such as ternary battery recovery and battery-grade nickel sulfate preparation.
Owner:BOTREE CYCLING SCI & TECH CO LTD
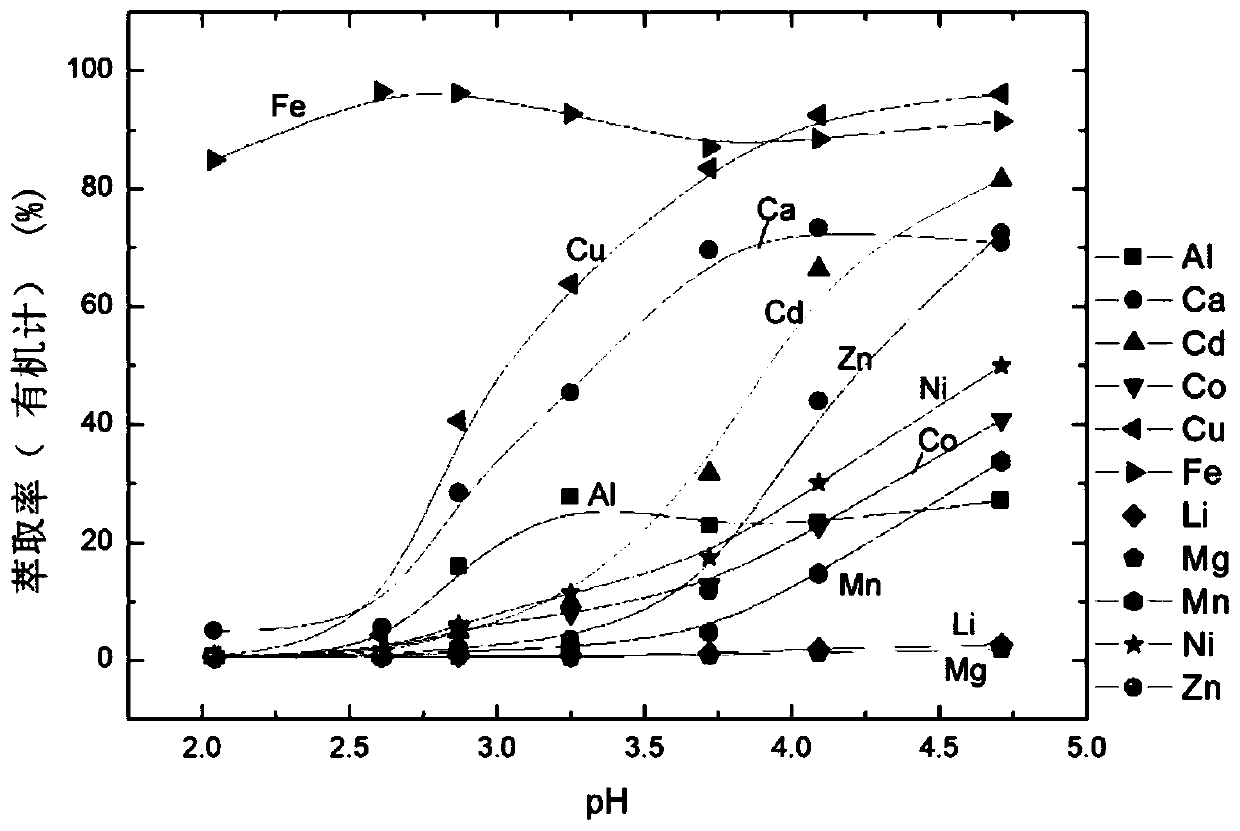
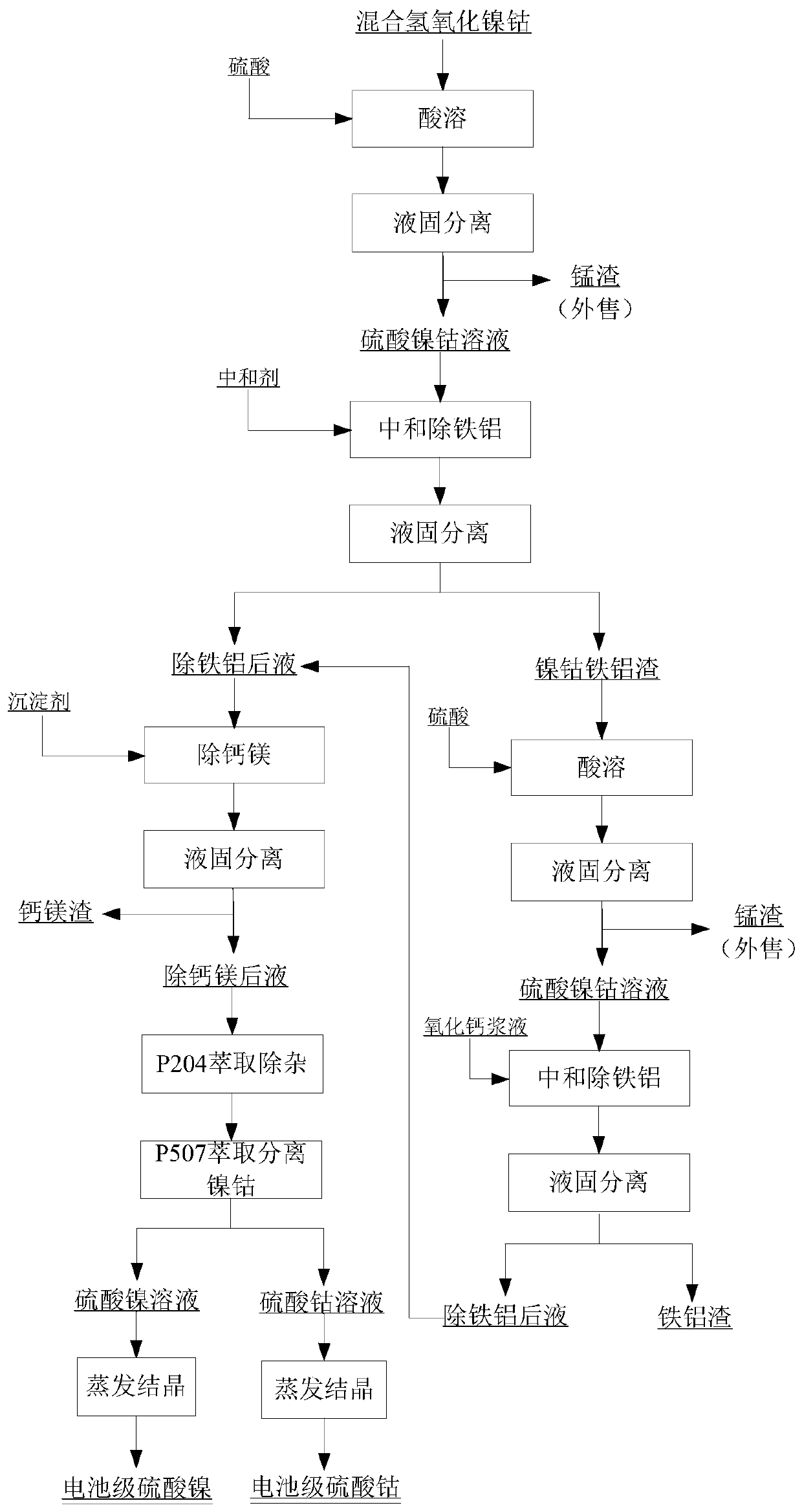
Method for preparing battery-grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate from mixed nickel cobalt hydroxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing battery-grade nickel sulfate and cobalt sulfate from mixed nickel cobalt hydroxide, and belongs to the technical field of nickel cobalt hydrometallurgy.The method comprises the following steps that the mixed nickel cobalt hydroxide is leached by using sulfuric acid, iron and aluminum in the solution are removed by using a nickel / cobalt / manganese-based neutralizer, liquid-solid separation is carried out to obtain iron-removed slag, nickel and cobalt are recycled through acid dissolution, a precipitator (one or more of nickel fluoride, and cobalt fluoride and manganese fluoride) is added into iron-removed liquid to remove calcium and magnesium ions in the system. Impurities such as Mn, Cu and Zn are removed from the calcium and magnesium removed liquid by using a saponified P204 extractant, nickel and cobalt are separated from the P204 raffinate by using a saponified P507 extractant to obtain battery-grade nickel sulfate and a cobalt sulfate solution, and evaporative crystallization is carried out to obtain a product. According to the method, the use amount of calcium oxide is greatly reduced, the amount of calcium ions introduced intothe system and the corresponding nickel-cobalt loss are greatly reduced, the influence of calcium sulfate crystallization on extraction is avoided, the P507 extraction operation amount is reduced, andthe purification cost is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING MINING & METALLURGICAL TECH GRP CO LTD
Method for keeping balance of sodium-magnesium-water system in technique for extracting nickel from lateritic nickel ore by wet process
InactiveCN102181665AHigh recovery rateContinuous productionProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisLaterite
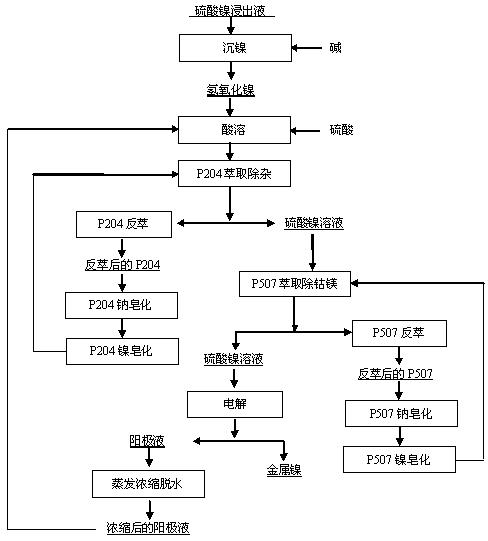
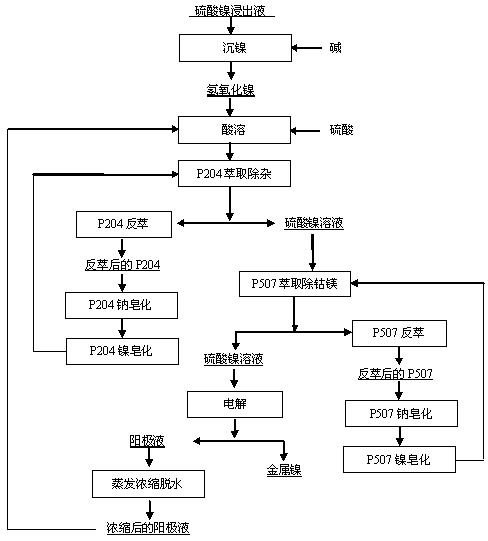
The invention discloses a method for keeping balance of a sodium-magnesium-water system in a technique for extracting nickel from lateritic nickel ore by a wet process, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (a) dissolving nickelous hydroxide, which is obtained by carrying out alkali nickel precipitation on nickel sulfate leach liquor, in sulfuric acid; (b) extracting the nickel sulfate solution obtained in the step (a) with a P204 extractant to remove impurities, wherein P204 sodium soap is converted into nickel soap before removing the impurities; (c) extracting the nickel