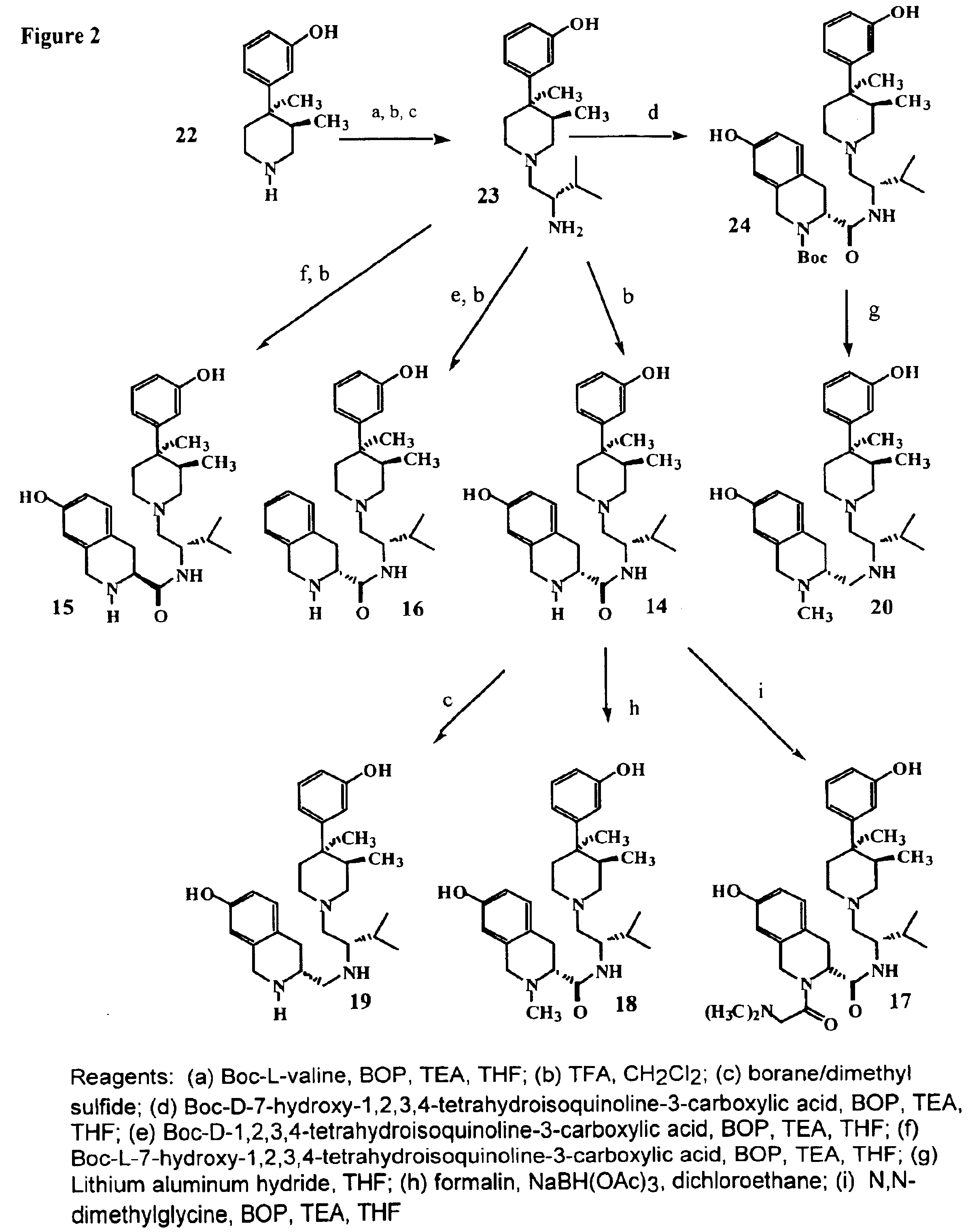
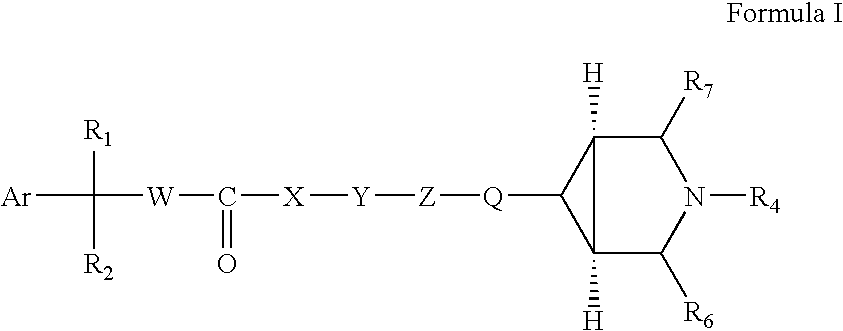
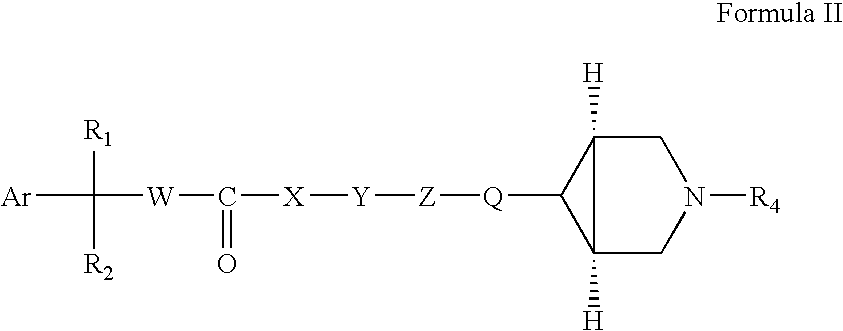
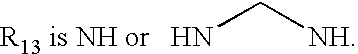Patents
Literature
156 results about "Cannabinoid receptor antagonist" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
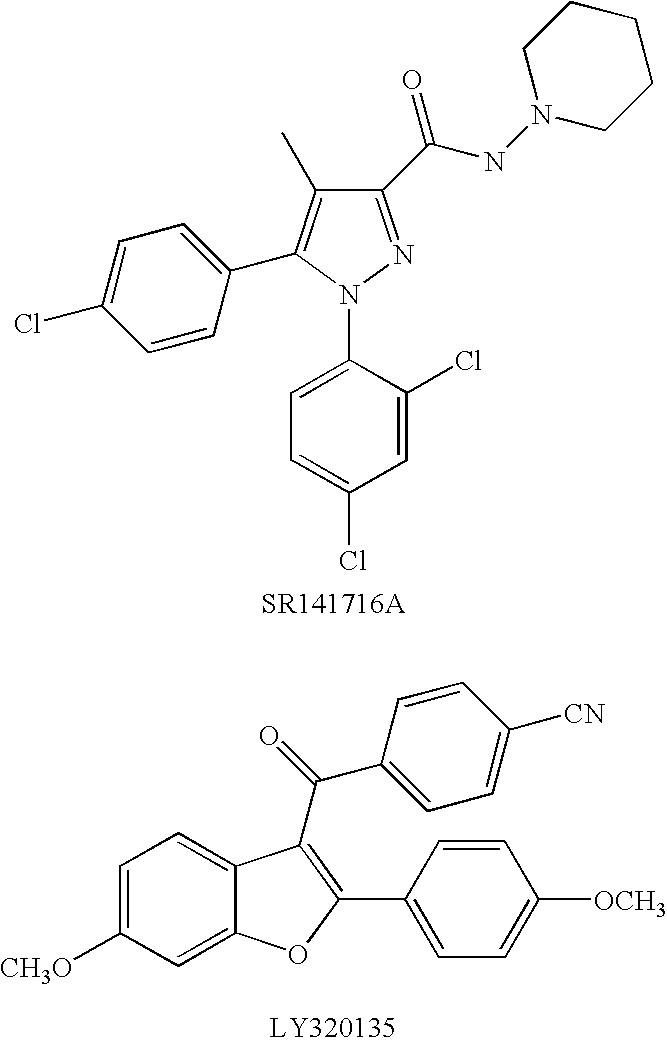
A cannabinoid receptor antagonist, also known simply as a cannabinoid antagonist or as an anticannabinoid, is a type of cannabinoidergic drug that binds to cannabinoid receptors (CBR) and prevents their activation by endocannabinoids. They include antagonists, inverse agonists, and antibodies of CBRs. The discovery of the endocannabinoid system led to the development of CB₁ receptor antagonists. The first CBR antagonist, rimonabant, was described in 1994. Rimonabant blocks the CB₁ receptor selectively and has been shown to decrease food intake and regulate body-weight gain. The prevalence of obesity worldwide is increasing dramatically and has a great impact on public health. The lack of efficient and well-tolerated drugs to cure obesity has led to an increased interest in research and development of CBR antagonists. Cannabidiol (CBD), a naturally occurring cannabinoid, is a non-competitive CB₁/CB₂ receptor antagonist. And Δ⁹-tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), a naturally occurring cannabinoid, modulate the effects of THC via direct blockade of cannabinoid CB₁ receptors, thus behaving like first-generation CB₁ receptor inverse agonists, such as rimonabant. CBD is a very low-affinity CB₁ ligand, that can nevertheless affect CB₁ receptor activity in vivo in an indirect manner, while THCV is a high-affinity CB₁ receptor ligand and potent antagonist in vitro and yet only occasionally produces effects in vivo resulting from CB₁ receptor antagonism. THCV has also high affinity for CB₂ receptors and signals as a partial agonist, differing from both CBD and rimonabant.
