Method for removing aluminum from ferrophosphorus slag after lithium extraction of waste lithium iron phosphate and preparation method of battery-grade iron phosphate
A technology of lithium iron phosphate and iron phosphorus slag, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of lengthy recovery process, low product purity, increased cost of impurity removal, etc., and achieve broad application prospects, The effect of high yield, good economic and social benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0064] The present invention also provides a method for preparing battery-grade iron phosphate, comprising the following steps:
[0065] The ferrophosphorus liquid is obtained according to the method for removing aluminum from the ferrophosphorus slag after extracting lithium from the above-mentioned waste lithium iron phosphate;
[0066] The ferrophosphorus liquid is mixed with an oxidizing agent and a pH regulator to generate an oxidation reaction.
[0067] In one embodiment, the oxidizing agent is selected from at least one of hydrogen peroxide, air, ozone or oxygen.
[0068] In one embodiment, the mass ratio of the oxidant to the ferrophosphorus slag after extracting lithium from the waste lithium iron phosphate is (0.3-0.9):1.
[0069] In one embodiment, the pH regulator is at least one selected from ammonia water, ammonium carbonate or ammonium bicarbonate.
[0070] In one embodiment, the parameters of the oxidation reaction include: the reaction temperature is 40°C-10...
Embodiment 1
[0078] Mix 400g of waste lithium iron phosphate with lithium-extracted phosphorus iron slag, 80g of iron powder, 2600g of pure water and 600g of 98% sulfuric acid to make slurry, and react at 80°C for 4.0 hours. After the reaction, Fe-containing 2+ 、Al 3+ 、PO 4 3- Acid slurry A.
[0079] Under the protection of carbon dioxide, 4 g of 2-pyridinecarboxylic acid was added to the slurry A, the reaction temperature was controlled at 100° C., and the reaction time was 2.0 hours. After the reaction was completed, the solid-liquid separation was carried out to obtain the ferrophosphorus solution after aluminum removal.
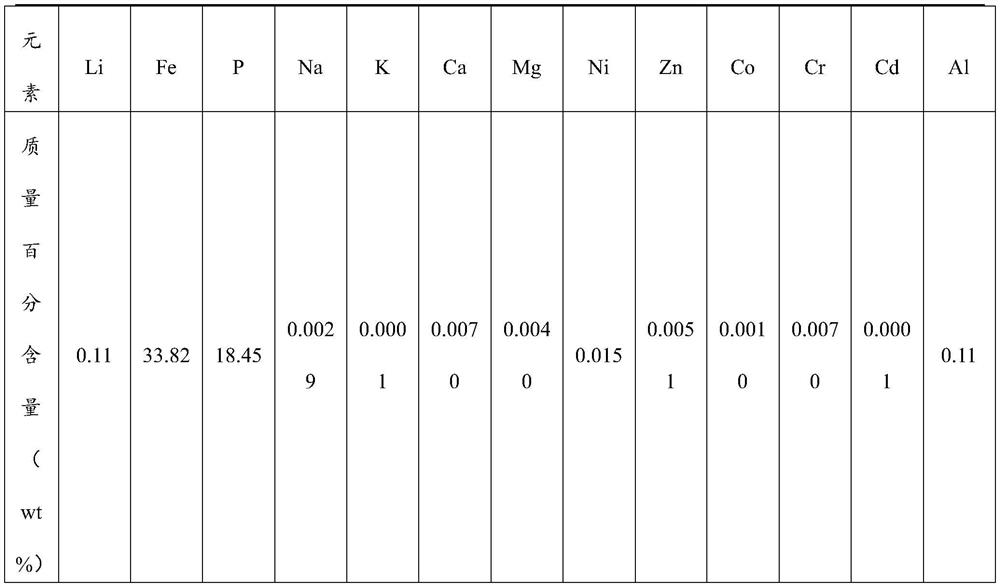
[0080] Ferrophosphorus solution was mixed with 400g of 30% hydrogen peroxide, adjusted to pH 1.8 with ammonia water, reacted at 100°C for 4 hours, separated from solid and liquid, and washed to obtain battery grade iron phosphate with a yield of 96.6%.