sulfate solution obtained in the step (b) with a P507 extractant to remove cobalt and magnesium, wherein P507 sodium soap is converted into nickel soap before removing the cobalt and magnesium; and (d) evaporating the anolyte, which is obtained by electrolyzing the nickel sulfate solution obtained in the step (c), thereby removing part of moisture. By using the method provided by the invention, the sodium, magnesium and water are balanced in the technique for extracting nickel from lateritic nickel ore by a wet process, so that the production can be carried out continuously, thereby increasing the recovery rate of nickel, lowering the treatment cost and having obvious economic efficiency.
Owner:广西银亿新材料有限公司
Method for producing nickel-cobalt metal powder
The invention discloses a preparation method for nickel cobalt metal powders, which belongs to the technical field for preparation of non-ferrous metal metallurgy, powder metallurgy and material preparation. The preparation method is characterized in that nanometer or ultrafine nickel and cobalt metal powders is adopted as a seed crystal, which is mixed with ammoniacal water solution with nickel sulfate, cobalt sulfate, ammonia and ammonium sulfate, the preparation method adopts a hydrometallurgical hydrothermal hydrogen reducing technology and a device thereof, and the nanometer, ultrafine or tenuous nickel powder, cobalt powder and nickel cobalt alloy powder are prepared through the procedures such as ingredient, high-pressure hydrothermal hydrogen reduction, filtration, washing, drying and the like. The preparation method can be used for the field such as hydrogen storage alloy, galvanization, catalyst, sintering activating agent, magnetic materials, electric conduction slurry, battery materials, wave-absorbing materials, hard alloy, multi-layer porcelain capacitor, powder metallurgy and the like. The preparation method has the advantages of simple raw materials, simple process, short technological process, low manufacturing cost, controllable manufacturing process, high production efficiency, even graininess of metal powders, controllable size and composition and good quality of products.
Owner:张建玲
A kind of method of direct electrolysis of sulfuric acid leaching of laterite nickel ore
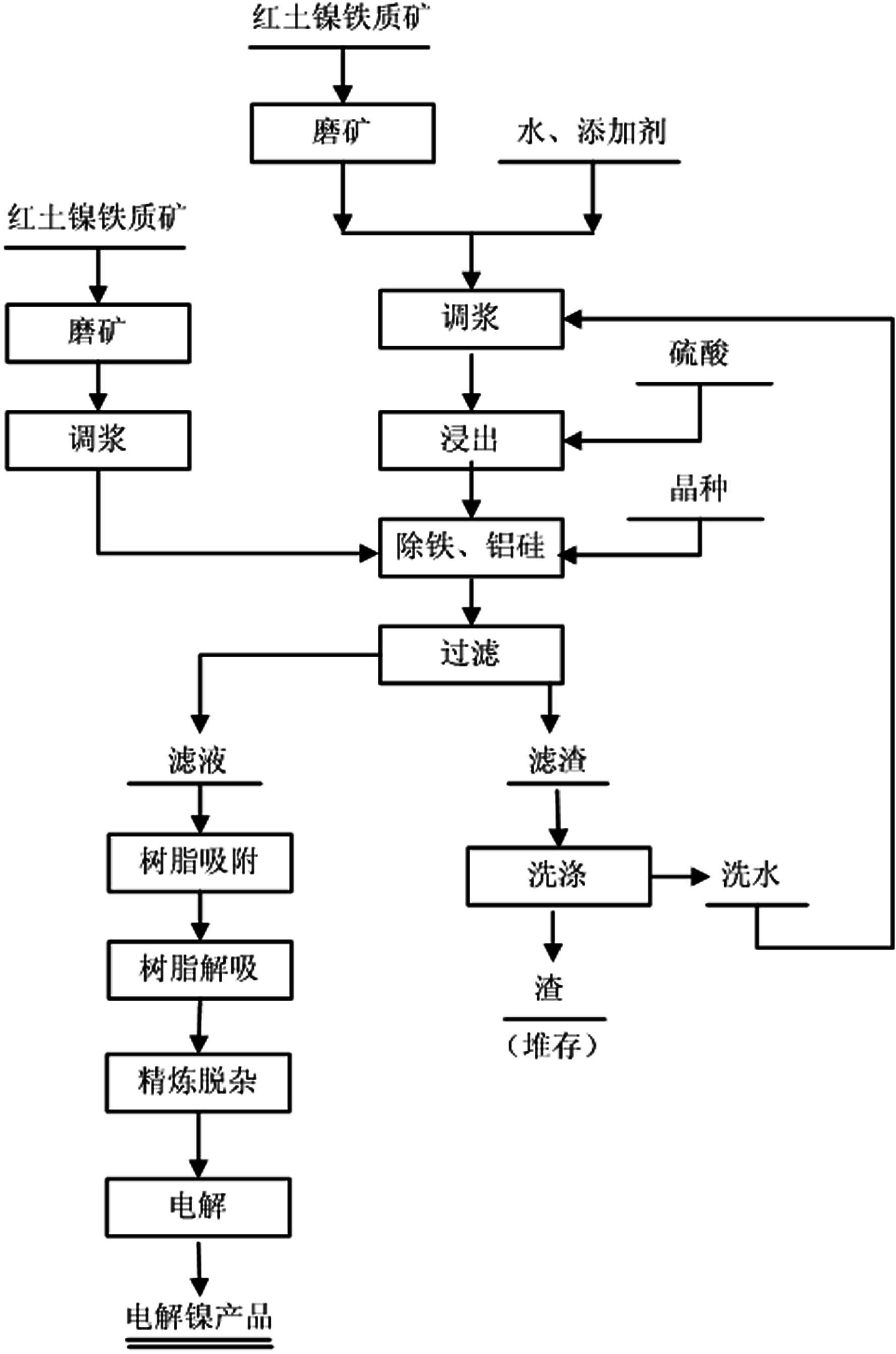
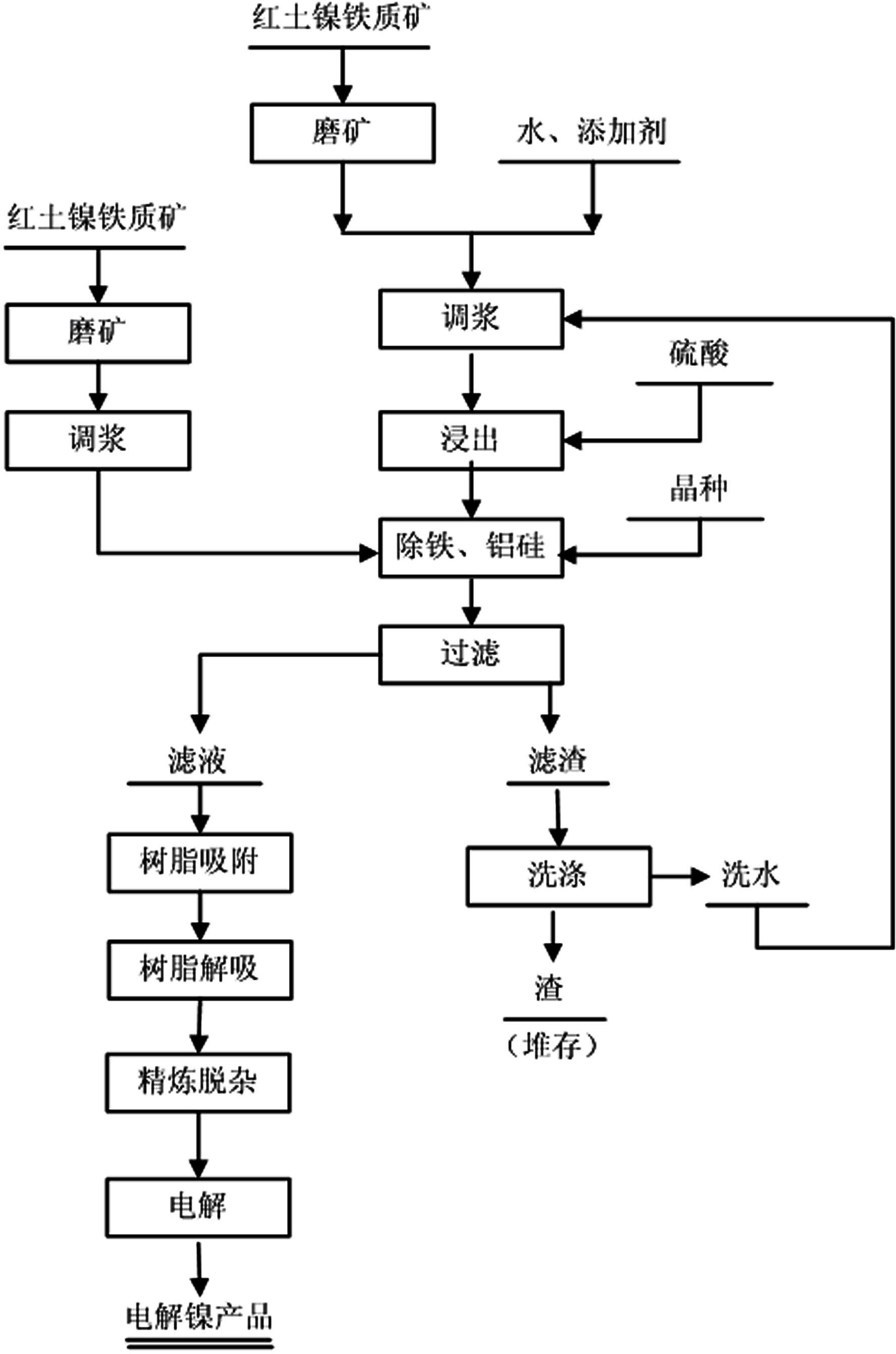
InactiveCN102286661AFully oxidizedEasy to leachPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisIon exchange