Muscarinic receptor antagonists
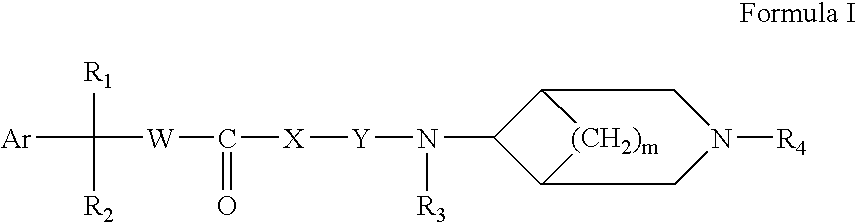
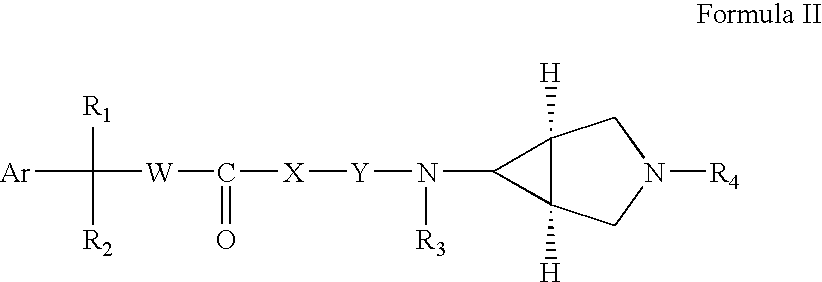
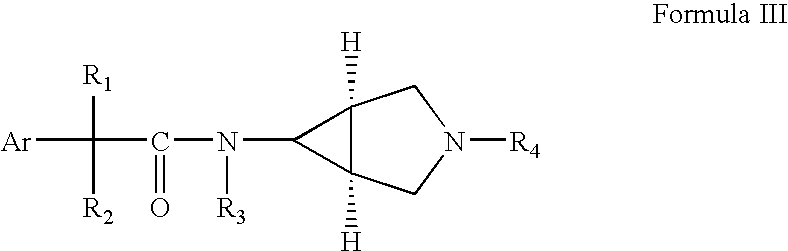
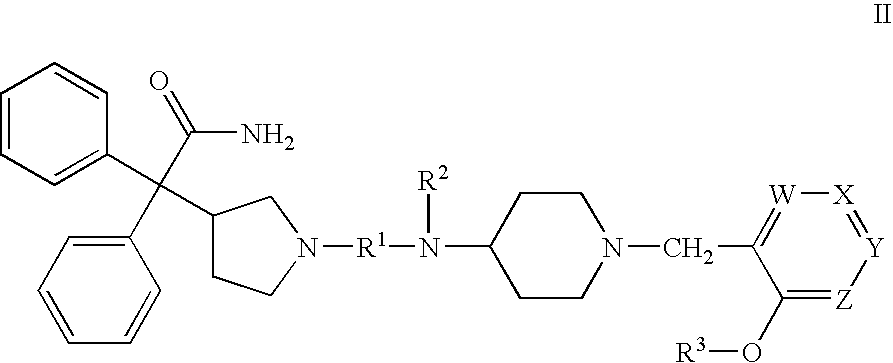
Disclosed are multibinding compounds which are muscarinic receptor antagonists. The multibinding compounds of this invention containing from 2 to 10 ligands covalently attached to one or more linkers. Each ligand is, independently of each other, a muscarinic receptor antagonist or an allosteric modulator provided that at least one of said ligand is a muscarinic receptor antagonist. The multibinding compounds of this invention are useful in the treatment and prevention of diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic bronchitis, irritable bowel syndrome, urinary incontinence, and the like.
Owner:THERAVANCE BIOPHARMA R&D IP LLC
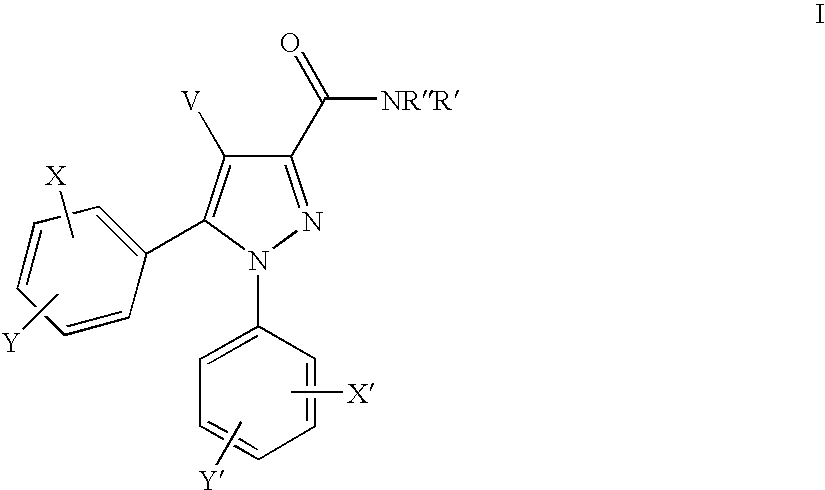
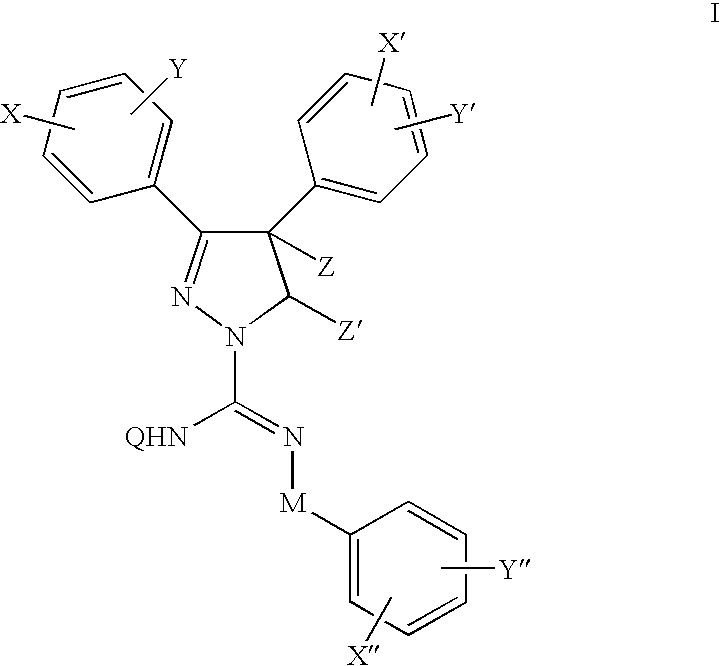
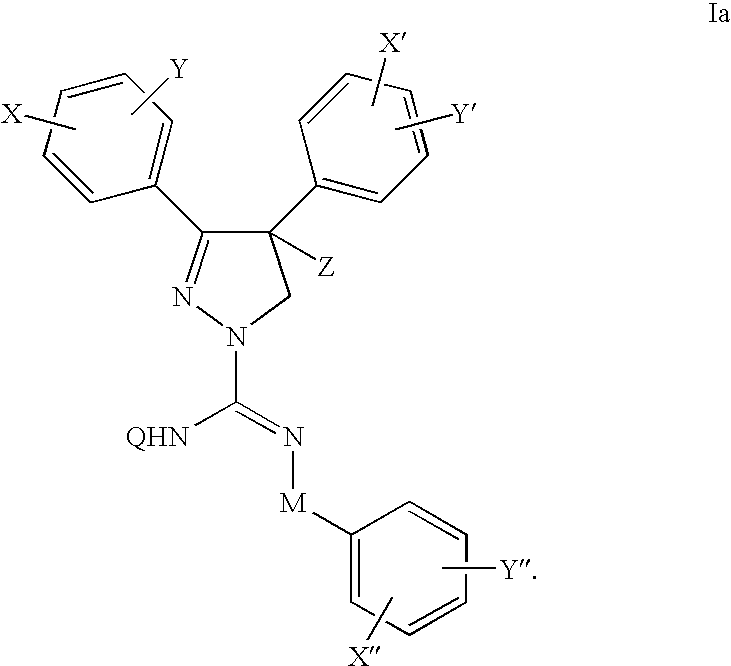
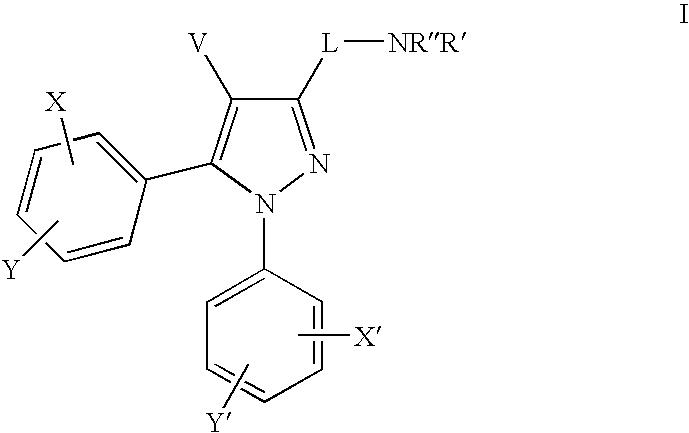
Cannabinoid receptor antagonists/inverse agonists useful for treating obesity
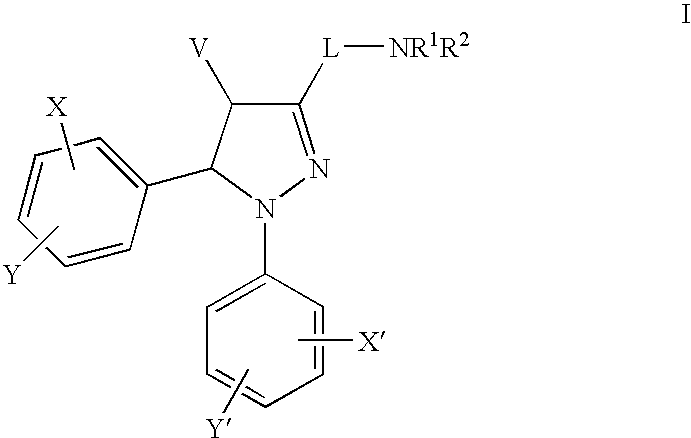
The present invention provides novel pyrazoles that are useful as cannabinoid receptor antagonists and pharmaceutical compositions thereof and methods of using the same for treating obesity, diabetes, and / or cardiometabolic disorders.
