Magnetic resonance spectroscopy to identify and classify microorganisms
A microbial and magnetic resonance technology, applied in the field of magnetic resonance spectroscopy analysis for microbial identification and classification, can solve problems such as time-consuming, expensive, and a lot of work
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
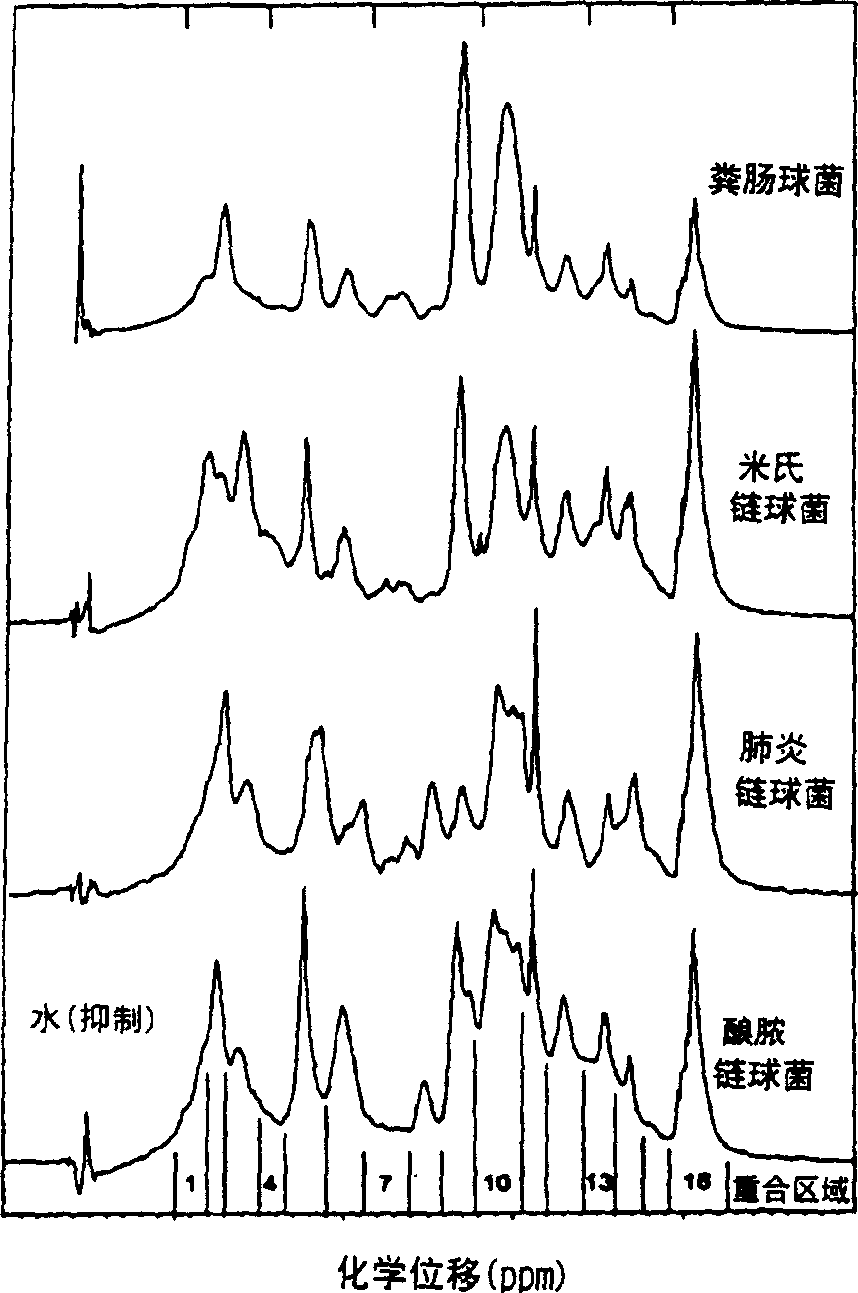
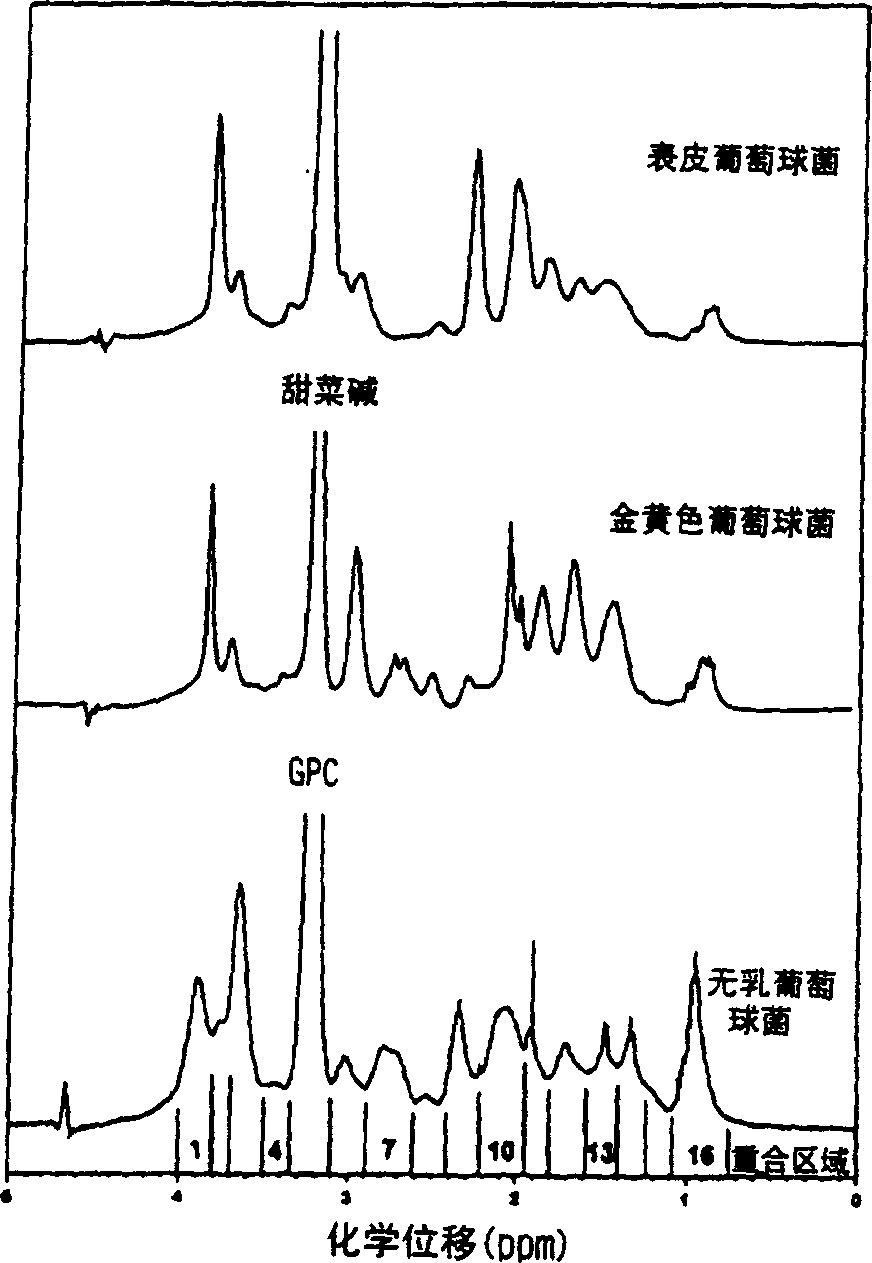
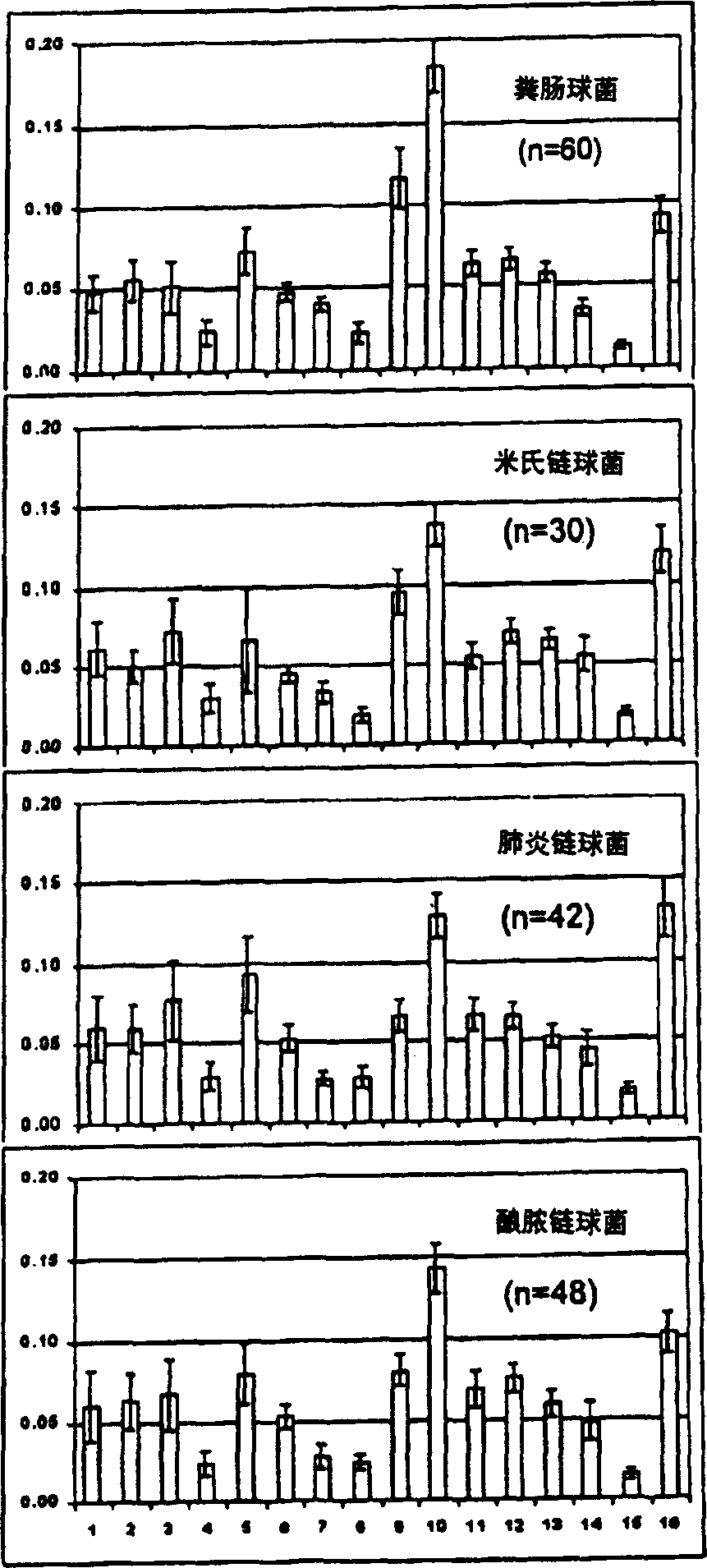
[0045] Embodiment 1: Bacterial detection
[0046] 1. Bacteria Storage and Culture
[0047] Isolates were from deposits of the Center for Infectious Diseases and Microbiology (CIDM) and the American Type Culture Collection, Institute of Clinical Pathology and Medical Sciences, Sydney, or the most recent clinical isolate from the Clinical Qualification Laboratory, CIDM Laboratory Services . Stored bacteria were suspended in 10% glycerol nutrient broth at -70°C. Horse blood agar (HBA) was prepared by adding sterile horse blood to autoclaved blood agar medium (Oxoid (UK) or Amyl Media (Australia)). The bacteria reduced from the stored bacteria were subcultured on 5% horse blood agar and incubated