A method for directly electrolyzing laterite nickel ore with sulfuric acid leaching, the invention relates to a method for leaching low-grade laterite nickel ore with sulfuric acid at normal pressure, and belongs to the technical field of hydrometallurgy. The steps of the method are: separately grinding and pulping the iron ore and magnesia ore in the laterite nickel ore, leaching the iron ore with sulfuric acid under high acidity and high acid ore ratio, adding magnesia ore slurry to adjust the pH value to precipitate jarosite Alkaline neutralizer is added to the mother liquor to remove aluminum and silicon. The filtered leachate is used to absorb nickel ions with ion exchange resin. The electrolytic nickel product is produced by electrolysis, and the magnesium sulfate-containing solution after the ion exchange resin is added with calcium hydroxide to precipitate, and the magnesium and calcium are separated by carbonization to obtain magnesium carbonate. The present invention solves the disadvantages of long process flow, large amount of magnesium-containing wastewater and difficult treatment, and makes the magnesium open to become a product, and the wastewater can be directly discharged or reused, and at the same time, part of the recovered magnesium can be returned to the process for recycling. agent.
Owner:YUNNAN TIN GROUP HLDG
Nickel-phosphorus chemical precipitation plating layer of aluminium alloy
InactiveCN101638778AExtend your lifeImprove performanceLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSodium acetateGram
The invention relates to a nickel-phosphorus chemical precipitation plating layer of an aluminium alloy, mainly containing the following components in content by weight: 20-30 grams / litre of hexahydrated nickel sulphate, 20-30 grams / litre of sodium hypophosphite, 15-20 grams / litre of sodium acetate, 6-10 grams / litre of butane diacid, 30-50 grams / litre of complexing agents, 20-60 PPM of stabilizingagent and 30-100 PPM of plating midbodies. The nickel-phosphorus chemical precipitation plating layer has the advantages of fast precipitation, well combining force of a plating layer, brightness andcompactness of the plating layer, excellent stable property of tank liquor, long service life, easy maintenance, and the like.
Owner:郑建国 +1
Pumping rod or oil sucking pipe electroplating iron-nickel/tungsten alloy double-layer coating and surface processing technology
ActiveCN101042044ANot easy to miss platingImprove protectionDrilling rodsDrilling casingsCorrosion resistantCarbon dioxide
It relates to a surface treatment process. It uses oxide inert electrodes as the anode to apply ferro plating. It uses ferric persulfate, nickel sulfate dip, nickel carbonate, boracic acid and citrate as the main material, the electrodeposition coating mainly composed of FexNiy, with x=20-45, y=55-80, being amorphous nanocrystalline structure. The coating is the bottom layer, then tungsten alloy to get the final dual layer plating surface treatment. The plating layer is corrosion resistant, with hardness of 480-950Hv, with extensive application.