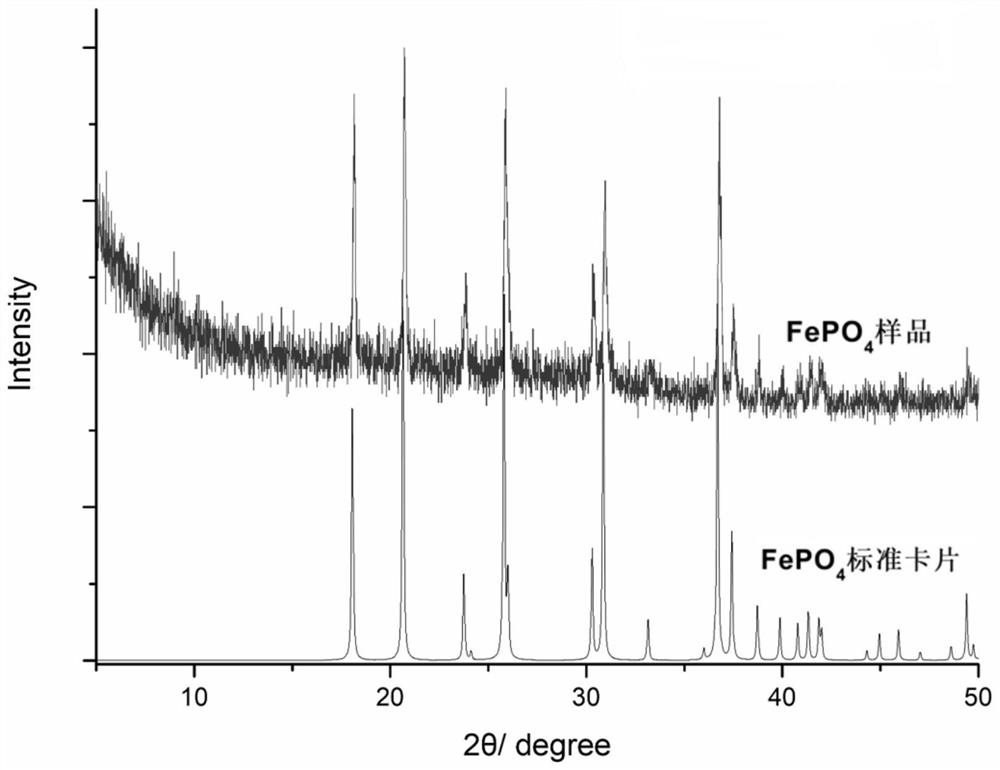
[0081] Carry out XRD test to the ferric phosphate that above-mentioned preparation obtains, obtain figure 1 Sho...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Mix 700g of waste lithium iron phosphate with phosphorus iron slag, 245g of iron powder, 8.4kg of pure water and 1050g of 85% phosphoric acid to make slurry, and react at 65°C for 5.0 hours. After the reaction is over, you can get Fe-containing 2+ 、Al 3+ 、PO 4 3- Acid slurry A.
[0085] Under the protection of nitrogen, 21g of isoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid was added to the slurry A, the reaction temperature was controlled at 80°C, and the reaction time was 3.0 hours. After the reaction, the solid and liquid were separated to obtain the phosphorus iron liquid after aluminum removal.
[0086] Introduce oxygen into the solution at a flow rate of 0.81L / min into the ferrophosphorus solution, and control the oxygen partial pressure of the solution to 1.2MPa through a pressure reducing valve, adjust the pH to 2.0 with ammonium carbonate, react at 60°C for 5 hours, and then separate the solid from the liquid , and washed to obtain battery-grade iron phosphate with a yield o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com