Method for E, coli to express lysostaphin in high efficiency via external secretion
一种溶葡萄球菌酶、大肠杆菌的技术,应用在大肠杆菌高效外分泌表达溶葡萄球菌酶领域,能够解决回收率高、不易清除、影响产品质量等问题,达到纯化简单、回收率高、污染少的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
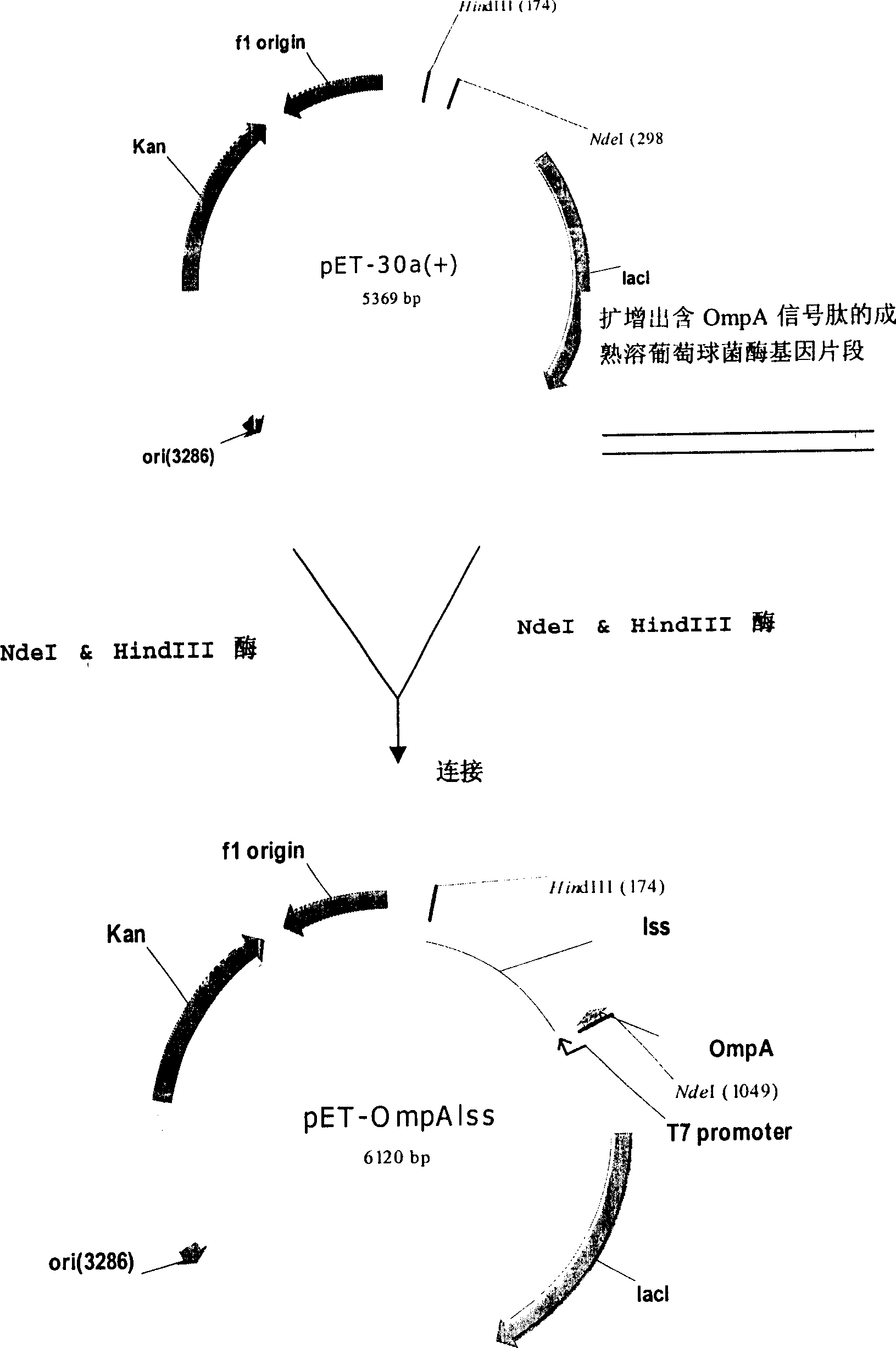
[0044] Example 1: Construction of recombinant lysostaphin secretion expression vector, namely OmpA signal peptide and mature lysate
[0045] Cloning of staphylococcal enzyme fusion gene.
[0046] First design and synthesize the following oligonucleotide sequence:
[0047] SEQ.ID.NO:1 5'-
[0048] TACAT ATGAAAAAGACAGCTATCGCGATTGCAGTGGCACTGGCAGGTTTCG
[0049] CTACCGTCGCTCAGGCT GCTGCAACACATGAACATTCAGCAC-3′
[0050] SEQ.ID.NO: 2 5'-CCAAAGCTTCAACTTTAGGAATGAG-3'
[0051] In the designed SEQ.ID.NO:1, the gene sequence of the NdeI restriction endonuclease site (italicized part) and the gene sequence of the OmpA signal peptide (underlined part) are added to the 5'end;
[0052] In the designed SEQ.ID.NO: 2, the gene sequence of the HindIII restriction endonuclease site (in italics) is added to the 5'end.
[0053] Using the total DNA of Staphylococus Simulans (NRRL B-2628) as the template, SEQ.ID.NO:1 and SEQ.ID.NO:2 as a pair of primers, using pyrobest enzyme (a high-fide...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Example 2: Establishment of recombinant lysostaphin secretory expression engineering bacteria
[0065] The recombinant plasmid pET-OmpAlss was transformed into E. coli TOP10, JM109 (DE3), BL21 (DE3), respectively. Pick positive clones, insert 50ml LB liquid medium (containing 30mg / ml kanamycin) and shake culture at 37℃, cultivate until the optical density value (wavelength 600nm) is 0.6, then add IPTG to the final concentration of 0.05mM induced protein Expression, continue to culture for 3 hours, centrifuge the fermentation broth, and determine the lysostaphin activity of the supernatant by colorimetry.
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3 Determination of Lysostaphin Activity by Colorimetry
[0067] The lysostaphin expression activity of TOP10, JM109 (DE3), BL21 (DE3) containing the recombinant plasmid pET-OmpAlss in Example 2 was determined by colorimetry. The specific determination method is as follows:
[0068] 1 principle
[0069] The quantitative detection of lysostaphin enzyme is colorimetric method, using Staphylococcus aureus cell wall peptidoglycan (KNR-PG) coupled with KNR brilliant blue dye as the color source substrate, according to the quantitative release of the enzyme during the action of the enzyme After removing the unreacted insoluble substrate of the small molecule soluble fragment product of the KNR dye group, the supernatant is colorimetrically determined to determine the enzyme activity. This method is simple and easy to implement, sensitive and intuitive.
[0070] 2 Instruments and reagents
[0071] 2.1 Instrument:
[0072] 2.1.1 Ultraviolet-visible spectrophotomet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com