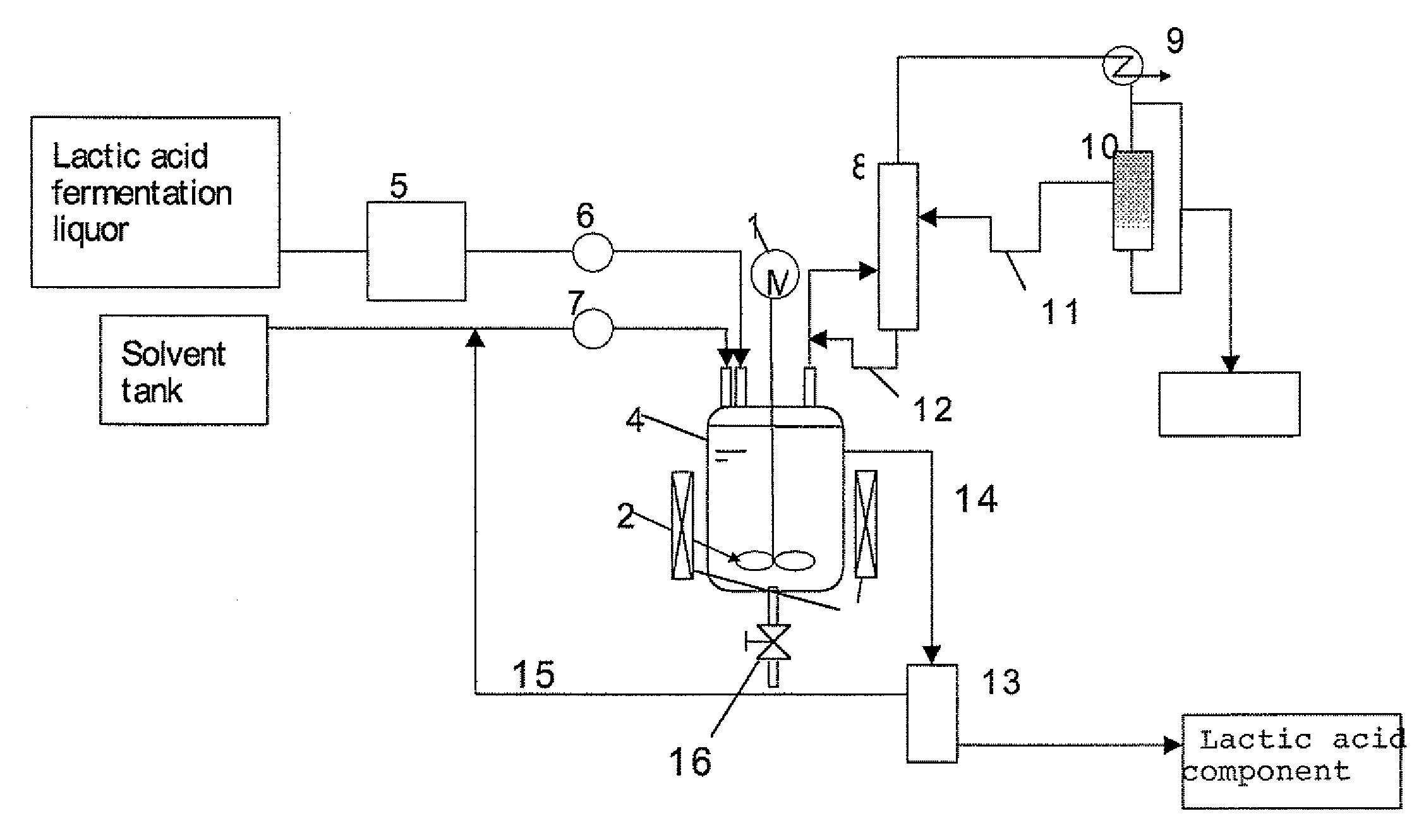
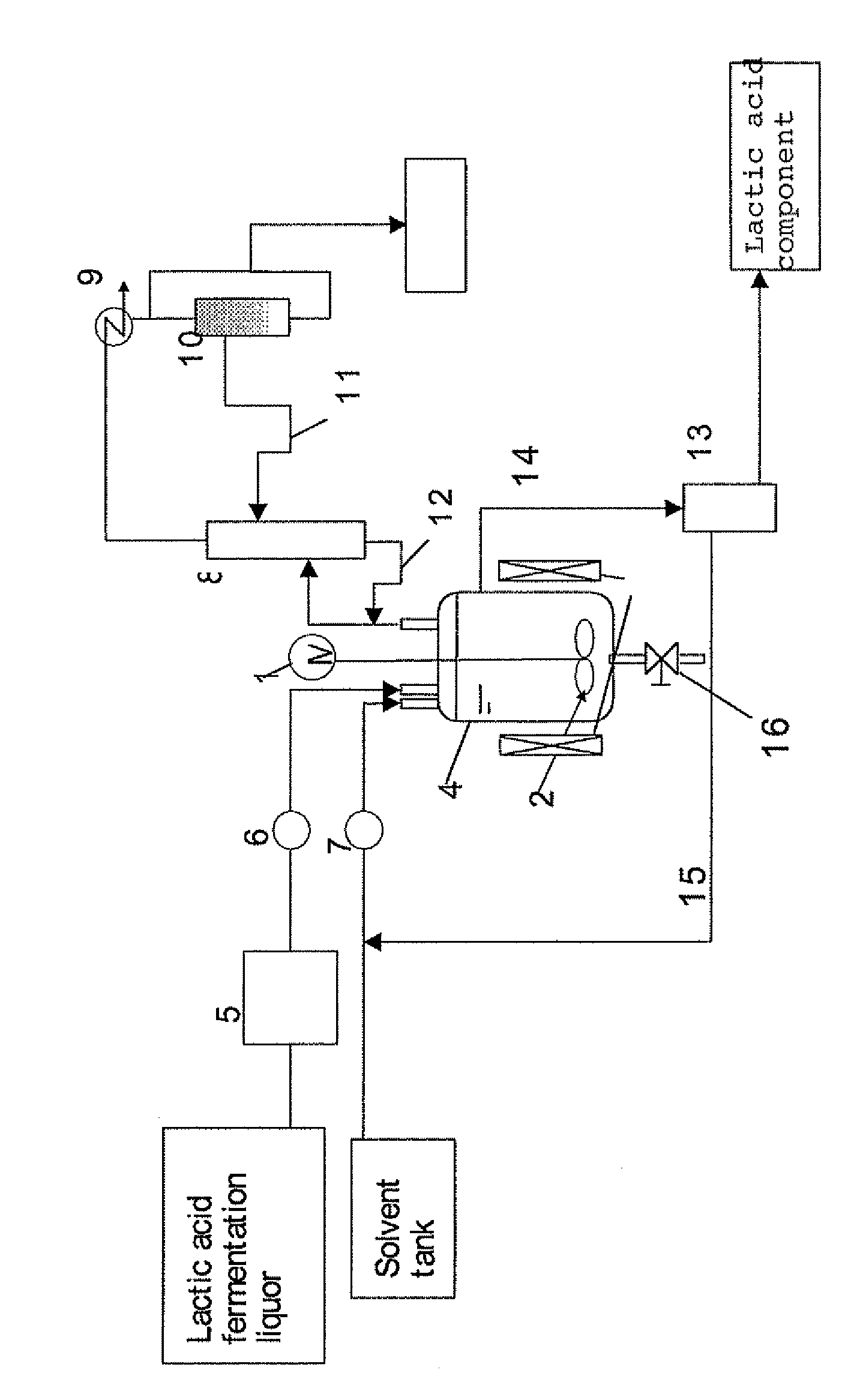
Method for Separation of Lactic Acid Component from Lactic Acid Fermentation Liquor, and Separation Apparatus
a technology of lactic acid and fermentation liquor, which is applied in the direction of solvent extraction, biomass after-treatment, separation process, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the number of steps of further reagents, the need to remove alcohols, and the possibility of incorporation of concomitant chemical substances or impurities, so as to achieve simple process and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0119]In a lactic acid fermentation liquid medium that contained 3.5 wt % of standard medium M17 (manufactured by Difco Laboratories) for streptococcus, supplemented with 14 wt % of glucose, lactic acid bacteria (streptococcus bacteria) were subjected to lactic acid fermentation in suspension culture while the pH of the medium was adjusted with ammonia to near 6, to obtain 20 g of lactic acid fermentation liquor (pH 6) in which the concentration of ammonium lactate was 10 wt %. The cells of bacteria were removed in advance from the lactic acid fermentation liquor by centrifugal separation. The pH of the lactic acid fermentation liquor was adjusted to 4.8 by addition of sulfuric acid. Subsequently, 50 ml of xylene was added thereto, and the mixture was heated at 130° C. with agitation in a reflux state. One hour later, the agitation was stopped and the mixture was allowed to stand while continuing heating at 130° C., to separate it into two layers. When the upper layer was collected ...
example 2