Owner:JENRIN DISCOVERY
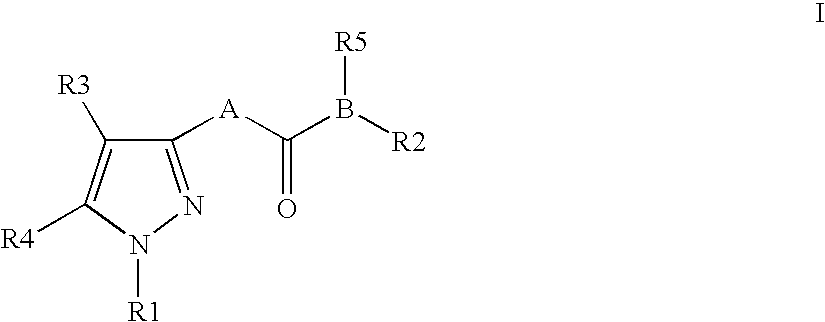
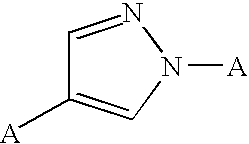
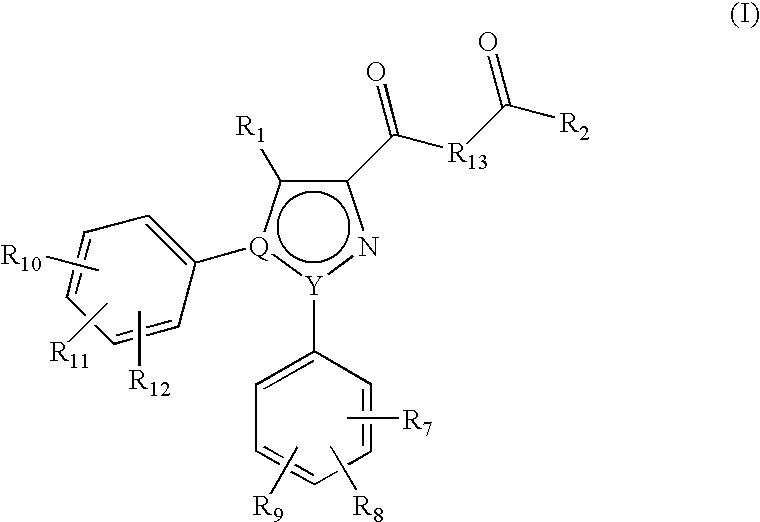
Pyrazole derivatives as cannabinoid receptor antagonists
InactiveUS20060100208A1Inhibit bindingBlock biological actionBiocideOrganic chemistryPyrimidine analogueChemistry
One aspect of the invention is concerned with cannabimimetic pyrazole analogs. Another aspect of the invention is concerned with new and improved pyrazole analogs having high affinities and / or selectivities for the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. A further aspect of the invention is concerned with pharmaceutical preparations employing the inventive analogs and methods of administering therapeutically effective amounts of the inventive analogs to provide a physiological effect.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Novel compounds, isomer thereof, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof as vanilloid receptor antagonist; and pharmaceutical compositions containing the same
This present invention relates to novel compounds, isomer thereof or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof as vanilloid receptor (Vanilloid Receotor 1; VR1; TRPV1 )antagonist; and a pharmaceutical composition containing the same. The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating a disease such as pain, migraine, arthralgia, neuralgia, neuropathies, nerve