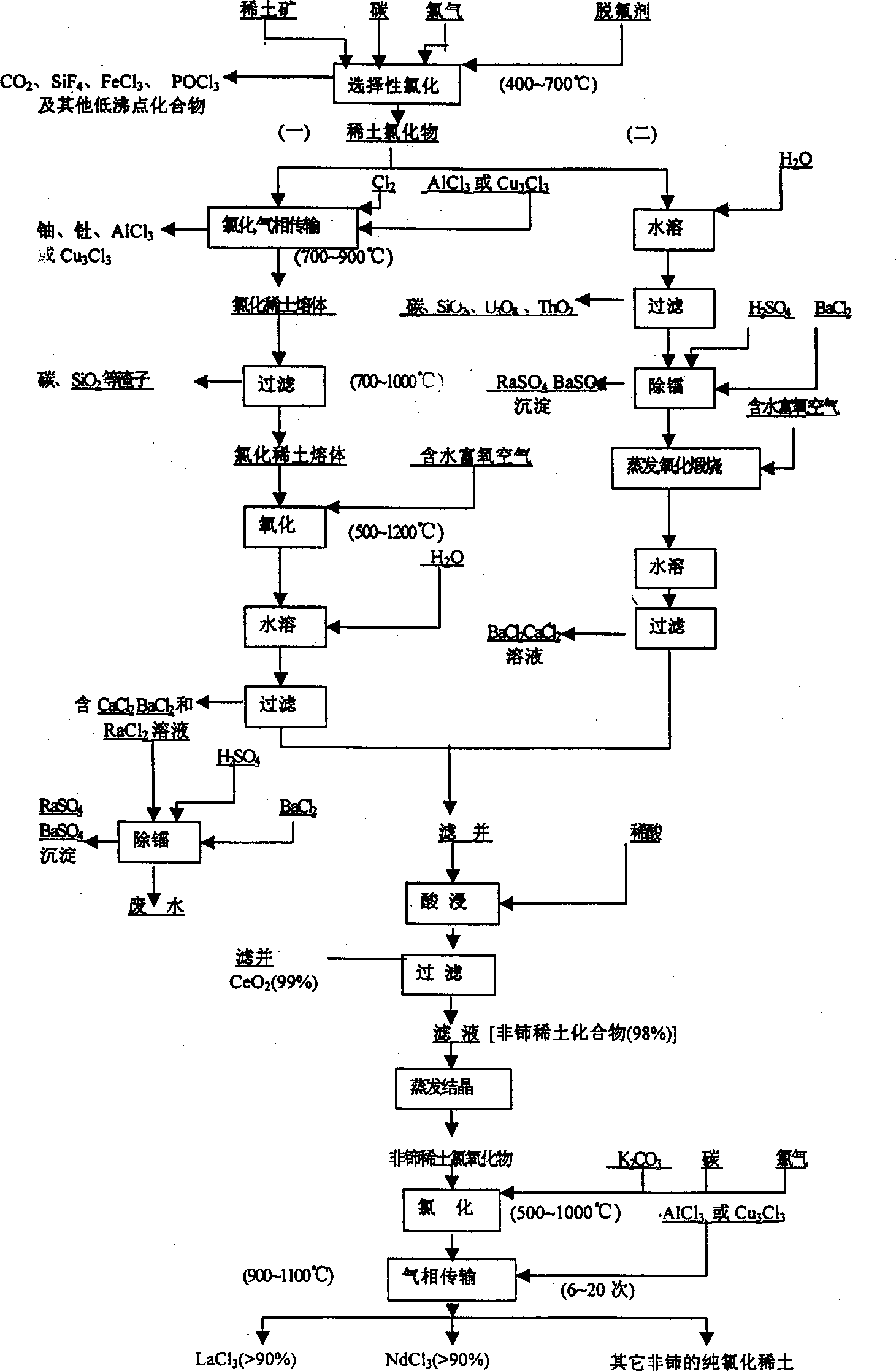
Carburizing chlorination process for extracting and separating cerium and non-Ce rare earth from rare-earth ore
A rare earth compound and rare earth technology, which is applied in the field of carbonization and chlorination of extracting and separating cerium and non-cerium rare earth from rare earth minerals, can solve the problem that alkaline earth metals and radioactive elements cannot be effectively separated, and the extraction and separation processes cannot be connected and affected. Production and product use, etc., to achieve the effect of large-scale industrial production, beneficial to environmental protection, and beneficial to operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Bastnaesite - monazite mixed concentrate, main chemical composition (%): REO (65.2), TFe (1.7), CaO (3.3), BaO (1.1), ThO 2 (0.2), Nb 2 o 5 (0.1), F(5.4), P(3.1), S(0.4), SiO 2 (0.6), the atomic ratio of cerium and non-cerium rare earth elements in the rare earth elements is 1.0.
[0023] After mixing 10 grams of concentrate with a particle size of 19 microns and 1.0 grams of activated carbon, react with chlorine and silicon tetrachloride at 550 ° C for 2 hours at an input rate of 0.15 grams and 1.5 milligrams per minute, respectively, fluorine, sulfur, phosphorus , iron and niobium are discharged in the form of gas or low-boiling volatiles.
[0024] The solid product was dissolved in water and then filtered, and sulfuric acid and barium chloride were added to the filtrate to co-precipitate and radium was filtered off. After the solution was evaporated to dryness, it was reacted with industrial oxygen at 700°C for half an hour. After condensation, it was dissolved in...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Bastnaesite concentrate, main chemical composition (%): REO(64.3), TFe(0.3), CaO(0.4), BaO(0.2), Al 2 o 3 (0.2), ThO 2 (0.3), F(10), SiO 2 (0.9); the atomic ratio of cerium and non-cerium elements in rare earth elements is 0.85.
[0028] This is an example of high fluorine content in the raw material, therefore, the gas flow with high silicon tetrachloride content is used when the concentrate is chlorinated. After mixing 10 grams of concentrated ore with a particle size of 22 microns and 1.0 gram of activated carbon, at 550 ° C, react with chlorine gas and silicon tetrachloride with input speeds of 0.15 grams and 2.5 milligrams per minute respectively for 2 hours. Exhaust as gas or low-boiling volatiles.
[0029] After replacing the collector, the chlorinated product is heated up to 800°C in a chlorine atmosphere, and at this temperature, the input rate is 0.1 grams of aluminum chloride per minute to react for half an hour, thorium and aluminum are transported in th...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Bastnaesite medium ore, main chemical composition (%): REO (16.8), TFe (2.6), MgO (1.7), CaO (6.4), BaO (11.2), Al 2 o 3 (10.7), PbO(0.6), ThO 2 (0.2), F(2.8), P(0.4), SiO 2 (41.6) The atomic ratio of cerium and non-cerium elements in the rare earth elements is the same as in Example 2.
[0035] This is an example where the rare earth content in the raw material is low and the content of elements such as silicon and alkaline earth metals is high.
[0036] For medium ore with a particle size of 35 microns, after dolomite and other carbonate minerals are dissolved out with dilute acid, 10 grams of dry mineral powder and 1.5 grams of activated carbon are mixed, and at 550 ° C, the input speed is 0.15 grams per minute. React with 1.5 mg of chlorine and silicon tetrachloride for 2 hours, filter the reaction product after soaking in water, and filter out a large amount of unreacted substances. Add sulfuric acid to the aqueous solution to remove radium.
[0037] After the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com