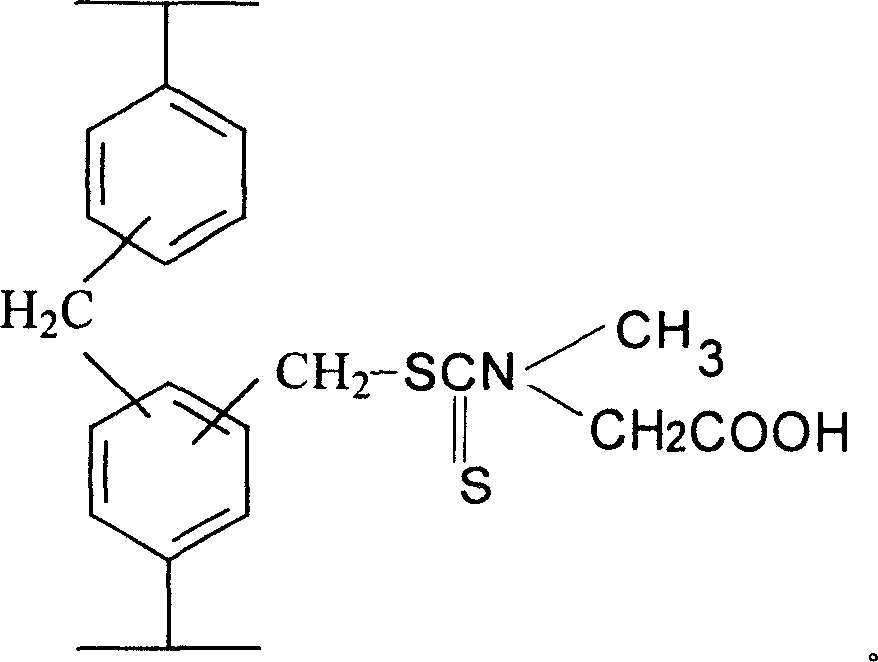
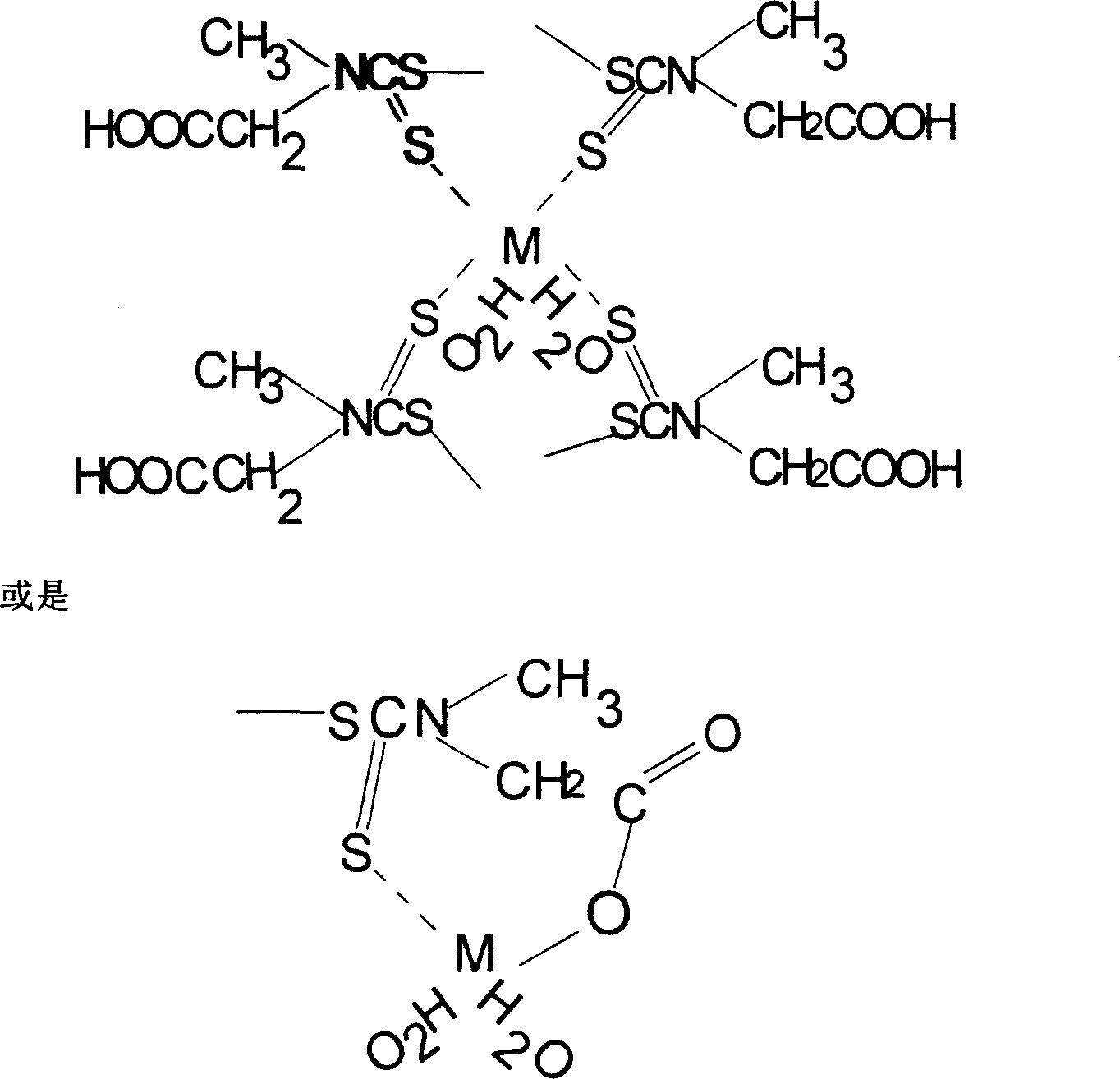
N-methyl, N-carboxymethyl dithio amidocarbonic acid chelating resin and its preparing method
A technology of carboxymethyldithiocarbamic acid and carboxymethylthiocarbamic acid, which is applied in the field of chelating resin and its synthesis, can solve the problem that the number of resin functional groups needs to be increased, and the selectivity has not been further studied and prepared. Complicated conditions and other issues, to achieve the effect of stable performance, easy synthesis, and wide application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] (a) Suspension polymerization.
[0024] Add a certain amount of dilute sodium hydroxide solution to the styrene monomer or directly filter the monomer through a resin column equipped with a strong base anion exchange resin to remove the polymerization inhibitor.
[0025] In a 1000mL beaker, add 210g styrene, 26g divinylbenzene, and 140g liquid paraffin, stir well and set aside.
[0026] In a 1000mL three-neck flask, add 600g of distilled water and raise the temperature to 40°C, then add 6g of gelatin, stir until completely dissolved, and at the same time raise the temperature to 50°C, add 2mL of methylene blue, stir well, add the above-mentioned styrene, divinylbenzene and liquid Add the initiator benzoyl peroxide 4.0g to the wax mixture; adjust the stirring speed to make the oil droplet size appropriate, gradually raise the temperature to 80°C at a speed of 1°C / 6min, keep it warm for 4 hours, and then gradually raise the temperature to 85°C Keep warm for 3 hours, keep...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The synthetic steps of another embodiment of the present invention are as follows:
