Process for preparing porous ceramic materials
A technology of porous ceramics and pore size is applied in the field of preparation of porous ceramic materials to achieve the effects of controllable size, shortened preparation time and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
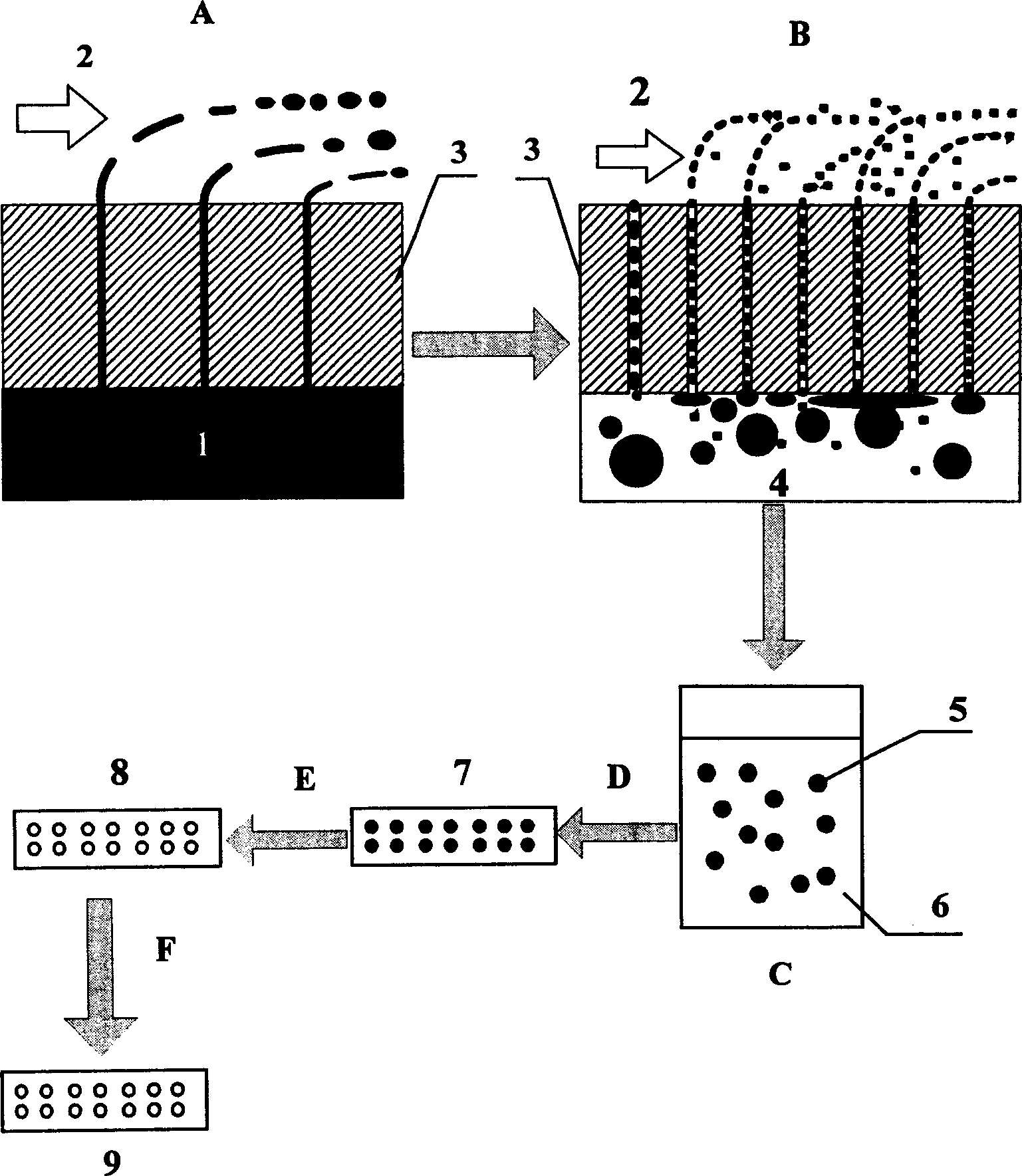
[0026] The flow chart of the preparation method of porous ceramics based on membrane jet emulsification technology is as follows: figure 1 shown. Ceramic membranes with an average pore diameter of 0.16 μm and 1.5 μm were respectively used as the emulsification medium for the two emulsifications, and a stirrer was used as a shear force providing device, and the stirring speed was 490 rpm. The primary membrane emulsification process uses isooctane as the dispersed phase, block polymer poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(propylene glycol)-poly(ethylene glycol) and formamide as the continuous phase, block polymer and formamide The weight ratio is 0.02. Under the pressure of 0.09MPa, the dispersed phase is pressed through the membrane pores, and the flux of the dispersed phase is 100L / (m 2 h). figure 2 This is an optical microscope photo of the prepared primary emulsion. It can be seen from the figure that the emulsion droplets are not uniform. With the primary emulsion as the dispersed ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Ceramic membranes with an average pore size of 0.16 μm and 1.5 μm were used as the emulsification medium for the two emulsifications respectively, and a pump was used as a shear force provider, and the membrane surface flow velocity was 0.4 m / s. The primary membrane emulsification process uses kerosene as the dispersed phase, N,N-dimethylformamide and Span 60 as the continuous phase, and the weight ratio of nonionic surfactant to formamide is 0.01. Under the pressure of 0.2MPa, the dispersed phase is pressed through the membrane pores, and the flux of the dispersed phase is 220L / (m 2 h). With the primary emulsion as the dispersed phase, under the pressure of 0.25MPa, the flux of the secondary membrane emulsification process can reach 250L / (m 2 h). The average particle diameter of the prepared emulsion was 1.6 μm. Disperse the emulsion into the formamide sol of tetrabutyl titanate, add the destabilizing agent ethylamine to the mixed sol to convert the sol into a gel, ...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Disperse the emulsion prepared in Example 1 into the formamide sol of tetrabutyl titanate, apply the sol on a ceramic substrate with a pore size of 50-1000 nm, and destabilize the sol through capillary action, so that the sol is transformed into Gel, the gel is aged and stripped at 70°C. After stripping the template, a porous gel is formed, and then heated and baked at 400°C for 20 hours. The obtained series of gradient pore materials, the top layer of TiO 2 The average pore size of the ceramic is 1.0 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com