Owner:湖南纳菲尔新材料科技股份有限公司
Diamond grinding wheel for cutting silicon crystal circle and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101633158AHigh strengthImprove rigidityGrinding devicesGrinding machinesNumerical controlCobalt sulphate
The invention discloses a diamond grinding wheel for cutting a silicon crystal circle and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preprocessing an aluminum alloy basal body; (2) configuring electroforming liquid: configuring the electroforming liquid according to the weight ratio of (38-43):(15-20):(43-57):(50-180):(4-8) of nickel sulphate, cobalt sulphate, deionized water, a diamond grinding material and a suspending agent; fully stirring evenly and obtaining the electroforming liquid; (3) carrying out insulation processing on the aluminum alloy basal body obtained in the step (1), putting the aluminum alloy basal body into the electroforming liquid, electroforming in an ultrasonic field, evenly precipitating the diamond grinding material in the electroforming liquid and metal on the basal body together and obtaining a grinding wheel blank body with a compound electroforming layer; and (4) taking out the grinding wheel blank body completing electroforming, and carrying out accurate processing on the grinding wheel blank body on a numerical control grinder and a numerical control lathe respectively according to the accuracy requirements of the required basal body and the required cutting edge. The diamond grinding wheel obtained by the invention meets the ultrathin and superfine technical conditions and also has favorable strength and rigidity.
Owner:赛尔科技(如东)有限公司
Method for plating nickel on iron powder surface
InactiveCN101429652APlating volume controllableUniformity controllableLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingReduction treatmentFiltration
The invention discloses a method for plating a layer of metallic nickel or nanometer nickel powder onto the surface of iron powder through a hydrothermal reduction technology, which belongs to the technical field of non-ferrous metallurgy and powder metallurgical material. The method comprises the following steps: adding nickel sulfate or nickel sulfate aqueous solution, ammonia water and ammonia sulphate into water according to the certain proportion to prepare mixed solution; adding a small amount of anthraquinone and additive into the mixed solution; then adding the iron powder to be plated by nickel into the mixed solution, shifting the mixed solution containing the iron powder into an autoclave, and sealing the autoclave; carrying out the hydrogen reduction treatment through applying high temperature and pressure to the aqueous solution; forming the compact metallic nickel layer or nanometer nickel powder plating layer through the nickel ions reduced and precipitated onto the surface of the iron power in the solution; and when the plating reaction is completed, cooling down the materials in the autoclave, discharging the iron powder with the surface plated by metallic nickel and the aqueous solution, and obtaining the iron powder product with the surfaced plated by metallic nickel after filtration and drying. The method has a simple production method, easy operation and the controllable plated nickel layer.
Owner:张建玲
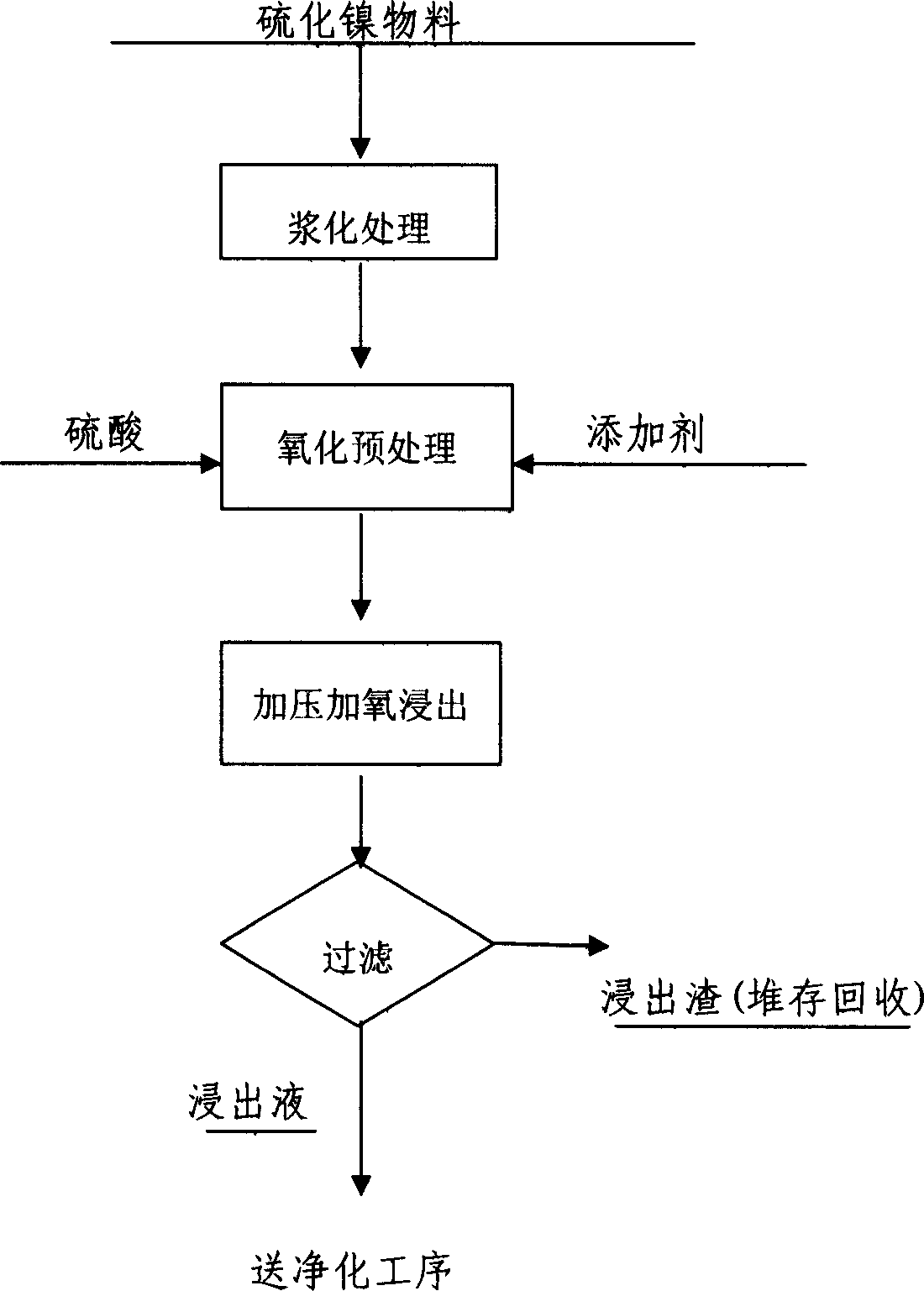
Wet treatment method of iron containing nickel sulfide material
The invention relates to a wet treatment method extracting nickel from iron containing nickel sulfide material. Its features are after slurring and oxidizing pretreatment to the iron containing nickel sulfide material; adopting pressurizing, adding oxygen, and additive method to effectively lixiviate nickel cobalt and restrain iron, reduce purifying deferrization reagent consumption and iron slag, reduce nickel losing, use sodium hydroxide to sink nickel after leaching solution, use sulphuric acid to dissolve nickel hydroxides, and gaining bright nickel sulphate solution after extracting and reclaiming cobalt. The nickel sulfate solution is produced out nickel sulfate by condensing crystallizing, or electricity nickel products by electro deposit, and both of them are according with GB.