injury, skin disorder, urinary bladder hypersensitiveness, irritable bowel syndrome, fecal urgency, a respiratory disorder, irritation of skin, eye or mucous membrane, stomach-duodenal ulcer, inflammatory diseases, ear disease, and heart disease.
Owner:AMOREPACIFIC CORP
Cannabinoid receptor antagonists/inverse agonists useful for treating metabolic disorders, including obesity and diabetes
The present invention provides novel pyrazoles that are useful as cannabinoid receptor antagonists and pharmaceutical compositions thereof and methods of using the same for treating obesity, diabetes, hepatic disorders, and / or cardiometabolic disorders.
Owner:JENRIN DISCOVERY
Combination therapy for controlling appetites
InactiveUS20050101542A1Reduce appetiteReduce and control appetiteBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsAppetite reducingCombination therapy
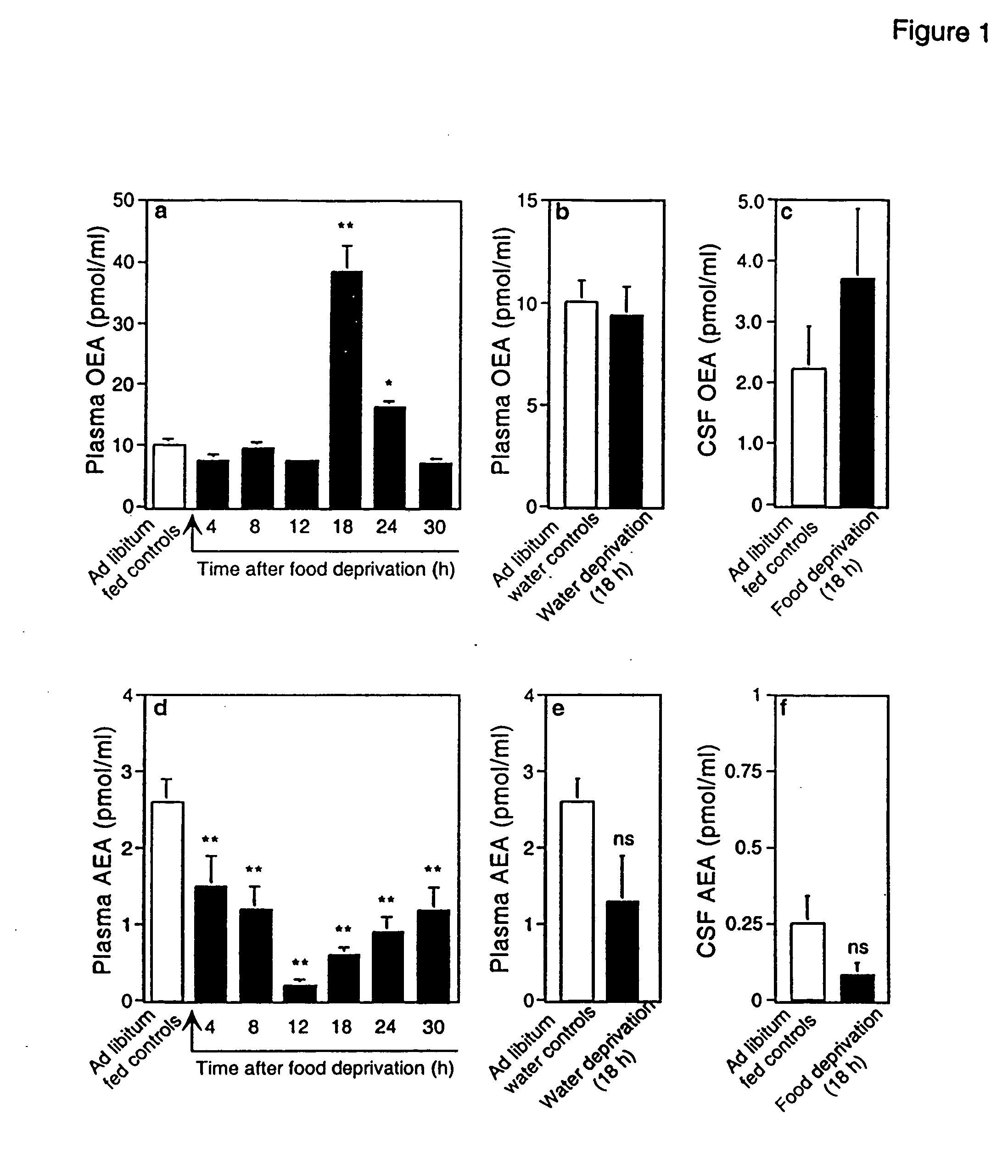
The invention provides methods and pharmaceutical compositions for administering a PPARα agonist (e.g., OEA-like agonist, OEA-like compound), an OEA-like appetite reducing compound, or a FAAH inhibitor and a CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonist to a subject in order to reduce the consumption or ingestion of food, ethanol or other appetizing substances as well as in treating appetency disorders related to the excess consumption of food, ethanol, and other appetizing substances. The combination therapy can also be useful for reducing body fat or body weight and modulating lipid metabolism.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
