Clindamycin phosphate and quality control method
A technology for clindamycin phosphate and content, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, measuring devices, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., and can solve problems such as risks caused by clinical use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Example 1. Detection of Clindamycin Phosphate Impurities Using Mobile Phases with Different pH Values
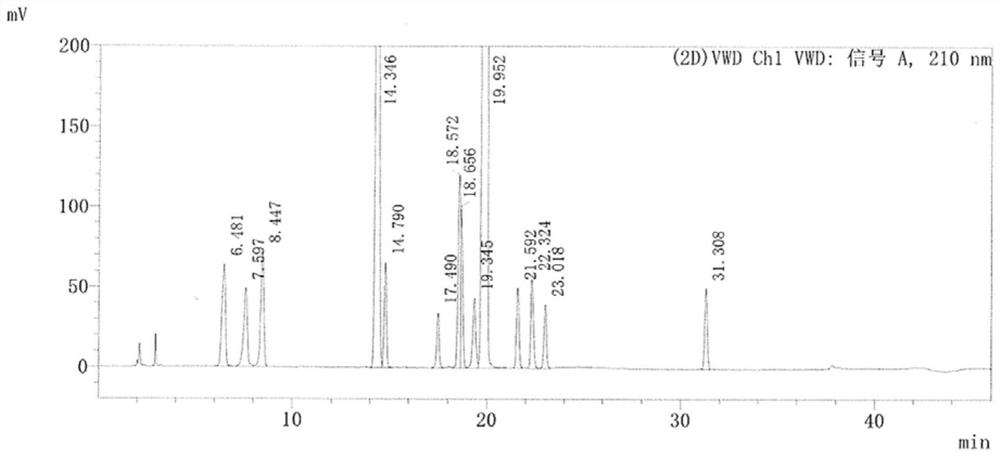
[0066] The detection method refers to USP43, but the pH value of its mobile phase is changed, and mobile phases with pH values of 3.9, 5.0, 5.8 and 6.0 are used respectively. The detection results are shown in Table 4 and Figure 1~4 shown.
[0067] Table 4. Test results
[0068]
[0069] Results: The flow of different pH values has a great influence on the separation of each component. When the pH is 6.0, the separation of all impurities can be guaranteed to meet the requirements, but under this pH condition, the impurity K does not peak within the running time.
Embodiment 2
[0070] Embodiment 2, the method for detecting clindamycin phosphate impurity A-L
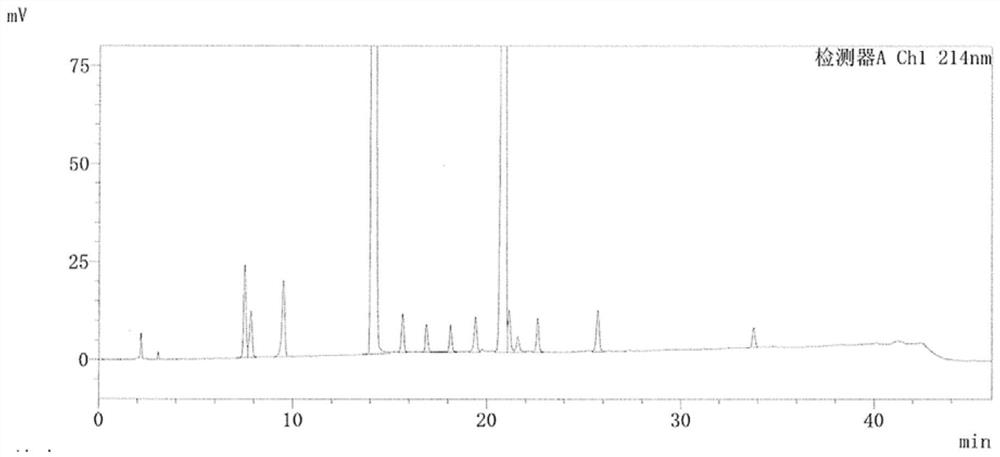
[0071] According to the results of Example 1, a method for detecting the clindamycin phosphate impurity was found, which can detect the clindamycin phosphate impurity A-L. The detection method refers to USP43, and the chromatographic conditions are changed as follows, and the detection results are as follows: Figure 5 shown.
[0072] Chromatographic conditions: use octadecylsilane bonded silica gel as filler (4.6mm×250mm, 5μm or a chromatographic column with equivalent performance); use phosphate buffer (pH6.0)-90% acetonitrile methanol solution (92:8) Be mobile phase A, be mobile phase B with phosphate buffer (pH6.0)-90% acetonitrile methanol solution (52:48); Carry out linear gradient elution as shown in Table 5 below; Flow rate is 1.2ml per minute; Column temperature is 40°C; the detection wavelength is 214nm; the injection volume is 20μl.
[0073] Table 5. Elution conditions
[0074] ...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Embodiment 3, the method for detecting clindamycin phosphate impurity A-P
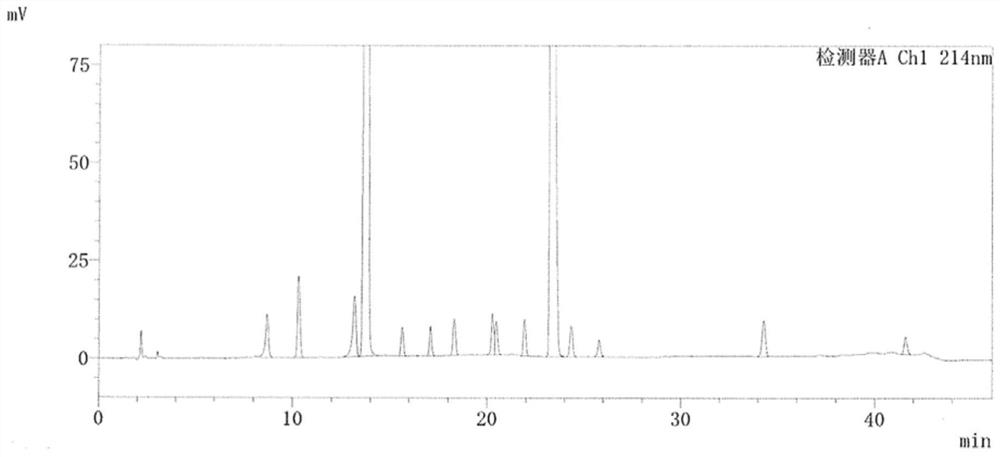
[0081] The mobile phase pH of the detection method described in Example 2 was adjusted to 5.96, the chromatographic column was replaced, and octylsilane bonded silica gel was used as a filler (Welch Ultimate XB-C8, 4.6mm×250mm, 5 μm), and the remaining chromatographic conditions and The detection method is the same as in Example 2. Detect impurity A-P, detection result is as table 7 and Figure 7 shown.
[0082] Table 7. Results of detection of impurities A-P
[0083]
[0084]
[0085] Using the above detection method, the minimum separation degree between impurities is 1.957, and impurities A-P can be effectively separated. It shows that the above detection method can effectively detect clindamycin phosphate impurity A-P at the same time.
[0086] The above-mentioned detection method formulates the detection standard of clindamycin phosphate as follows:
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com