[0120]As in Example 1 above, 20 g of lactic acid fermentation liquor (pH 6) was obtained in which the concentration of ammonium lactate was 10 wt %. The cells of bacteria were removed from the lactic acid fermentation liquor as in Example 1. The pH of the lactic acid fermentation liquor was adjusted to 2.5 by addition of sulfuric acid. Subsequently, 50 ml of xylene was added thereto, and the mixture was heated at 130° C. with agitation in a reflux state. One hour later, the agitation was stopped and the mixture was allowed to stand while continuing heating at 130° C., to separate it into two layers. When the upper layer was collected and cooled down to room temperature, precipitation was observed. The precipitation was due to lactic acid, and the yield of the extraction was 20% (see Table 1 below).
example 3
[0123]As in Example 1 above, 20 g of lactic acid fermentation liquor (pH 6) was obtained in which the concentration of ammonium lactate was 10 wt %. The cells of bacteria were removed from the lactic acid fermentation liquor as in Example 1. The pH of the lactic acid fermentation liquor was adjusted to 4.8 by addition of sulfuric acid. Subsequently, 50 ml of xylene was added thereto, and the mixture was heated to 100° C. with agitation. A vapor was condensed, water from which was removed, and then refluxed, and about 17 g of water was thus removed over approximately 2 hours. Subsequently, the mixture was heated to 130° C. One hour later, the agitation was stopped and the mixture was allowed to stand, to separate it into two layers. When the upper layer was collected and cooled down to room temperature, precipitation was observed. The precipitation was due to lactic acid, and the yield of the extraction was 20% (see Table 2 below).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com