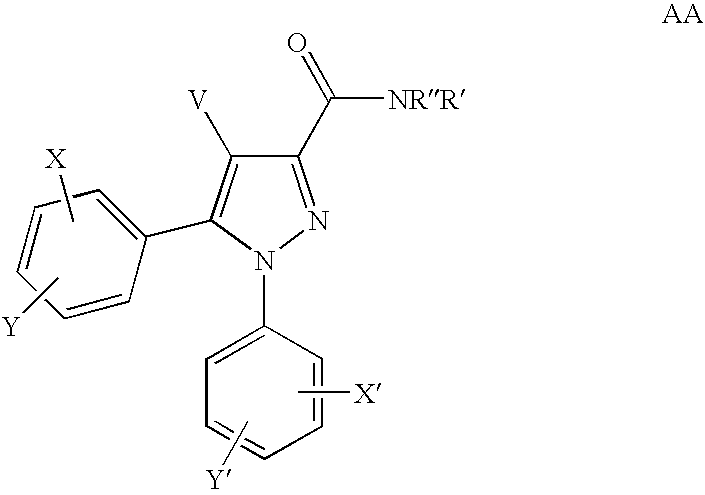
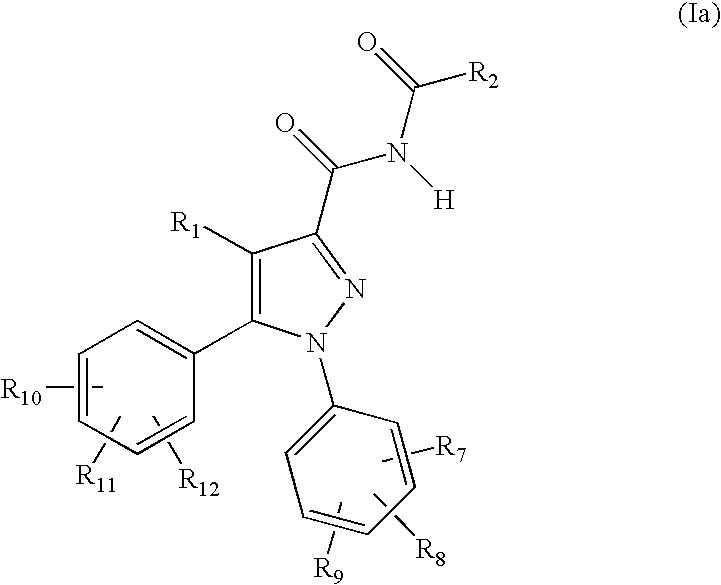
Substituted n-phenyl-5-phenyl-pyrazolin-3-yl amides as cannabinoid receptor antagonists/inverse agonists useful for treating obesity
The present invention provides novel pyrazolines that are useful as cannabinoid receptor antagonists / inverse agonists and pharmaceutical compositions thereof and methods of using the same for treating obesity, diabetes, dyslipidemias, cardiovascular disorders, hepatic disorders, and a combination thereof.
Owner:JENRIN DISCOVERY
Compositions for affecting weight loss
Disclosed are compositions for affecting weight loss comprising a first compound and a second compound, where the first compound is an opioid antagonist and the second compound is a cannabinoid receptor antagonist. Also disclosed are methods of affecting weight loss, increasing energy expenditure, increasing satiety in an individual, or suppressing the appetite of an individual, comprising identifying an individual in need thereof and treating that individual to antagonize opioid receptor activity and to antagonize cannabinoid receptor activity.
Owner:OREXIGEN THERAPEUTICS INC
Pharmaceutical combination
ActiveUS20130172277A1High potencyImprove efficacyBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismMuscarinic antagonistAdrenergic