Owner:云锡元江镍业有限责任公司
Electroplating pretreatment method for acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) plastic surface
InactiveCN102409320ASimple processEasy to operateLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPretreatment methodSodium phosphates
The invention relates to an electroplating pretreatment method for an acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) plastic surface. The electroplating pretreatment method comprises the following process steps of: eliminating stress, performing alkali washing for oil removal, pickling, roughening, performing neutralizing treatment, performing chemical activation, and performing the conventional electroplating, wherein in the chemical activation process, plastic base materials are put in to an activation solution and are subjected to hyperthermic treatment in a water bath for a certain period of time, each liter of the activation solution comprises 10 to 12g of nickel sulfate, 20 to 25g of sodium hypophosphite and 5 to 8g of sodium citrate, the pH is 9 to 11, and the temperature is between 70 and 75 DEG C. In the invention, a novel method in which metal palladium activation is not used is provided, can be used for replacing a sodium borohydride and methanol activation process and contributes to environment friendliness; and on the basis of pretreatment, the plastic surface can be directly electroplated, so that the problems of complicated treating processes, high PdCl2 prices, high pollution possibility of a plating solution and the like are solved.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
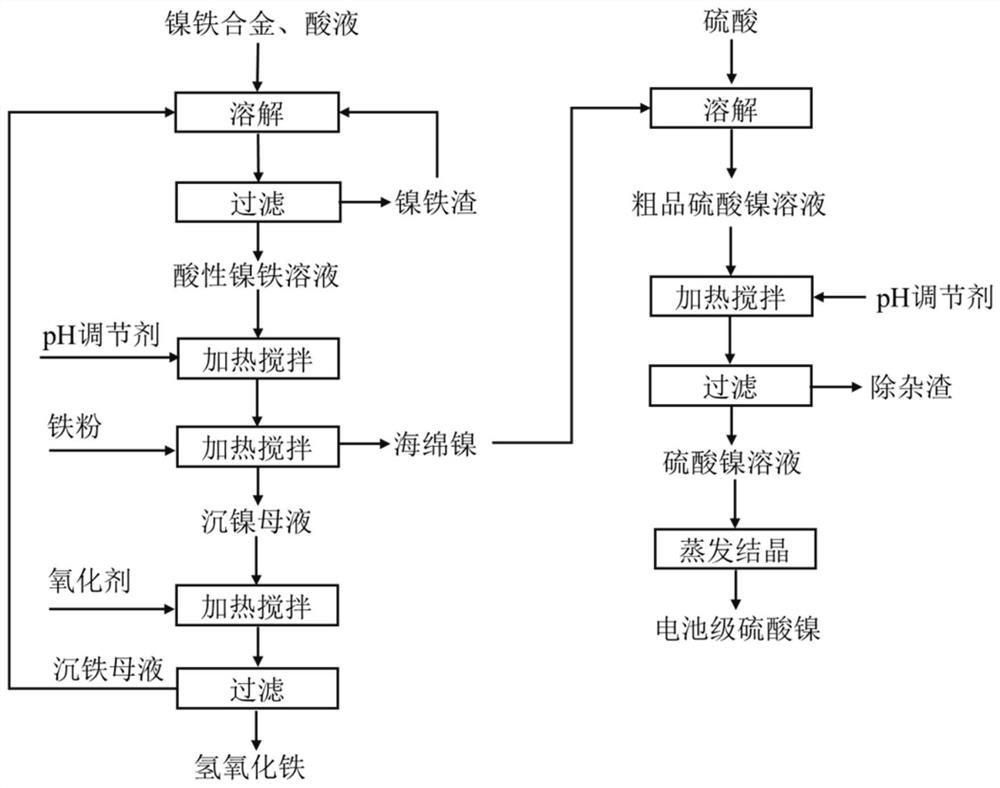
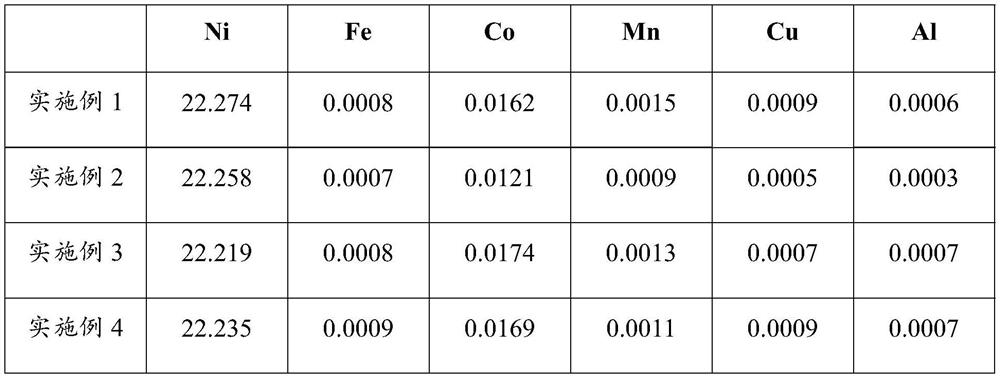
Method for separating nickel and iron from nickel-iron alloy and application
ActiveCN112941314AAchieve separationHas economic valueIron oxides/hydroxidesNickel sulfatesFerric hydroxideIron powder
The invention belongs to the field of hydrometallurgy, and discloses a method for separating nickel and iron from a nickel-iron alloy and application. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving the nickel-iron alloy in an acid solution, filtering, and taking filtrate to obtain an acidic nickel-iron solution; adjusting the pH value of the acidic nickel-iron solution, heating, stirring, adding iron powder, and continuously heating and stirring to obtain sponge nickel and nickel precipitation mother liquor; enabling the nickel precipitation mother liquor to be subjected to oxidation iron precipitation to obtain ferric hydroxide slag and iron precipitation mother liquor; and dissolving sponge nickel into sulfuric acid, filtering, collecting filtrate, heating, and adjusting the pH value to obtain a nickel sulfate solution; According to the method, after the nickel-iron alloy is dissolved by using the acid liquor, nickel in the solution is replaced by iron powder to obtain sponge nickel, the nickel precipitation mother liquor is oxidized to generate ferric hydroxide, the nickel content is lower than 0.4%, the iron precipitation mother liquor can be returned to a leaching section, and the sponge nickel is subjected to acid dissolution, impurity removal and evaporative crystallization to obtain a battery-grade nickel sulfate product.
Owner:HUNAN BRUNP RECYCLING TECH +2
Method for recycling nickel-cobalt-manganese-lithium from waste power lithium ion battery black powder
ActiveCN111519031AHigh recovery rateImprove recycling ratesWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingLithium carbonateManganese
The invention discloses a method for recycling nickel-cobalt-manganese-lithium from waste power lithium ion battery black powder. The method comprises the steps of conducting leaching and filtering through a sulfuric acid and sulfur dioxide system, adding lime milk into filtrate, adjusting the pH to 10-12, controlling precipitation, and conducting filtering to obtain a nickel-cobalt-manganese enriched product and lithium-containing filtrate; conducting purifying and impurity removal on the lithium-containing filtrate, adding a sodium carbonate solution for precipitation of lithium to obtain lithium carbonate; leaching the nickel-cobalt-manganese enriched product through sulfuric acid, adjusting the pH to 4-6, removing impurity iron and aluminum, and conducting solid-liquid separation to obtain purified slag and purified liquid; and adjusting the pH of the purified liquid to 4-5, conducting manganese extraction with P204 as an extraction agent, conducting cobalt extraction with P507 asan extraction agent, and conducting nickel extraction with P507 as an extraction agent. Through the method provided by the invention, the lithium recovery rate is greatly increased; moreover, sodium hydroxide generated from precipitation of lithium can be returned and continuously used in the lime milk nickel-cobalt-manganese enrichment process; and meanwhile, the yield of nickel sulfate, cobalt sulfate and manganese carbonate is increased.
Owner:XUZHOU GUOMAO VALUABLE & RARE METAL COMPREHENSIVE UTILIZATION INST
Method for preparing nickel sulfate solution and battery grade ferric phosphate from nickel-containing pig iron
ActiveCN106829907AImprove use valueReduce processing costsNickel compounds preparationNickel sulfatesSulfatePhosphate
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nickel sulfate solution and battery grade ferric phosphate from nickel-containing pig iron. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out raw materials pretreatment, acid leaching treatment, sedimentation treatment, ferric phosphate drying treatment, nickel-containing filtrate extraction treatment and reverse extraction to obtain the nickel sulfate solution. The method for preparing the nickel sulfate solution and the battery grade ferric phosphate from the nickel-containing pig iron has the characteristics of simpleness in technology, high recovery rate of the nickel-containing pig iron, low cost and good performance of a product.
