Treatment method for reducing and recycling jarosite slag
A treatment method, a technology of ferrite slag, which is applied in the field of hydrometallurgical comprehensive recovery, can solve problems such as difficult treatment, low utilization value of iron vanadium phase, stable structure and properties of zinc ferrite, etc., achieves mild conditions and broad industrial application prospects , Ease of industrial application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0101] The method of reducing and increasing the value of the jarosite slag produced by zinc smelting in this embodiment is carried out according to the following steps:
[0102] (1) Add 3 g of the jarosite residue into the solvent water and stir evenly, the mass ratio of the solvent water to the jarosite residue is 15:1-30:1;
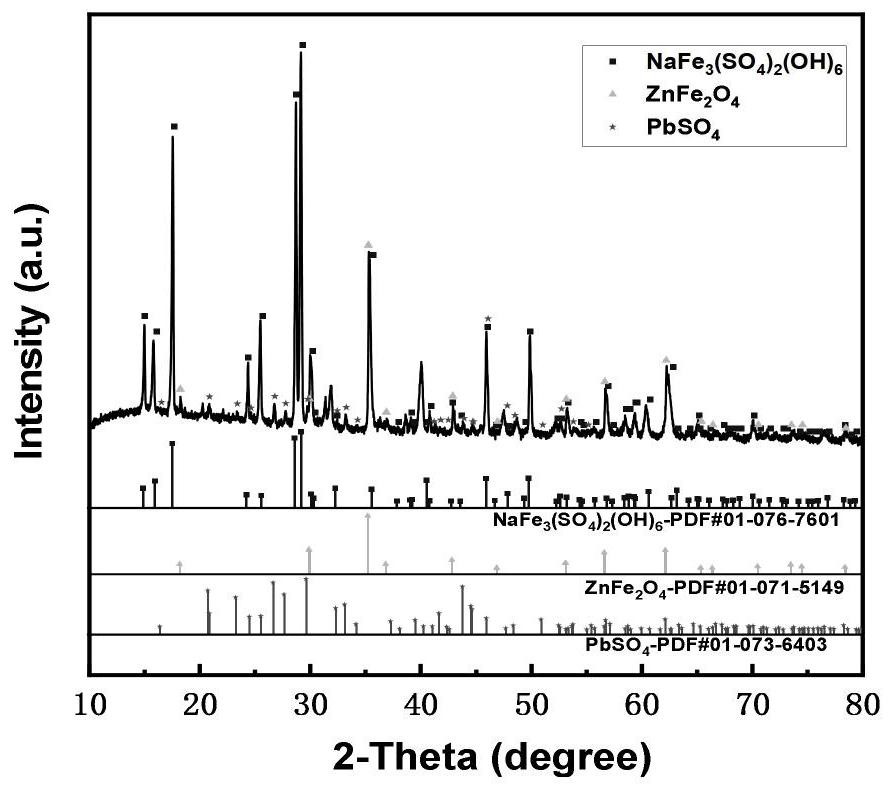
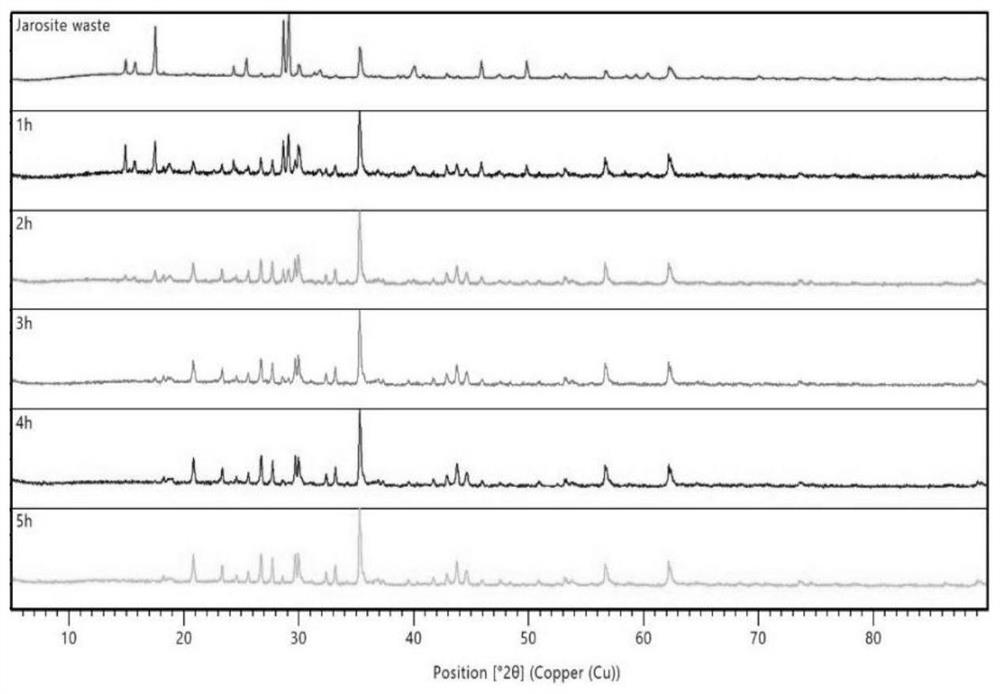
[0103] (2) Add the leaching agent oxalic acid into the jarosite residue-solvent system, the mass ratio of the extractant to the jarosite residue is 1:1, mix evenly, and carry out the water bath reaction at a stirring speed of 300rpm and 60°C, and the reaction time is 5h; the reaction process was sampled once per hour and carried out XRD measurement, the measurement results are shown in image 3 ; It shows that the iron-vanadium phase can be completely reacted in 2h.
[0104] (3) Centrifuge the reaction product obtained by reacting for 5 h in step (2). After centrifugation, leach residue and centrifugal supernatant can be obtained, and the leachate (ce...
Embodiment 2
[0106] Compared with Example 1, the only difference is that the reaction temperature of step (2) is 50°C. The reaction process was sampled once an hour and carried out XRD measurement, the measurement results are shown in Figure 7 . from Figure 7 It can be seen that the iron-vanadium phase can be completely reacted within 2 hours.
Embodiment 3
[0108] Compared with Example 1, the only difference is that the reaction temperature of step (2) is 40°C. The reaction process was sampled once an hour and carried out XRD measurement, the measurement results are shown in Figure 8 , It can be seen from the figure that the sodium ferrite phase disappears after 2h.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com