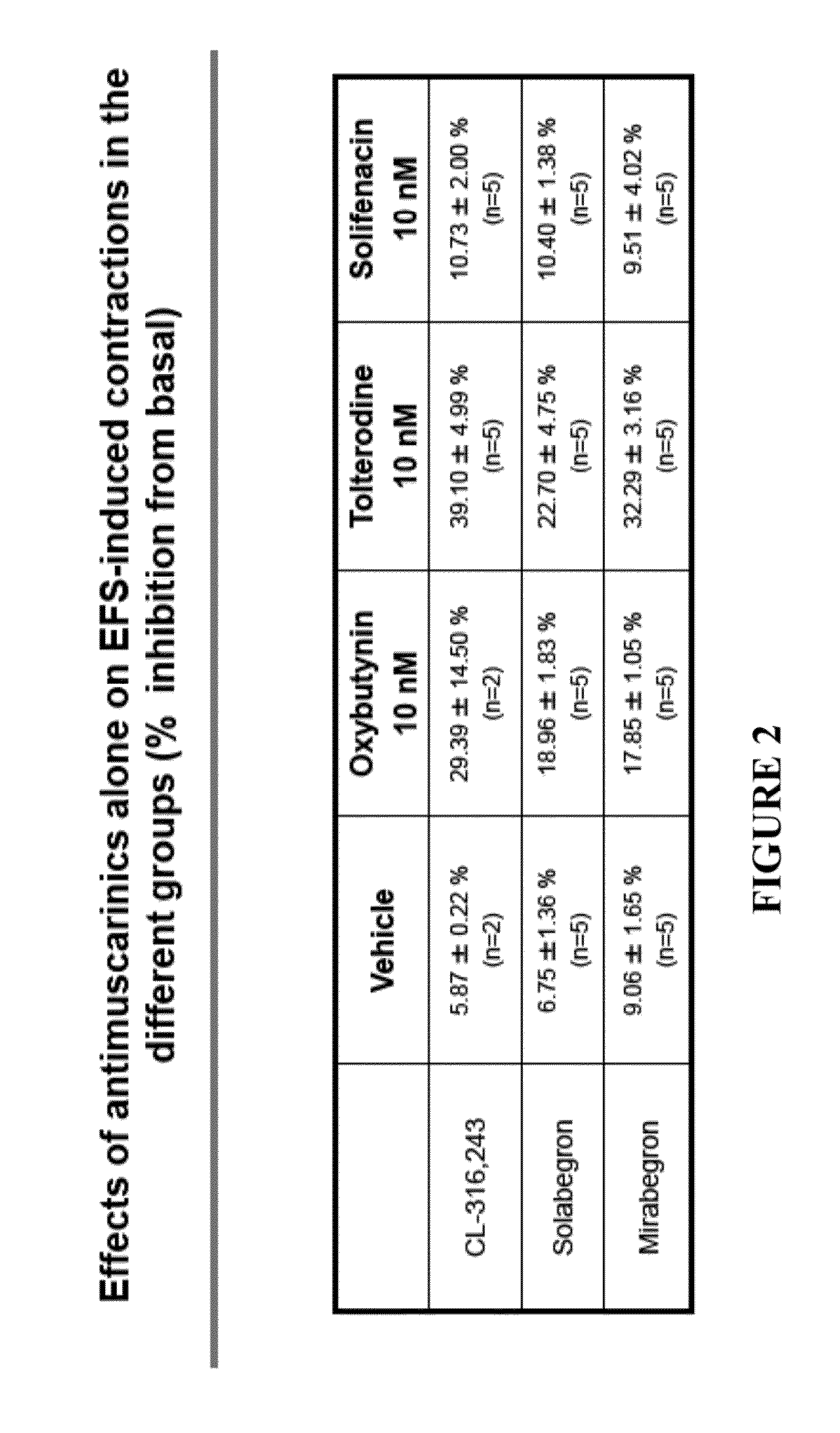
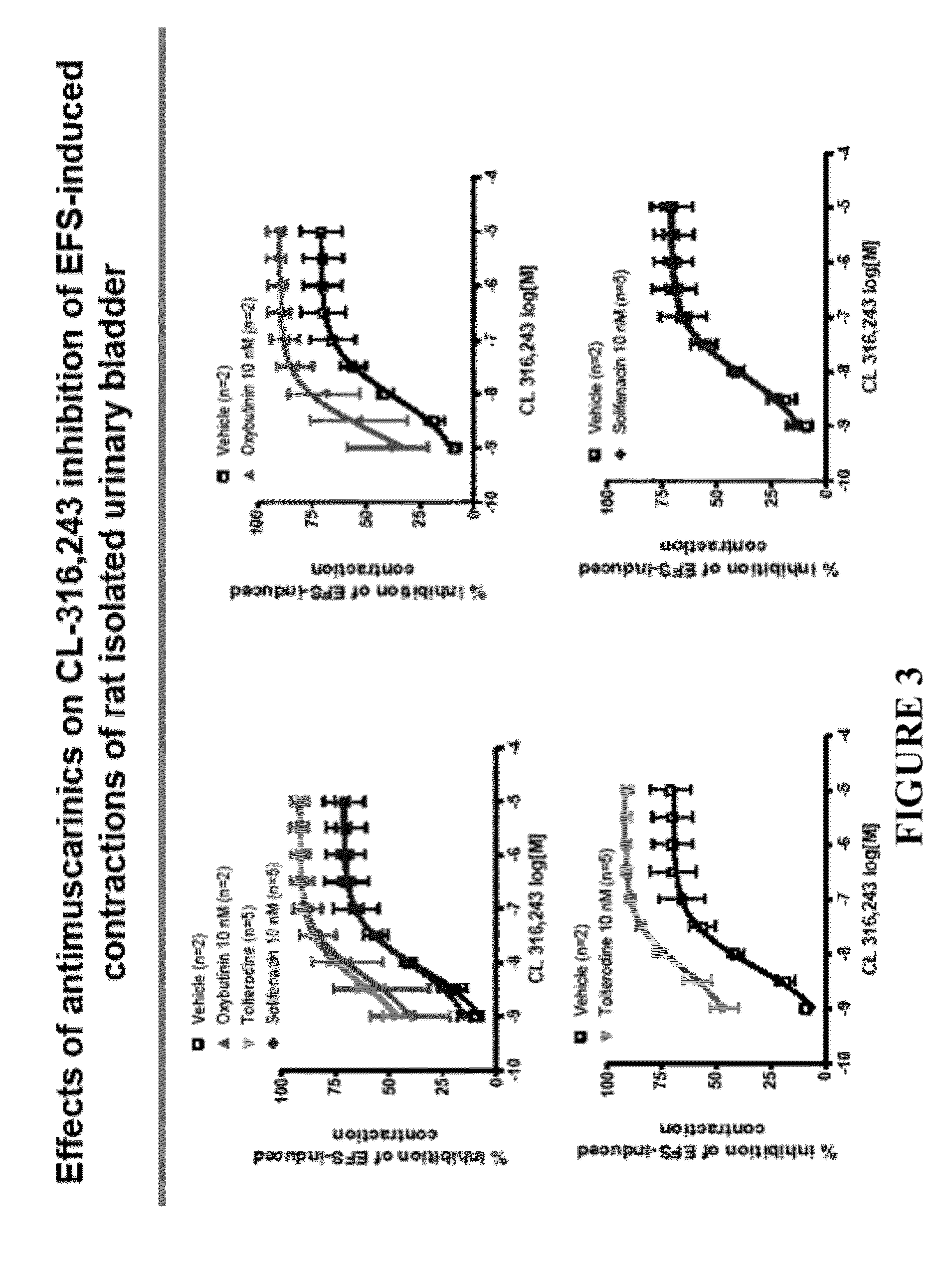
Pharmaceutical combinations comprising a beta-3 adrenergic receptor agonist and a muscarinic receptor antagonist, and methods for their use are disclosed. Methods of using the pharmaceutical combinations for the treatment of one or more symptoms associated with overactive bladder, for example, frequency of urgency, nocturia, and urinary incontinence, are also disclosed.
Owner:B3AR THERAPEUTICS INC
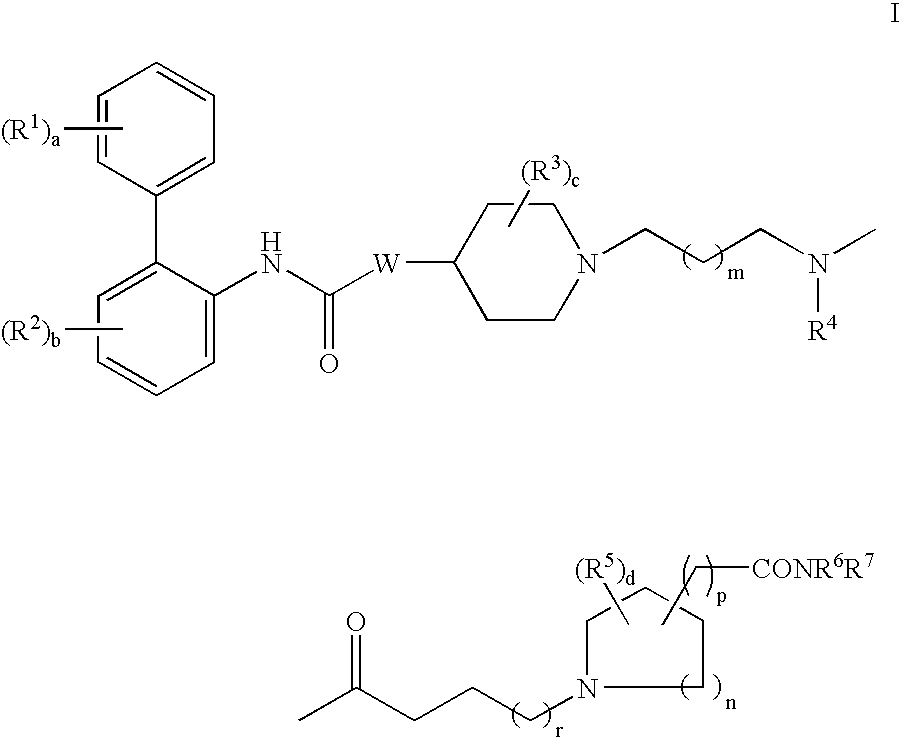
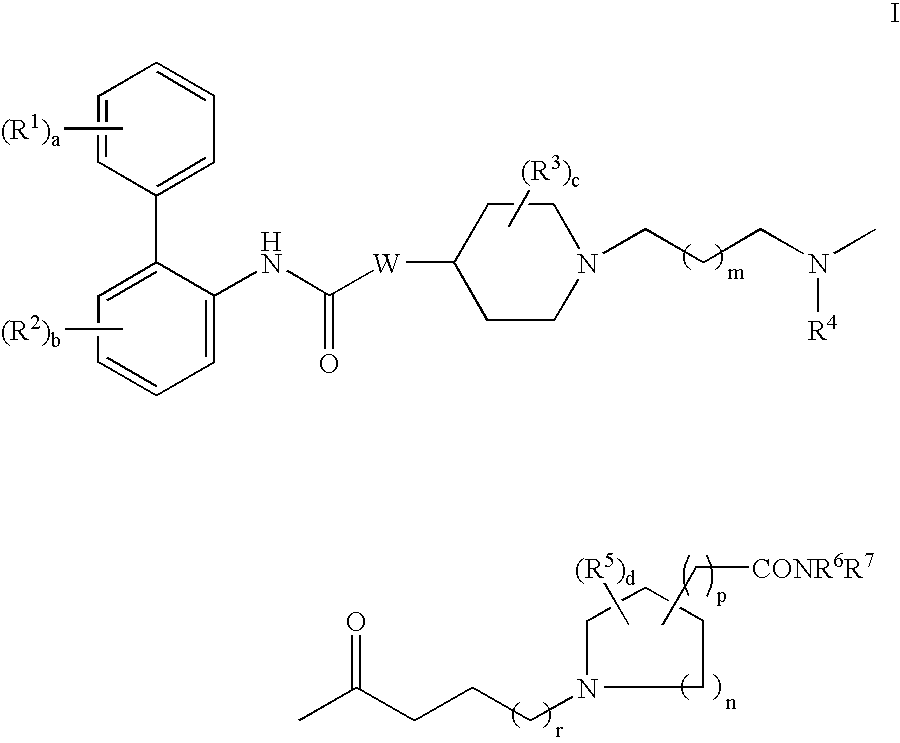
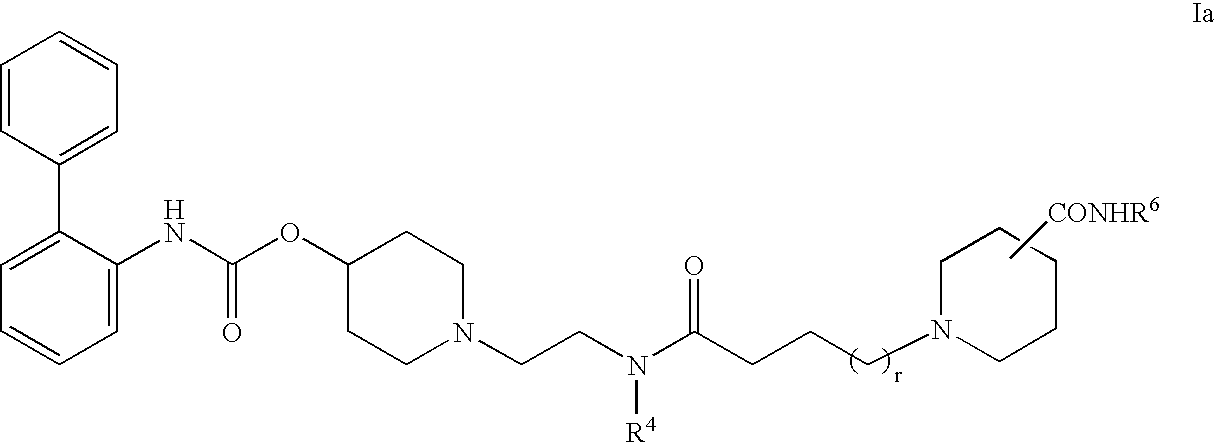
Biphenyl compounds useful as muscarinic receptor antagonists
ActiveUS7569588B2Long duration of actionImprove performanceBiocideOrganic chemistryStereochemistryBiphenyl compound
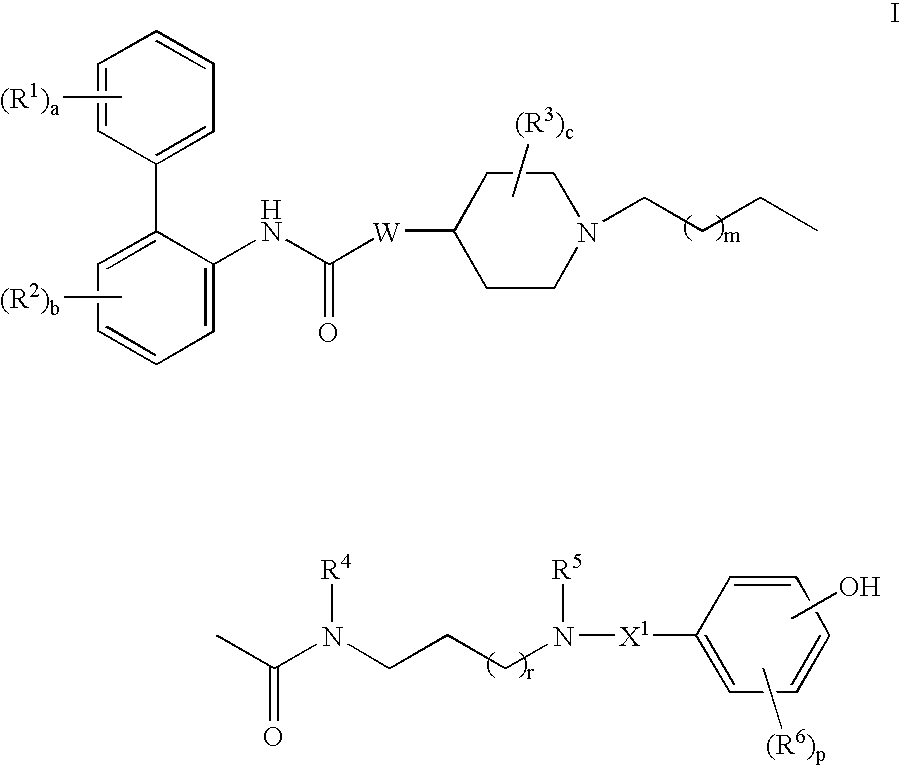
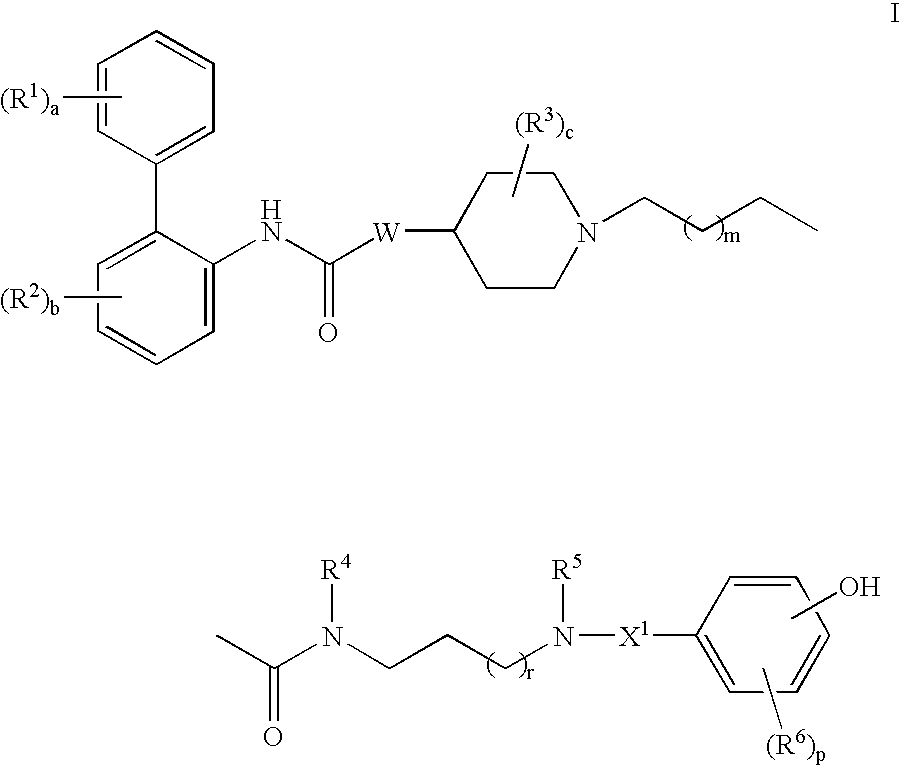
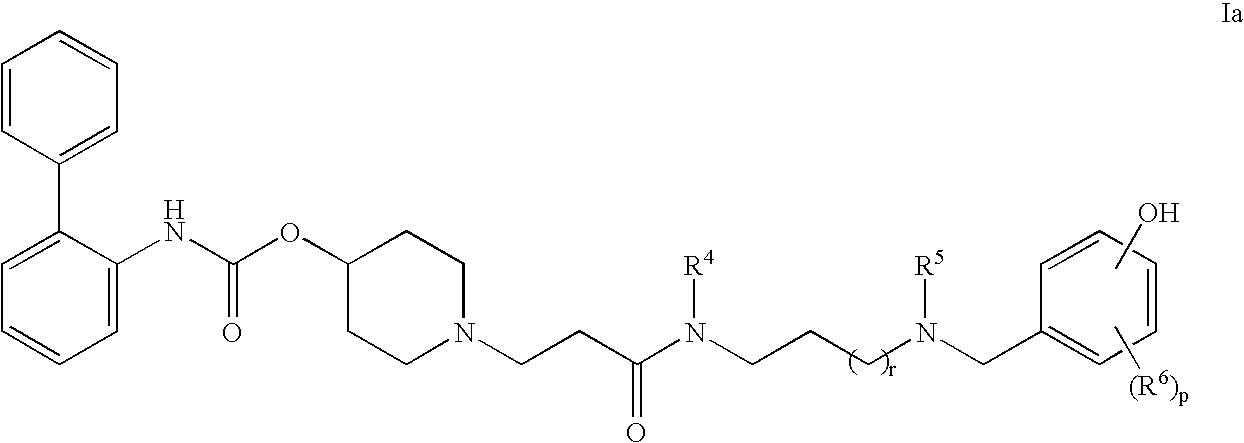
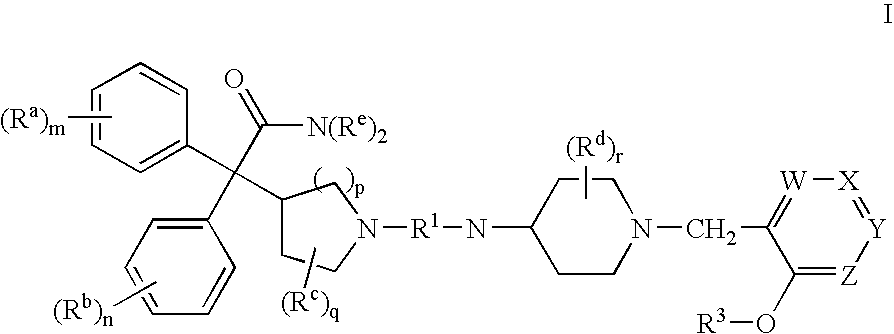
This invention provides compounds of formula I:wherein a, b, c, m, p, r, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, W and X1 are as defined in the specification. The compounds of formula I are muscarinic receptor antagonists. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds, processes and intermediates for preparing such compounds and methods of using such compounds to treat pulmonary disorders.