Owner:GUANGDONG JIANA ENERGY TECH CO LTD +1
Graphene oxide nickel-phosphorus composite plating solution, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN104862676AImprove responseReduce energy consumptionLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSodium acetateReduction treatment
The present invention discloses a graphene oxide nickel-phosphorus composite plating solution, a preparation method and applications thereof, wherein per liter of the graphene oxide nickel-phosphorus composite plating solution comprises 0.5-1 g of graphene oxide being subjected to reduction treatment, 25-40 g of nickel sulfate, 15-20 g of sodium hypophosphite, 15 g of sodium acetate, 8-10 g of citric acid, 4 ml of lactic acid, 41 mg of a composite stabilizer, and the balance of distilled water. The preparation method comprises preparation of the graphene oxide being subjected to reduction treatment and preparation of the graphene oxide nickel-phosphorus composite plating solution. According to the present invention, the obtained graphene oxide nickel-phosphorus composite plating solution can perform plating on iron and steel at a low temperature of 50-70 DEG C, and the obtained graphene oxide nickel-phosphorus composite plating layer thickness is uniform and the surface is smooth and does not have gap; and the preparation method is simple, and the continuous production can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Preparation method of porous nickel oxide/tin dioxide micro/nano spheres
InactiveCN102680539AHigh purity powderPorous pore size distribution is uniformMaterial resistanceTin dioxideMicro nano
The invention discloses a preparation method of porous nickel oxide / tin dioxide micro / nano spheres, which comprises the following steps: stirring tin tetrachloride pentahydrate, nickel sulfate hexahydrate, sodium hydroxide and ammonia water which are used as raw materials, heating, separating, washing, drying and the like to obtain micro / nano spherical hydroxy nickel stannate; and roasting a micro / nano spherical NiSn(OH)6 precursor at high temperature, and cooling to respectively obtain porous micro / nano spherical NiO / SnO2 powder. The micro / nano spherical NiO / SnO2 product prepared by the method disclosed by the invention is light green powder, and has the advantages of large specific area and good product quality. The impedance gas sensing element prepared from the micro / nano spherical NiO / SnO2 powder has high sensitivity, and the sensitivity S value for 100ppm methylbenzene and formaldehyde gases is respectively up to 19.8 and 27.6.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
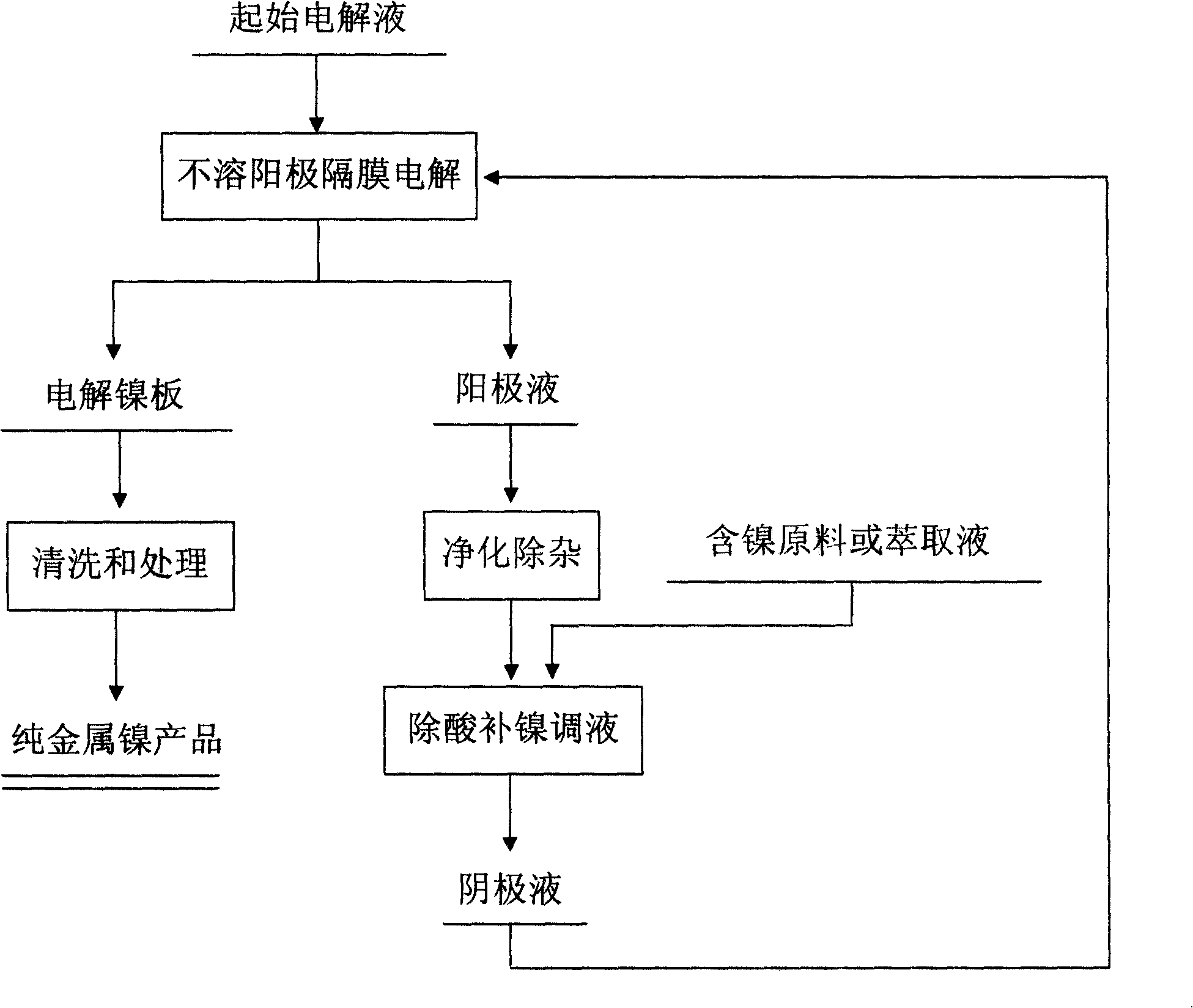
Method for producing electrolytic nickel using various nickel-containing raw material
InactiveCN101265589AAchieve balanceWide variety of sourcesPhotography auxillary processesSolventNickel ions
A method using various raw materials containing nickel to prepare electrolytic nickel is provided. The materials containing nickel obtained from various nickel smelting and nickel renewable resource recovery processes are taken as the raw materials, sulfate system electrolyte solution is adopted, pure metallic nickel is prepared by the method of insoluble anode diaphragm electrolysis; the acidity of the anolyte is adjusted by the direct neutralization method or the solvent extraction method in the electrolytic process, nickel ion is supplied, acid concentration is lowered, thereby changing into eligible catholyte, returning to the electrolytic process realizes the balance of nickel ion and acid concentration in the whole electrolytic process; the electrolyte system adopts falcial sulphate liquor, nickel sulphate, sodium sulphate, and boric acid are prepared into the catholyte which mainly contains: boric acid 1-25g / L, sodium sulphate70-150g / L, and nickel sulphate 50-120g / L, vitriol is added to adjust the pH value to about 2.0-2.5; the acidity of the anolyte is adjusted by the direct neutralization method or the solvent extraction method.
Owner:张建玲
Graphene-nickel-phosphorus chemical plating liquid, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103556136AGood wear resistance of substrateImprove wear resistanceLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSodium acetatePhosphorous acid
The invention discloses a graphene-nickel-phosphorus chemical plating liquid, and a preparation method and an application thereof. Each liter of the graphene-nickel-phosphorus chemical plating liquid comprises 0.25-1g of graphene, 20-25g of nickel sulfate, 15-20g of sodium hypophosphate, 15g of sodium acetate, 8-10g of citric acid, 4ml of lactic acid, 4ml of propionic acid, 41mg of a composite stabilizer, and the balance distilled water; and the composite stabilizer is composed of thiourea, potassium iodate and potassium iodide, and a mass ratio of thiourea to potassium iodate to potassium iodide is 1:20:20. The preparation method of the chemical plating liquid comprises the following steps: sequentially adding graphene, nickel sulfate, sodium hypophosphate, sodium acetate, citric acid, lactic acid, propionic acid and the composite stabilizer into distilled water for dissolving, and adjusting the pH value of the obtained solution to 4.2-5.6 to obtain the graphene-nickel-phosphorus chemical plating liquid. The graphene-nickel-phosphorus chemical plating liquid can be used for plating the surface of a steel alloy workpiece to form a nickel-phosphorus-graphene chemical composite coating having a good wear resistance and a high hardness.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Method of removing impurities out of nickel chloride leachate
The invention discloses a method of removing impurities out of nickel chloride leachate. The method comprises the following steps: in a sequence of extracting metals by using an extraction agent p-507, adding sulfonated kerosene serving as a diluent into p-507; then, sequentially reacting with a NaOH solution and a nickel chloride solution or a nickel sulfate solution; after reaction, carrying out phase separation; and finally, obtaining the extraction agent with the organic nickel load being 14.09-14.43g / L. According to the method disclosed by the invention, p-507 is converted into the extraction agent with the organic nickel load being 14.09-14.43g / L. The extraction agent can further separate impurities such as cobalt, copper, zinc, manganese, calcium and magnesium from the nickel chloride leachate. The nickel chloride extracted by the extraction agent satisfies the production requirements of electroplating-grade nickel chloride products. The method disclosed by the invention is simple, reliable and strongly operable in process and has good removal effect on impurities such as cobalt, copper, zinc, manganese, calcium and magnesium, does not introduce other impurities, expands a novel process of producing electroplating-grade nickel chloride products by nickel cobalt hydroxide raw materials, and has a good economic value.