at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Conditioned for 18-24 hours. Newly grown bacteria and bacteria subcultured on HBA after storage were inoculated on duplicate HBA dishes, and incubated at 37°C for 18-24 hours, and then incubated at room temperature (20-30°C) before spectroscopic detection. ) stored f...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Example 2: Using MRS to Discriminate Cryptococcal and Glioma in Mouse and Cell Culture
[0093] 1. Preamble
[0094] Characterization of clinical isolates of Cryptococcus neoformans and glioma cell lines in culture and in experimental mice using MRS. 1D and 2D collections from in vitro cultured fungi (16 strains of Cryptococcus neoformans, 3 species of Candida albicans, 3 species of Aspergillus fumigatus, 3 species of Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and C6 glioma cell lines 1 H MR spectroscopy. Brain biopsies were taken from healthy mice and experimentally infected mice or gliomas (19 healthy brains, 19 cryptococci and 20 gliomas) and were analyzed using homogeneous and heterogeneous nuclei 2D correlation spectroscopy (COSY, TOCS, 1 H, 13 C-HSQC and HMBC) for unambiguous signal assignment between cell suspensions and tissue samples. The results indicated that the MR spectra of C. neoformans and C. neoformans were dominated by the resonance of the disaccharide a, a-trehalose...
Embodiment 3
[0133] Example 3: Identification of pathogenic fungi
[0134] 1. Microorganisms
[0135] 205 cultures of pathogenic yeasts Candida albicans, Candida parapsilosis, Candida tropicalis, Candida krusei, and Candida glabrata were grown on Sabouraud dextrose agar at 30°C for 48 hours. 69 and 70 isolates of the pathogenic yeast Cryptococcus neoformans var. neoformans and var. gattii, respectively, were cultured on Sabouraud dextrose agar at 37°C for 48 hours. Yeasts were biochemically identified using the API 20C AUX system (BioMerieux, Marcy 1'Etoile, France). Cryptococci were biotyped and serotyped (Crypto Check agglutinationtest, Iatron Labs). In addition, fingerprint PCR was used to compare the serotypes of the corresponding species. Colonies were scraped from Petri dishes and suspended in PBS / D immediately prior to MR experiments 2 O middle.
[0136] 2. MR spectrum detection
[0137] with assembly with 5mm { 1 H, 13 C) MR spectra were acquired with a Bruker Avance 360MHz ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com