Owner:THERAVANCE BIOPHARMA R&D IP LLC
A1 adenosine receptor antagonists
ActiveUS20050245546A1Avoid actionMaintain liquidityBiocideOrganic chemistryVasopressin AntagonistsDisease cause
Owner:CV THERAPEUTICS INC
Cannabinoid receptor antagonists/inverse agonists useful for treating obesity
Owner:JENRIN DISCOVERY
Therapeutic carbamates
InactiveUS7238709B2Reduce dose requiredLong duration of actionBiocideSenses disorderCarbamateMedicinal chemistry
Owner:THERAVANCE BIOPHARMA R&D IP LLC
Diphenyl cyclopentyl amides as cannabinoid-1 receptor inverse agonists
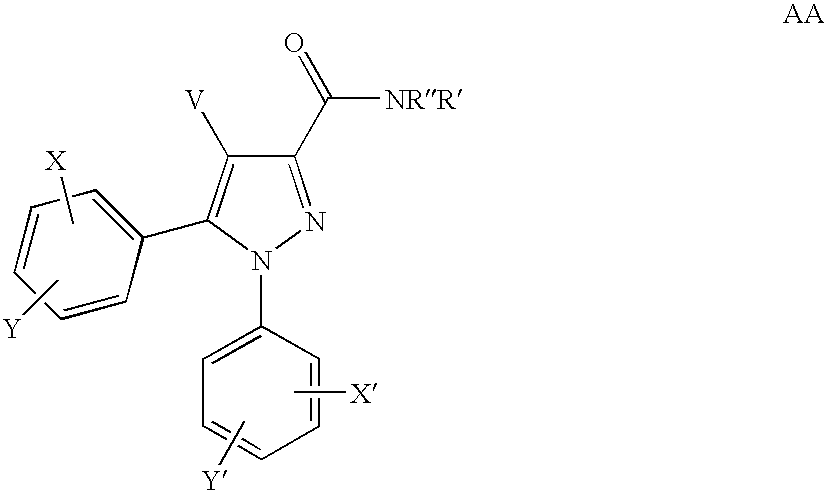
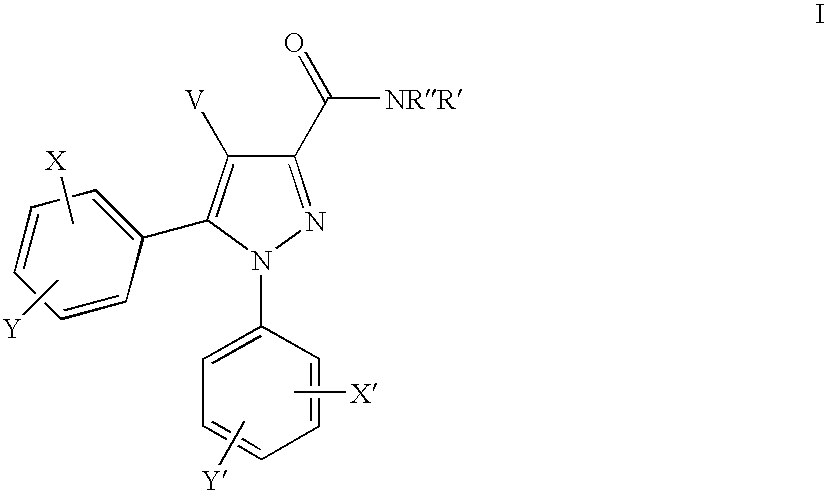
Novel compounds of structural formula (I) are antagonists and / or inverse agonists of the Cannabinoid-1 (CB1) receptor and are useful in the treatment, prevention and suppression of diseases mediated by the CB1 receptor. The compounds of the present invention are useful as psychotropic drugs in the treatment of psychosis, memory deficits, cognitive disorders, migraine, neuropathy, neuro-inflammatory disorders including multiple sclerosis and Guillain-Barre syndrome and the inflammatory sequelae of viral encephalitis, cerebral vascular accidents, and head trauma, anxiety disorders, stress, epilepsy, Parkinsons disease, movement disorders, and schizophrenia. The compounds are also useful for the treatment of substance abuse disorders, the treatment of obesity or eating disorders, as well as, the treatment of asthma, constipation, chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction, and cirrhosis of the liver.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
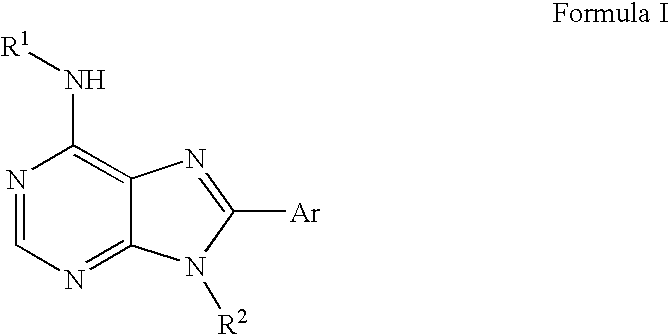
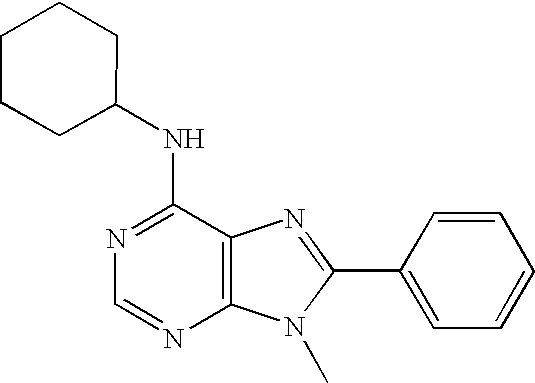
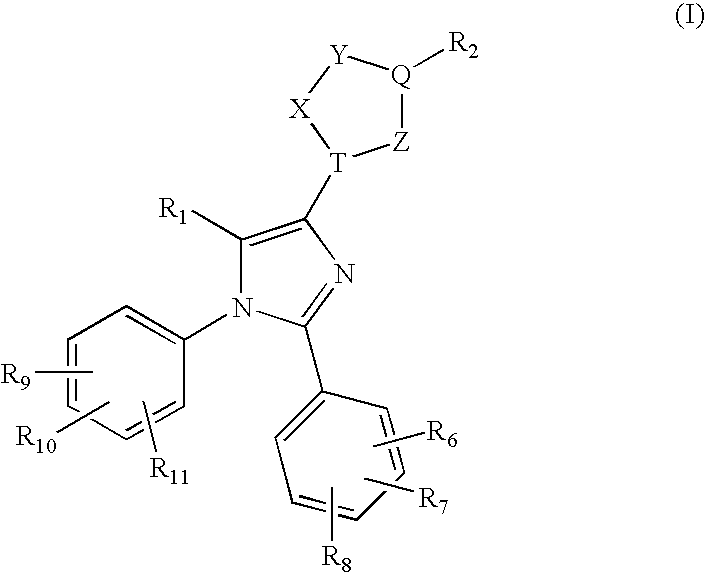
Heteroaryl-imidazole derivatives as cannabinoid cb1 receptor antagonists
A heteroaryl-imidazole compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof is effective as a cannabinoid CB1 receptor inverse agonist or antagonist, which is useful for preventing or treating obesity and obesity-related metabolic disorders. The present invention also provides a method for preparing a heteroaryl-imidazole compound of formula (I), a pharmaceutical composition containing a heteroaryl-imidazole compound of formula (I), and a method for preventing or treating obesity and obesity-related metabolic disorders.
Owner:THE GREEN CROSS CORP
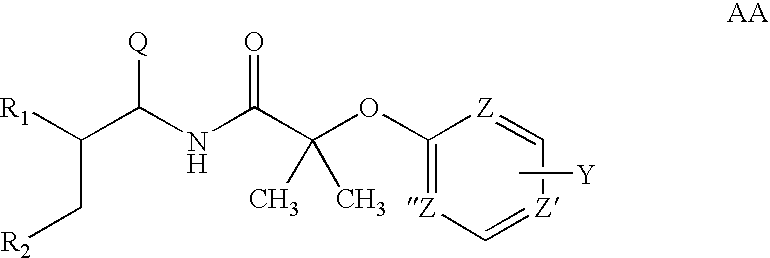
Substituted 2-methyl-2-phenoxy-n-propyl-propionamides as cannabinoid receptor antagonists/inverse agonists useful for treating obesity
The present invention provides novel substituted 2-methyl-2-phenoxy-N-propyl-propionamides and derivatives thereof that are useful as cannabinoid receptor antagonists / inverse agonists and pharmaceutical compositions thereof and methods of using the same for treating obesity, diabetes, and / or cardiometabolic disorders.