Owner:金川集团镍盐有限公司
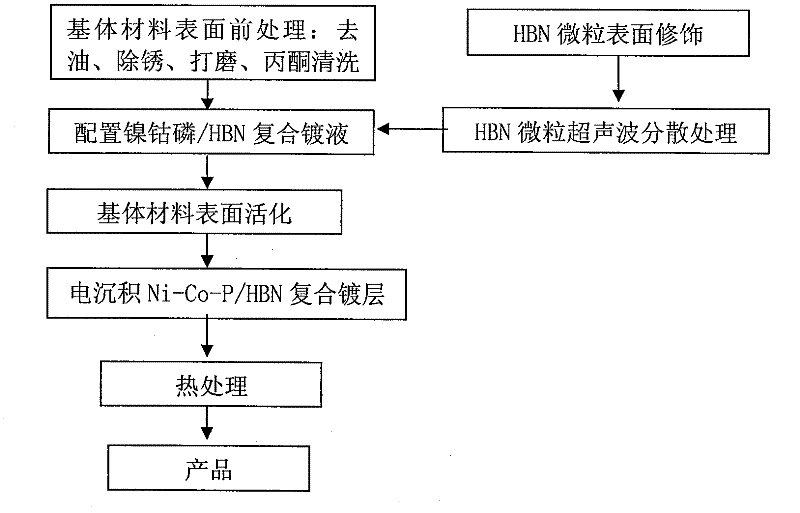
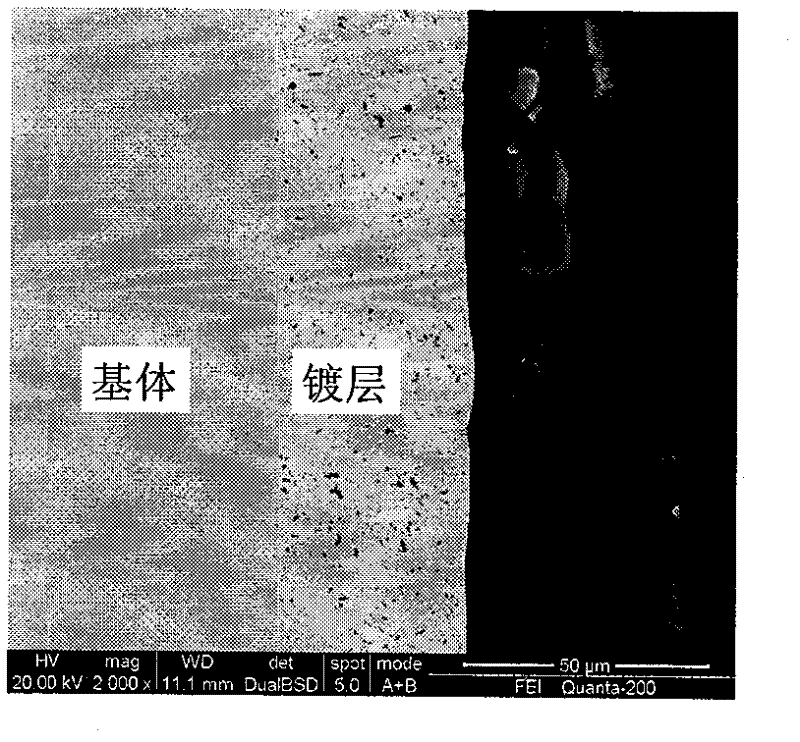
Pulse-electrodeposited Ni-Co-P/HBN composite plating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102534732AImprove electrodeposition efficiencyEasy to useElectrolytic coatingsPolyvinyl alcoholHexagonal boron nitride
A pulse-electrodeposited Ni-Co-P / HBN composite plating and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method adopts a metal material as a substrate, and comprises the following steps: firstly pretreating the substrate surface, preparing a composite plating solution with nickel sulfate, cobalt chloride, sodium hypophosphite, citric acid, trisodium citrate, boric acid, and polyvinyl alcohol as main components and hexagonal boron nitride HBN powder as a dispersed phase, performing surface modification and dispersion treatment of the HBN particles by using a surfactant through ultrasonic vibration, allowing the HBN particles to disperse uniformly in the plating solution through reasonable setting of pulse electrodeposition parameters and full stirring, performing codeposition and heat treatment of the HBN particles and the substrate metal nickel cobalt phosphor in a state of applying pulsed current so as to obtain a corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant and antifriction pulse-electrodeposited Ni-Co-P / HBN composite plating. The invention overcomes defects of single component of current composite plating, coarse plating crystal grain, low interface bonding strength with the substrate, non-ideal comprehensive properties of corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and antifriction, and the like; the pulse-electrodeposited Ni-Co-P / HBN composite plating of the invention is applicable to wear-resistant, antifriction and corrosion-resistant surface plating of friction kinematic pair parts in industries of machinery, metallurgy, chemical engineering, and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for recycling precious metals from stainless steel acid pickling sludge
InactiveCN103695655AIncrease added valueRealize economic valueProcess efficiency improvementCopper sulfateMaterials science
The invention provides a method for recycling precious metals from stainless steel acid pickling sludge, belonging to the field of non-ferrous metallurgy and waste utilization. The method mainly comprises the following steps: 1) thickening and filter pressing; 2) leaching; 3) iron removal and filter pressing; 4) P204 extraction: filtering and clarifying the mother liquid and feeding into a P204 extraction box; performing continuous saponification and counter-current extraction, and separating out an organic phase A and a filtrate A; extracting to remove impurity elements such as Zn, Cu, Mn, Ca and the like; 5) P507 extraction: feeding the filtrate A separated by the step 4) into a P507 extraction box, performing continuous saponification and counter-current extraction in the extraction box at room temperature, and separating out an organic phase B and a filtrate B; performing reverse extraction of the organic phase B by use of dilute hydrochloric acid to obtain a high-purity cobalt chloride solution, and enriching nickel in the filtrate B by use of dilute sulphuric acid to obtain a high-purity high-concentration nickel sulfate solution. The method provided by the invention finally obtains products such as copper sulfate, nickel sulfate, high-purity nickel, cobalt oxalate and the like, realizes resource recycling of precious metals in sludge, and has the comprehensive benefits of economic benefits, environmental benefits and social benefits.
Owner:王洪
Electroplating sludge resource recovery process
InactiveCN102786192AGood effectAvoid influenceSludge treatmentWaste water treatment from metallurgical processZinc hydroxideSludge
The invention discloses an electroplating sludge resource recovery process. After acid solution, purification, copper precipitation and purification, dezincification and nickel precipitation, Cu(OH)2, Zn(OH)2 and Ni(OH)2 are obtained. The application range of the zinc hydroxide and the nickel hydroxide produced by the process technology disclosed by the invention is wider, and therefore the electroplating sludge resource recovery process overcomes the defect that the application range of nickel sulfate is limited.
