Preparation method and application of modified starch polysaccharide derivative
A technology of starch polysaccharides and derivatives is applied in the field of starch processing, which can solve the problems that are not involved, and achieve the effects of improving performance and taste, excellent bonding performance, and white appearance and color.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0044] A method for preparing modified starch polysaccharide derivatives, comprising the following steps:
[0045](A) 35-45wt% starch, 5.0-12.0wt% of anti-gelling agent and a residual amount of water mixed to prepare a starch slurry, and then adjust the slurry pH with alkali to 7.5-10.5, add starch 0.005-0.02wt% of the mixed enzyme, the reaction, to obtain an enzyme-modified starch slurry.
[0046] Preferably, the starch is plantain taro starch, tapioca starch, sago starch, potato starch, corn starch and high-branched chain waxy corn starch in one or both kinds; If it is two starches, the mass ratio is 0.8-1.2:1. The gelling agent is sodium chloride, sodium sulfate and potassium citrate in one or more. The mixture of enzymes is a mixture of proteases and lipases with a mass ratio of 1:1-5, the viability unit of protease is 80000-100000U / g, the viability unit of lipase is 8000-10000U / g.
[0047] (B) The pH of the enzyme-modified starch slurry obtained with alkali regulation ste...
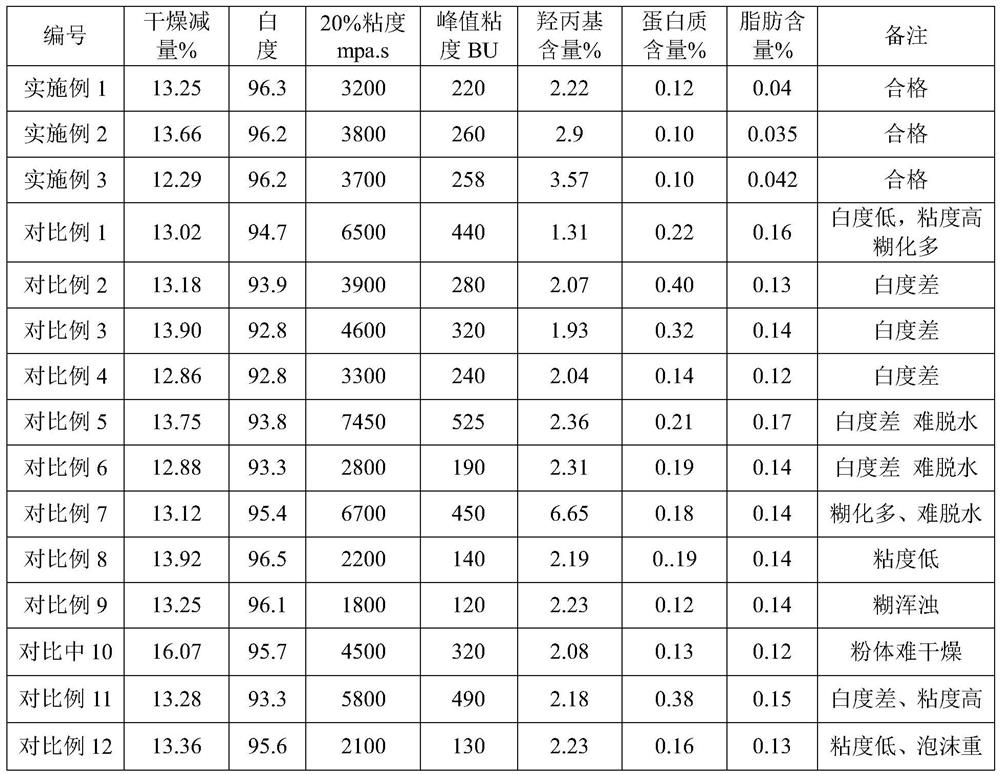
Embodiment 1
[0055] A, first dissolve 65g of sodium chloride in 1400g of deionized water, and then slowly add 1:1 tapioca starch and 1000g of plantain taro starch, formulated into a pulp, and then use 3.5% sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH value of the slurry to 8.5-8.7, add 1:2 mixed enzyme 0.08g (including protease activity unit 90000u / g, lipase vitality unit 8500u / g), control the pH value and react for 2h to complete.
[0056] B. Continue to adjust the pH of the starch slurry with 3.5% sodium hydroxide alkali to 10.8-11.0, and heat up to 28.5 °C, add 42g of propylene oxide, carry out a 20h hydroxypropyl etheration reaction, and then add 35g of sodium hypochlorite (content 10.0%) solution for 2h reaction, the process uses Braband to test the peak viscosity of 250-300BU.
[0057] C. After the completion of the reaction, 0.6g of OSA and 0.85g of sodium trimeta phosphate were added, and the synchronous esterification and crosslinking treatment were 2.5h, and the pH of the control syste...
Embodiment 2
[0060] A, first dissolve 90g of sodium sulfate in 1300g of deionized water, and then slowly add 1000g of high-branched glutinous corn starch, formulated into a pulp, and then use 3.0% sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH of the slurry to between 8.8-9.0, add 1:2 mixed enzyme 0.07g (of which protease activity unit 90000u / g, lipase activity unit 8500u / g), control the pH value and react for 2h to complete.
[0061]B. Continue to adjust the pH of the starch slurry with 3.0% sodium hydroxide alkali to 11.0-11.2, and heat up to 30 °C, add 55g of propylene oxide, carry out a 20h hydroxypropyl etherification reaction, and then add 22g of hydrogen peroxide (content 27.5%) of the solution, carry out a 1.5h reaction, the process uses Braband to test the peak viscosity of 220-350BU.
[0062] C. After the completion of the reaction, 0.5g of OSA and 0.95g of sodium trimeta phosphate were added, and the synchronous esterification and crosslinking treatment were 2.0h, and the pH of the cont...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| whiteness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com