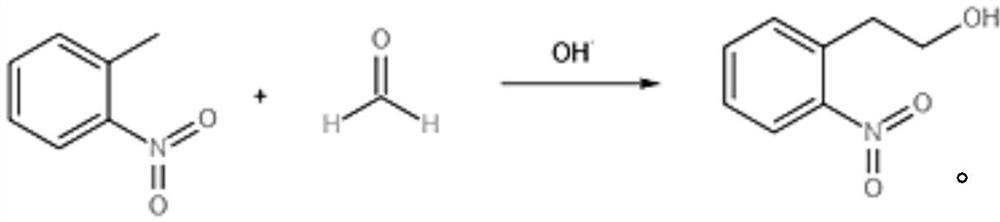
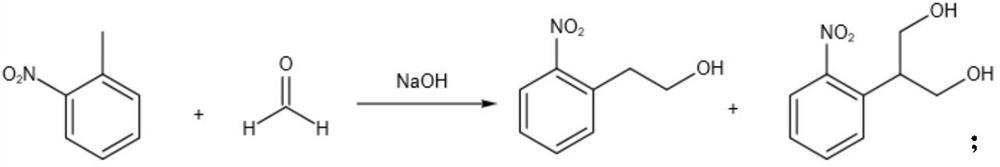
Method for continuously preparing 2-(2-nitrophenyl) ethanol
A nitrophenyl, continuous method technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, organic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as high energy consumption of rectification, reduced heat exchange efficiency, loss of catalytic effect, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] 2-nitrotoluene was dissolved in DMSO to prepare a solution with a mass concentration of 40%, and tetra-n-butylammonium hydroxide equivalent to 1% of the molar weight of 2-nitrotoluene was added, and the solution was defined as solution A;
[0038] Mix 80% formaldehyde aqueous solution with DMSO to prepare a formaldehyde solution with a mass concentration of 20%, which is defined as B;
[0039] Use a metering pump to pump the two streams of materials A and B into a tubular reactor made of stainless steel for continuous reaction. The tubular reactor is soaked in a constant temperature water bath at 45°C in advance, and the flow rate is controlled by two metering pumps to achieve material The molar ratio is 2-nitrotoluene: formaldehyde = 1:0.8, residence time = 45min. The reaction solution flowing out from the reactor directly flows into the excess NaHSO 4 Quench the powder in a large beaker. Collect the effluent for a period of time (such as 20 minutes), obtain the weig...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Adopt the method of embodiment 1, change the concentration of A, B two stock materials, other parameters are constant, investigate the impact of different concentrations on reaction result, specifically see table 1:
[0042] Table 1, the impact of different concentrations on the reaction results
[0043]
[0044] The result of table 1 shows: concentration too low or too high all have unfavorable influence to reaction, when concentration is too low, though can obtain higher selectivity, raw material conversion rate is relatively low; When concentration is too high, conversion rate increases, selectivity decreases.
[0045] Note: In the present invention, if there is no special instruction, the selectivity is calculated by gas chromatography peak area, and the calculation formula is: product peak area ÷ sum of product and disubstituted by-product area × 100%, and the yield is based on the converted 2-nitro Toluene meter.
Embodiment 3
[0047] Adopt the method of embodiment 1, adjust the flow velocity of two metering pumps, to change the molar ratio of A, B two stock materials, other parameters are constant, investigate the influence of different molar ratios on reaction result, the results are shown in Table 2:
[0048] Table 2: Effects of different molar ratios (2-nitrotoluene: formaldehyde) on the reaction results
[0049] The molar ratio of 2-nitrotoluene conversion rate selectivity yield 1:1 79.1% 86.2% 82.4% 1:0.9 82.3% 90.9% 84.3% 1:0.8 73.2% 98.1% 94.2% 1:0.7 65.8% 98.8% 94.9% 1:0.6 56.4% 99.1% 95.4% 1:0.5 47.5% 99.5% 96.1%
[0050] The results in Table 2 show that the reaction is unfavorable if the molar ratio between the two materials is too low or too high, and it is optimal when the molar ratio of the two materials is 1: (0.8-0.9).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com