Owner:HENGFENG COUNTY YUANSHENG METAL RESOURCE RECYCLE
Rare earth-nickel-cobalt-boron multi-element alloy anticorrosion and wear-resistant plating, electroplating liquid and preparation method of electroplating liquid
The invention provides a rare earth-nickel-cobalt-boron multi-element alloy anticorrosion and wear-resistant plating, an electroplating liquid and a preparation method of the electroplating liquid. The plating is of an amorphous mingled nanocrystalline structure, and the microhardness of the plating is HV700-HV1300; and the plating comprises the following components by weight percent: 1wt%-40wt% of cobalt, 0.1wt%-1.5wt% of boron and the balance of nickel and trace rare earth. The electroplating liquid comprises the following components: 180-250g / L of nickel sulfate, 20-50g / L of cobalt sulfate, 30-60g / L of nickel chloride, 2-4g / L of dimethylamine-borane, 30-50g / L of boric acid, 0.001-2g / L of rare earth, 3-5g / L of sodium tartrate, 10-30g / L of sodium citrate or citric acid, and deionzied water which is added to achieve a metered / constant volume. The preparation method of the electroplating liquid comprises the following steps: dissolving nickel sulfate, cobalt sulfate, boric acid and nickel chloride with the deionized water and regulating the pH value; and adding sodium citrate or citric acid, sodium tartrate, rare earth and dimethylamine-borane for the constant volume and sufficiently stirring. The preparation method of electroplating liquid is simple to operate, is high in current efficiency and energy-saving and environmentally-friendly; and the plating is of the amorphous mingled nanocrystalline structure, and has bright, smooth and flaw-free appearance, extremely low porosity, high hardness and good anticorrosion and wear-resistant properties and comprehensive mechanical properties.
Owner:黄激扬
Method for producing nickel sulfate and cobaltous sulfate through purification of laterite nickel ore sulfuric acid leaching solution and silica gel chelate resin
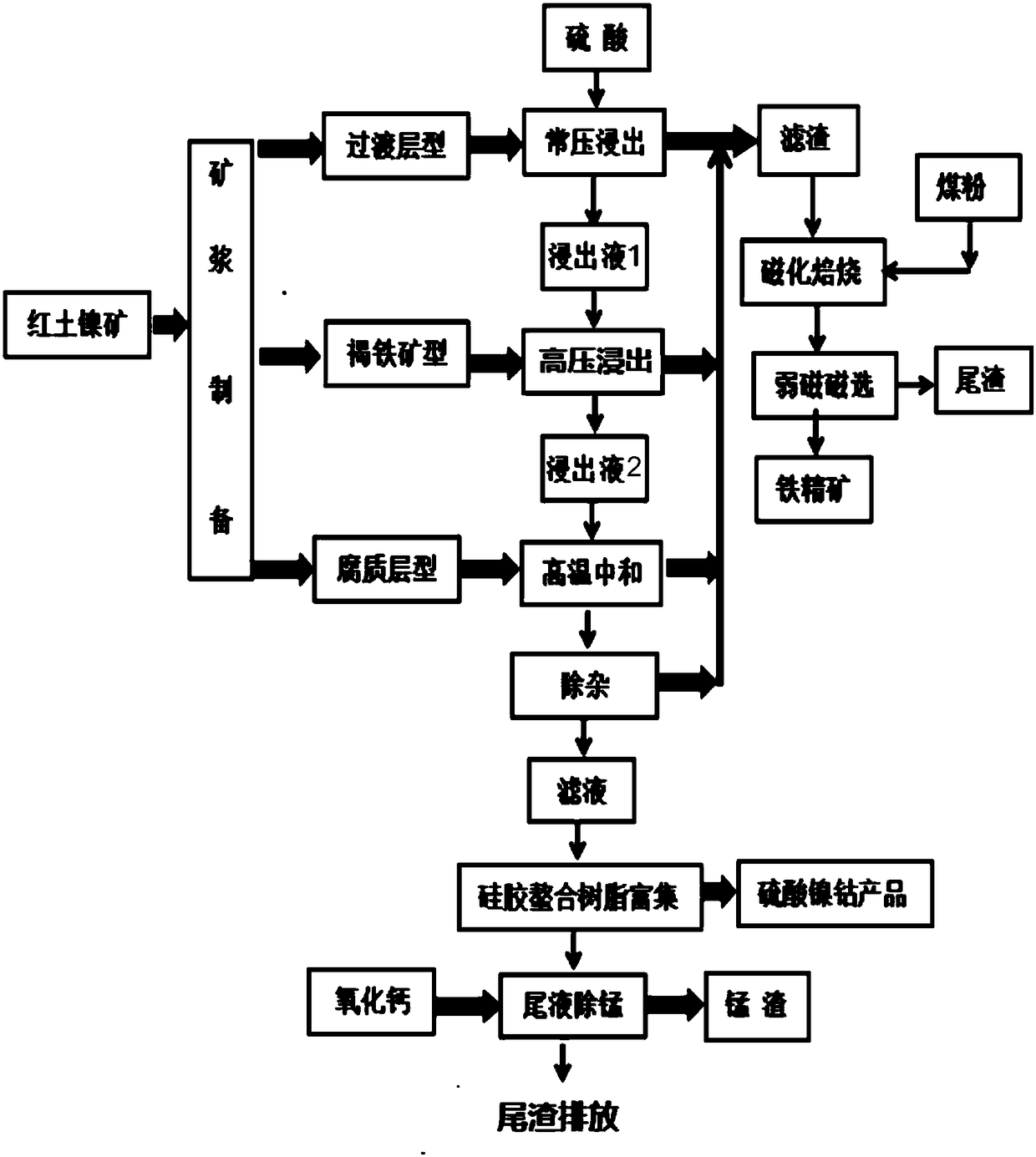
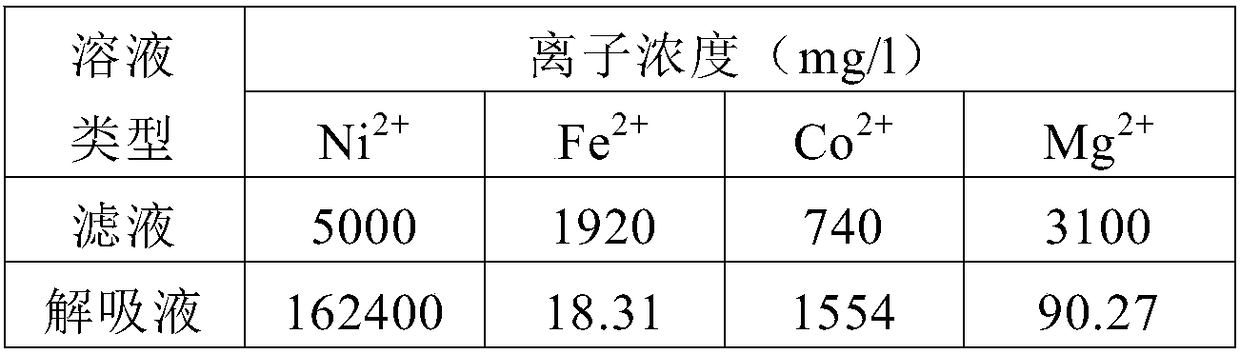
InactiveCN108396157ASolve the solid-liquid separation processReduce production and operation costsProcess efficiency improvementMagnetic separationManganeseSilica gel
The invention provides a method for producing nickel sulfate and cobaltous sulfate through purification of a laterite nickel ore sulfuric acid leaching solution and silica gel chelate resin. The method comprise the steps that (1), laterite nickel ores (the limonite type, transition layer type and detritus layer type) are subjected to ore grinding to -0.15 mm of ore powder accounting for 95% or above; (2), sulfuric acid and water are added into the transition layer type of laterite nickel ore after ore grinding for atmospheric pressure leaching to separate a leaching solution 1 from filter residues 1; (3), the limonite type of laterite nickel ore is placed into an autoclave, and sulfuric acid and water are added for high pressure leaching to separate a leaching solution 2 from filter residues 2; (4), the leaching solutions are added into the detritus layer of laterite nickel ore for neutralization impurity-removing leaching to separate a neutralization solution from filter residues 3; (5), hydrogen peroxide is added for reaction precipitation, and solid-liquid separation is conducted to separate a filtrate from filter residues 4; (6), the filtrate is subjected to silica gel chelateresin separation to produce nickel sulfate and cobaltous sulfate; (7), pulverized coal is added into the filter residues, magnetizing roast is conducted, then weak magnetic separation is conducted, and iron ore concentrate and tailings are separated; (8), manganese removing of a tail liquid is conducted; and (9), the tailings is discharged.
Owner:李宾
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com