[0037] (a) Utilize styrene as a monomer, divinylbenzene as a crosslinking agent, utilize liquid wax as a porogen, use magnesium carbonate as a dispersant, use benzoyl peroxide as an initiator, and adopt a suspension polymerization method to synthesize low Cross-linked macroporous polystyrene-divinylbenzene copolymer, choose steam distillation or use ethanol as solvent extraction to remove the residual porogen in the resin channels, and then dry it by airflow to obtain low cross-linked macroporous polystyrene - divinylbenzene resin, i.e. white balls.
[0038] Wherein the dosage of the crosslinking agent is 4% of the total amount of the monomer and the crosslinking agent, the dosage of the porogen is 40% of the weight of the monomer, and the crosslinking degree of the low crosslinking macroporous polystyrene is 2%.
[0039] (b) Soak the white ball in chloromethyl ether 4 times its weight...
Embodiment 3
[0042] The specific steps are the same as in Example 2, except that in step (a), the amount of the crosslinking agent is 12% of the total amount of the monomer and the crosslinking agent, the amount of the porogen is 60% of the weight of the monomer, and the low crosslinking macroporous polystyrene The degree of crosslinking is 6%. The chloromethylation reaction is carried out at a temperature of 45° C. in step (b). The N-methyl that makes, the functional group content of N-carboxymethyl dithiocarbamate chelating resin is 2.19mmol / g.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com