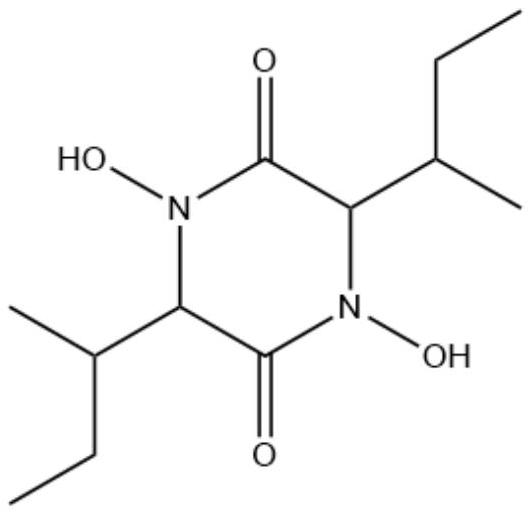
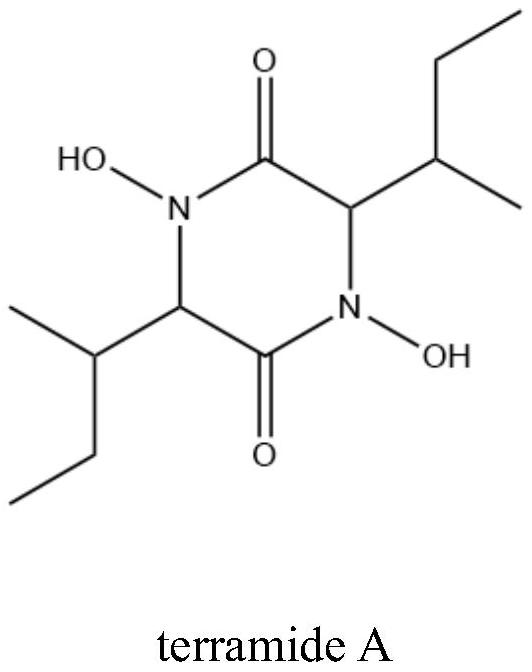
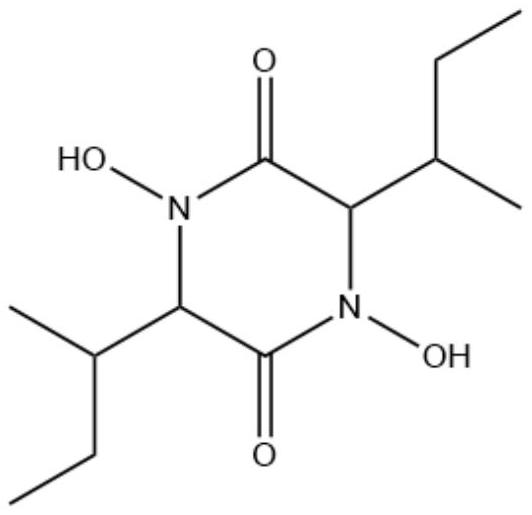
Marine-derived Aspergillus terreus M7 with antibacterial effect, and separation and application of secondary metabolite of Aspergillus terreus M7
A technology of Aspergillus terreus and Aspergillus genus, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of increasing antibiotic resistance and achieve the effect of simple operation and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1: Bacterial strain morphological identification and molecular biological identification
[0036] (1) Seed liquid preparation: Inoculate the glycerol tube of the strain M7 isolated from the sponge sample from the South China Sea stored in a -80°C ultra-low temperature refrigerator on a PDA plate, and culture at 28°C for 3 days. PDA plate (fungus medium: 5.0g potato powder; 20.0g glucose; 20.0g agar; sea crystal 33.0g; H 2 (1L; adjust the pH to 6.0) after the obvious hyphae grow out, add an appropriate amount of sterile water, wash the mycelium with a sterile inoculation loop, and inoculate the spore suspension into 200ml PDB liquid medium (fungus Medium: 10.0g potato powder; 20.0g glucose; 33.0g sea crystal; H 2 (0 1L; adjust pH to 6.0), 28°C, 200rpm, 3 days.
[0037] Morphological identification: Inoculate the seed liquid on the MEA plate with 2ul per point by the three-point method (20.0g maltose extract; 1.0g peptone; 20.0g glucose; 0.005g CuSO 4 .5H 2...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2: strain fermentation
[0047] (1) seed solution preparation: preparation method is the same as embodiment 1 (1)
[0048] (2) Small-batch fermentation: inoculate the seed liquid into rice solid medium, corn solid medium, and soybean solid medium according to the ratio of 1ml / 10g, and the culture time is 30 days; the culture conditions are light and dark respectively; the culture temperature Both are at 28°C. Set up two parallels for each group.
[0049] For small batches of fermentation products, soak overnight in 3 times the volume of ethanol, ultrasonically extract for 30 minutes the next day, and filter under reduced pressure to obtain the filtrate. Repeat this step three times. The obtained filtrates were combined, and the fermented extract was obtained by rotary steaming under reduced pressure, and 3 ml of methanol was added to dissolve the extract to obtain the fermented crude extract, which was used for antibacterial experiments.
[0050] The indi...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Embodiment 3: Separation and purification of target compound
[0054] (1) Dissolve the fermented extract in methanol, mix the sample with silica gel G (100-200 mesh), and then separate it with a silica gel G chromatography column, and gradually elute with dichloromethane-methanol, and the elution gradient is CH 2 Cl 2 、CH 2 Cl 2 -MeOH(80:1),CH 2 Cl 2 -MeOH(60:1),CH 2 Cl 2 -MeOH(40:1),CH 2 Cl 2 -MeOH(20:1),CH 2 Cl 2 -MeOH (10:1). Active components were screened with Acinetobacter baumannii as indicator bacteria. See 2(2) for active ingredient screening. The active fractions were combined for the next step of separation.
[0055] (2) The combined active components were dissolved in methanol and then introduced into a Sephadex LH-20 gel column for further purification. The sample after passing through the column was screened for active components with Acinetobacter baumannii as indicator bacteria. See 2(2) for active ingredient screening. The active fractio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com