Method for recycling precious metals from stainless steel acid pickling sludge
A pickling sludge and stainless steel technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve problems such as high energy consumption and operating costs, secondary air pollution, complex operation and management, etc., achieve low production costs, reduce pollution, and solve resource problems effect of shortage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
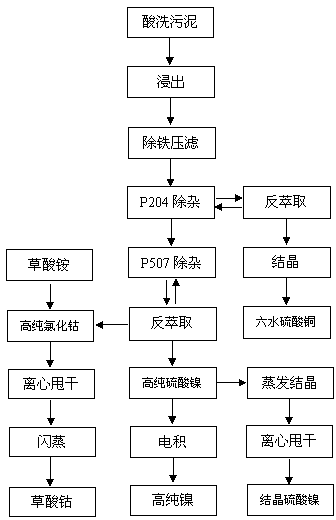
[0027] Raw materials: 5000kg of low-grade stainless steel sludge, of which Ni 0.8%, Co 0.03%, Cu0.5%, according to figure 1 Described processing step, concrete steps are as follows:
[0028] 1. First put the sludge into the central drive high-efficiency thickener for thickening, add flocculant polyacrylamide (PAM) accounting for 3‰ of the sludge weight into the thickener, and then pass through a 100m2 filter press to make the filter cake The moisture content is 11%.
[0029] 2. Add concentrated sulfuric acid with a mass concentration of 98% to the filter cake to make the pH value reach 1.6, keep the temperature at 90°C, stir evenly at a stirring speed of 80rpm for 4 hours, and then filter through a 100m2 filter press to separate the filtrate. Determine the iron content in the filtrate.
[0030] 3. The filtrate is adjusted with soda ash (or sodium bicarbonate) at room temperature, and when the pH of the filtrate is kept at 3.5, add hydrogen peroxide with a mass concentra...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Raw materials: 5000kg of low-grade stainless steel sludge, of which Ni 0.9%, Co 0.025%, Cu0.8%, according to figure 1 The process steps described.
[0038] 1. Put the sludge into a center-driven high-efficiency thickener for thickening. In the thickening project, add flocculant polyacrylamide (PAM) accounting for 3‰ of the sludge weight, and then pass through a 100m2 filter press to make the filter cake thicker. The moisture content is 9%.
[0039] 2. Add concentrated sulfuric acid with a mass concentration of 98% to make the pH value reach 1.5, keep the temperature at 80-100°C, stir evenly at a speed of 80rpm for 6 hours, and then filter through a 100m2 filter press to separate the filtrate. Determine and analyze the iron content in the filtrate.
[0040] 3. At room temperature, keep the pH of the filtrate at 3.2, add hydrogen peroxide with a mass concentration of 30% (the amount of hydrogen peroxide added is about 0.5-1% of the total weight of the filtrate) to ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Raw materials: 5000kg of low-grade stainless steel sludge, of which Ni 0.6%, Co 0.05%, Cu0.5%, according to figure 1 The process steps described.
[0047] 1. First put the sludge into the thickener for thickening. In the thickening project, add flocculant polyacrylamide (PAM) accounting for 3‰ of the sludge weight, and then filter through a 100m2 filter press to make the moisture content of the filter cake 12%. .
[0048] 2. Add sulfuric acid with a mass concentration of 98% to make the pH value reach 1.5, keep the temperature at 80°C, stir evenly at a speed of 80rpm for 8 hours, and filter through a 100m2 filter press.
[0049] 3. At room temperature, keep the pH of the filtrate at 3.0 by adding hydrogen peroxide with a mass concentration of 30% (the amount of hydrogen peroxide added is about 0.5-1% of the total weight of the filtrate) to oxidize the Fe element, and then add sodium carbonate to make the solution The pH value is maintained at 3.0. At this time, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com