Engineering bacteria for producing 5-amino acetyl propionic acid and its constructing method
A technology of aminolevulinic acid, engineering bacteria, applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, genetic engineering, biochemical equipment and methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] The method for constructing an engineered strain for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0021] 1. Extraction of Genomic DNA of Agrobacterium radiata
[0022] 1) Place the overnight cultured bacterial solution in a 1.5ml centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 13,000×g for 1 min, and then remove the supernatant;
[0023] 2) After dissolving with 475μl TE buffer, add lysozyme to a final concentration of 100μg / ml, and keep it at 37°C for 20min;
[0024] 3) Add 10% (w / v) sodium dodecyl sulfonate (SDS) solution to a final concentration of 2% (w / v), and add 20 mg / ml proteinase K to a final concentration of 100 μg / ml. After mixing, Incubate at 37°C for 1h;
[0025] 4) Add 1 / 5 volume of 5mol / L NaCl and mix well, then add 1 / 5 volume of 2×hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), and keep it at 65°C for 30min;
[0026] 5) Add an equal volume of a mixture of phenol, chloroform and isoamyl alcohol, the volume ratio of phenol: chloroform: is...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The expression of 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase under the action of the inducer isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG)
[0048] 1) Cultivate the engineered bacteria BL21(DE3)pET28a-AR-hemA of the present invention in a 250ml shake flask containing 50ml of LB medium, first incubate at 37℃, 200rpm for 1.5h; then cool to 28℃, use 4μl1mol / L IPTG induction, after continuing to culture for 4h, take 30ml of bacterial solution and centrifuge at 8000×g for 10min to remove the supernatant;
[0049] 2) Resuspend in 3ml of 50mmol / L Tris·Cl (pH 7.5), sonicate the cells, and the conditions are 400w working for 5min, intermittent 5min, repeating 30 times, 13,000×g centrifugation for 10min;
[0050] 3) Take the supernatant for 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, the electrophoresis conditions are 200v, 500mA, and the time is 1h10min;
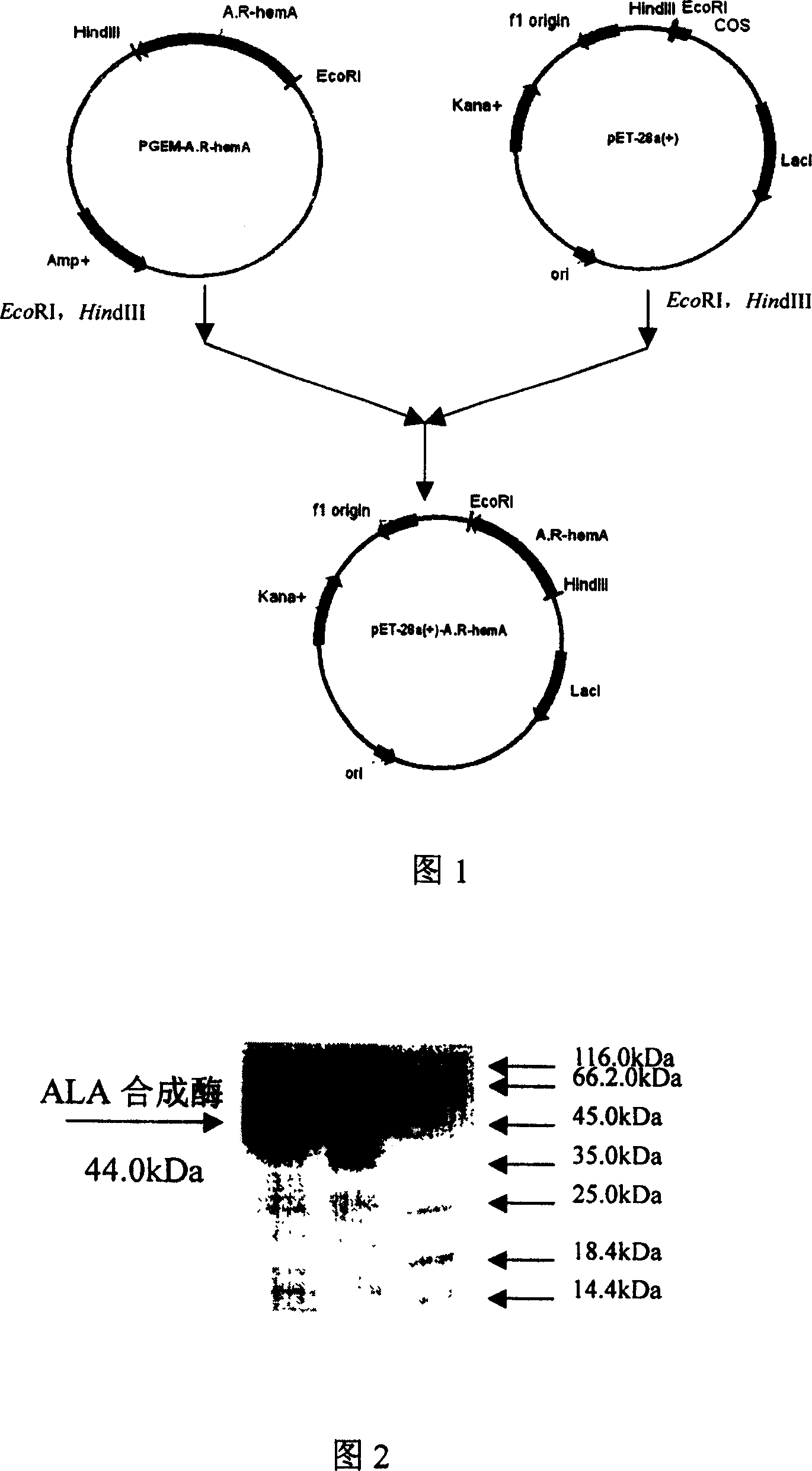
[0051] 4) According to the results of electrophoresis, there is an expression of 23.7% of the total protein at about 44.0kDa (see Figure 2). This si...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Determination of Specific Activity of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Synthase
[0054] 1) 500μl containing 50mmol / L Tris-HCl (pH7.5), 20mmol / L MgCl 2 , 0.1mol / L glycine, 0.1mmol / L pyridoxal phosphate, 0.2mmol / L succinate coenzyme A and the cell extract after rupture, react at 37℃ for 10min;
[0055] 2) Take 300μl of the above reaction solution and 150μl of 10% trichloroacetic acid, mix in a 1.5mL centrifuge tube, and centrifuge at 13,000×g for 5 minutes;
[0056] 3) Take 300μl of supernatant and mix 400μl of 1mol / L acetate buffer (pH 4.6) and 35μl of acetylacetone, and bath in boiling water for 15min;
[0057] 4) After cooling, add 700μl of newly prepared Ehrlich reagent (in a 50ml graduated cylinder, add 30ml of glacial acetic acid, 1g of p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, 5ml of 70% perchloric acid, 5ml of water, and dissolve it with Dilute with glacial acetic acid to 50ml), measure the absorbance at 554nm after 5min reaction, the concentration of ALA (mg / L)=26.35×OD 554 -0.09(R 2 =0.99...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com