Method for testing free carrier absorption loss and battery sample
A carrier absorption and free technology, which is applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of increasing the cost of testing methods, increasing the investment of testing costs, and complicated testing methods, so as to save investment in equipment costs, fast testing, and wide testing range. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0085] A method for testing free carrier absorption loss in this embodiment includes the following steps:
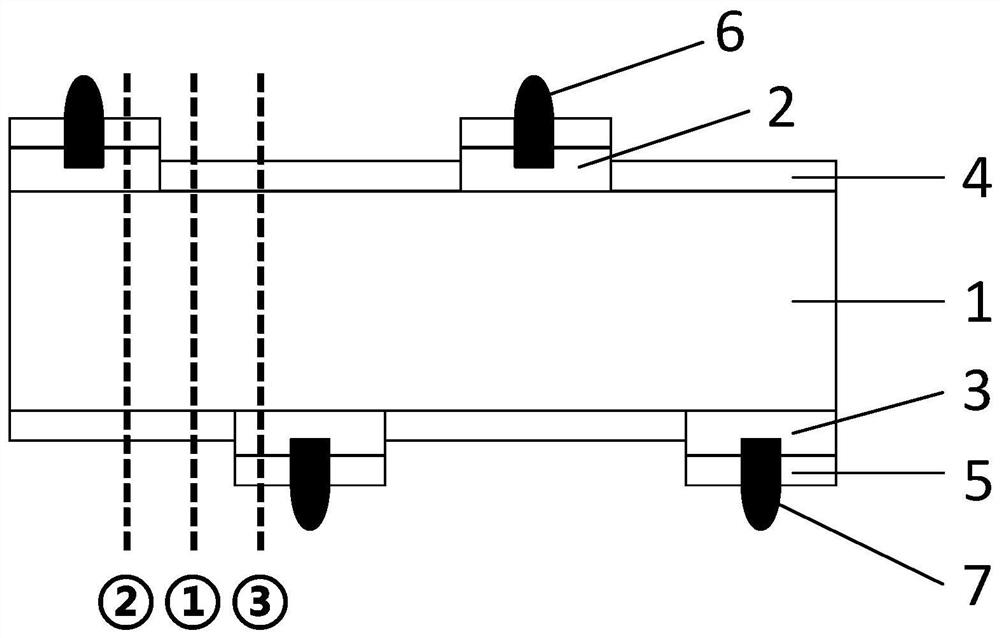
[0086] Step 1. Prepare battery samples of specific structure (see figure 1 ):
[0087] Step 11. Select silicon wafer 1 with N-type conductivity, resistivity of 7Ω·cm, and thickness of 160 μm, perform damage removal treatment on silicon wafer 1, texture, and then perform single-sided polishing on the rear surface of silicon wafer 1 , to obtain a silicon wafer 1 with a textured front surface and a polished rear surface.
[0088] Step 12 , respectively forming a front heavily doped layer and a rear heavily doped layer with opposite conductivity types on the front surface and the rear surface of the silicon wafer 1 . In actual operation, boron ion implantation is performed on the front surface of the silicon wafer 1 by means of ion implantation, and phosphorus ion implantation is performed on the rear surface of the silicon wafer 1, followed by annealing treatment to activ...
Embodiment 2
[0105] For a method for testing free carrier absorption loss in this embodiment, refer to Embodiment 1 for specific steps, and the difference from Embodiment 1 is as follows:
[0106] In step 11, the resistivity of the selected silicon wafer 1 is 5Ω·cm.
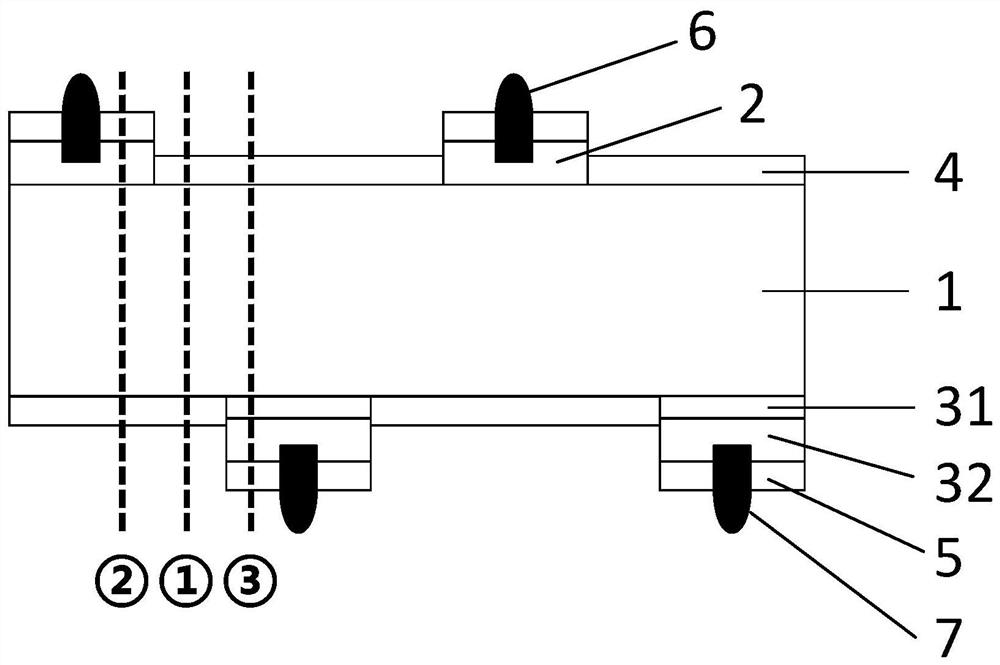
[0107] In step 12, see image 3 , the preparation process of the front heavily doped layer on the front surface of the silicon wafer 1 is the same as that in Example 1, and the rear surface of the silicon wafer 1 is changed to deposit an ultra-thin tunnel oxide layer 31 and an in-situ phosphorus-doped polysilicon layer ( Namely, the heavily doped polysilicon layer 32), therefore, after annealing, a passivation contact structure composed of the tunnel oxide layer 31 and the phosphorus-doped polysilicon layer is formed on the rear surface of the silicon wafer 1 as the rear heavily doped layer.
[0108] The square resistance of the front heavily doped layer (corresponding to the first heavily doped layer 2 ) in this embodiment ...
Embodiment 3
[0115] For a method for testing free carrier absorption loss in this embodiment, refer to Embodiment 1 for specific steps, and the difference from Embodiment 1 is as follows:
[0116] In step 11, the resistivity of the selected silicon wafer 1 is 5Ω·cm, and the conductivity type is P-type.
[0117] In step 12, see Figure 5 , the front surface of the silicon wafer 1 is implanted with phosphorus ions, so after annealing, a phosphorus-doped emitter is formed on the front surface of the silicon wafer 1, that is, the front heavily doped layer; and the rear surface of the silicon wafer 1 is not doped , so the rear heavily doped layer of Example 1 is omitted. The square resistance of the front heavily doped layer (corresponding to the first heavily doped layer 2) is 90-120Ω / sq, the junction depth is 0.4-0.6μm, and the peak concentration is 6.0-8.0E+19cm -3 .
[0118] In step 13, the locally disposed second heavily doped layer 3 and its preparation process are omitted, so the batt...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com