Owner:JENRIN DISCOVERY
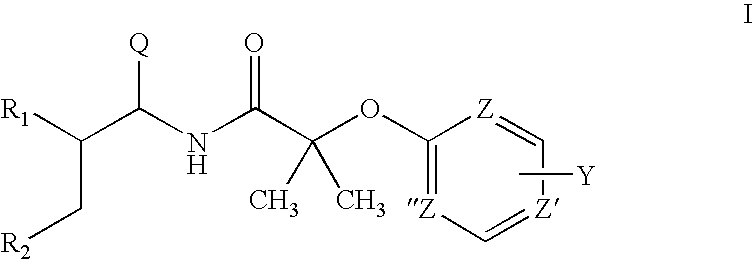
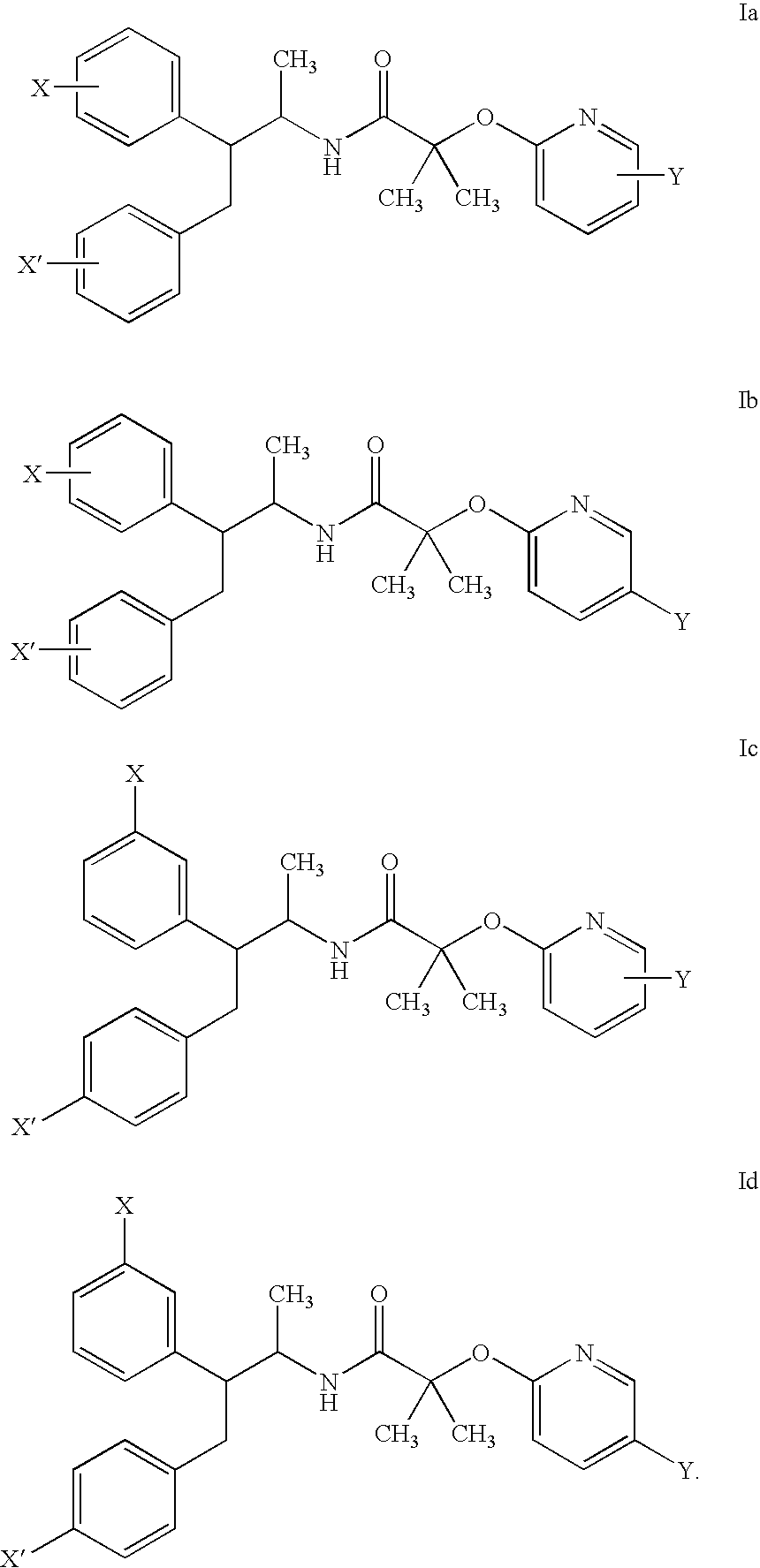
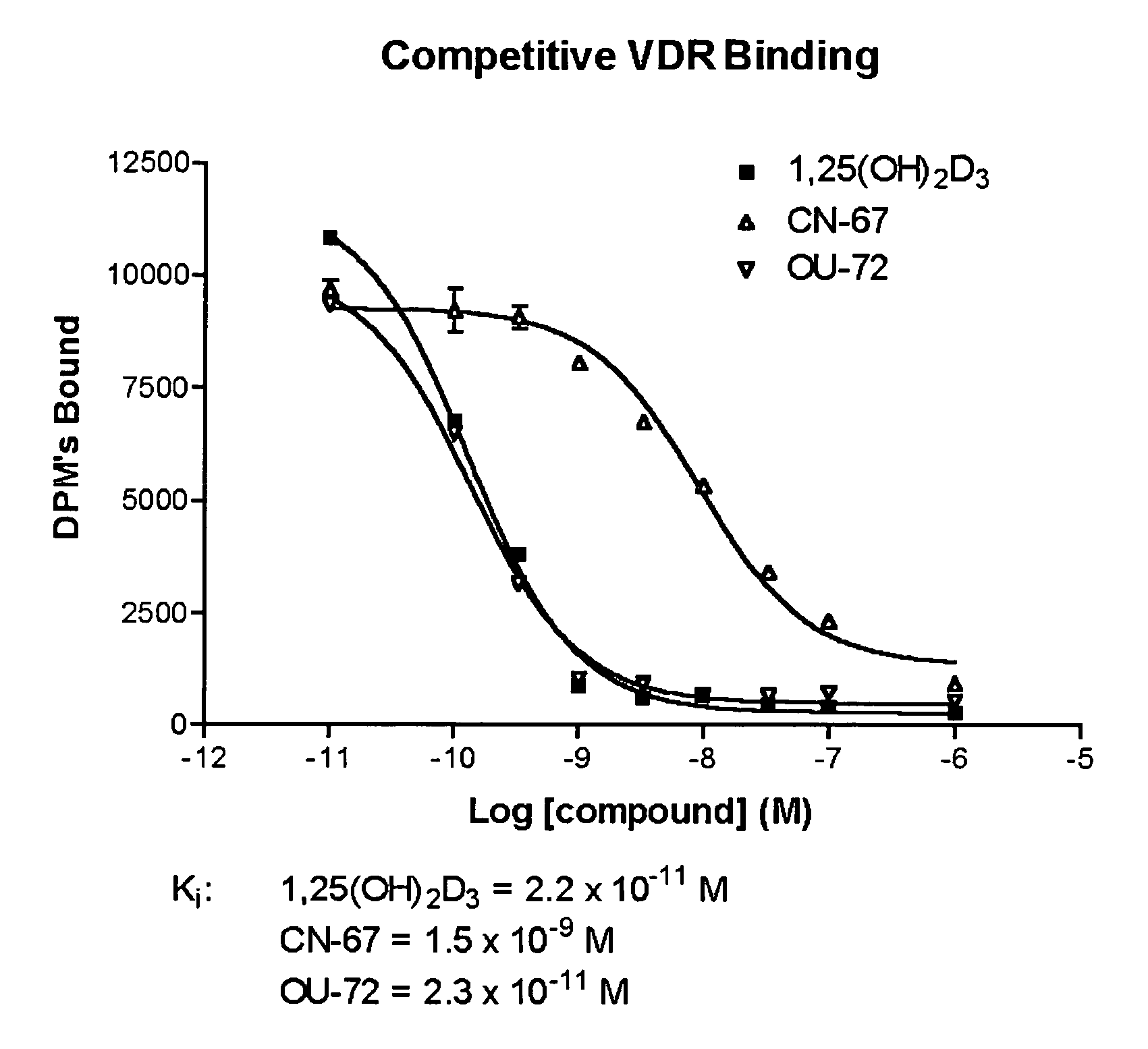
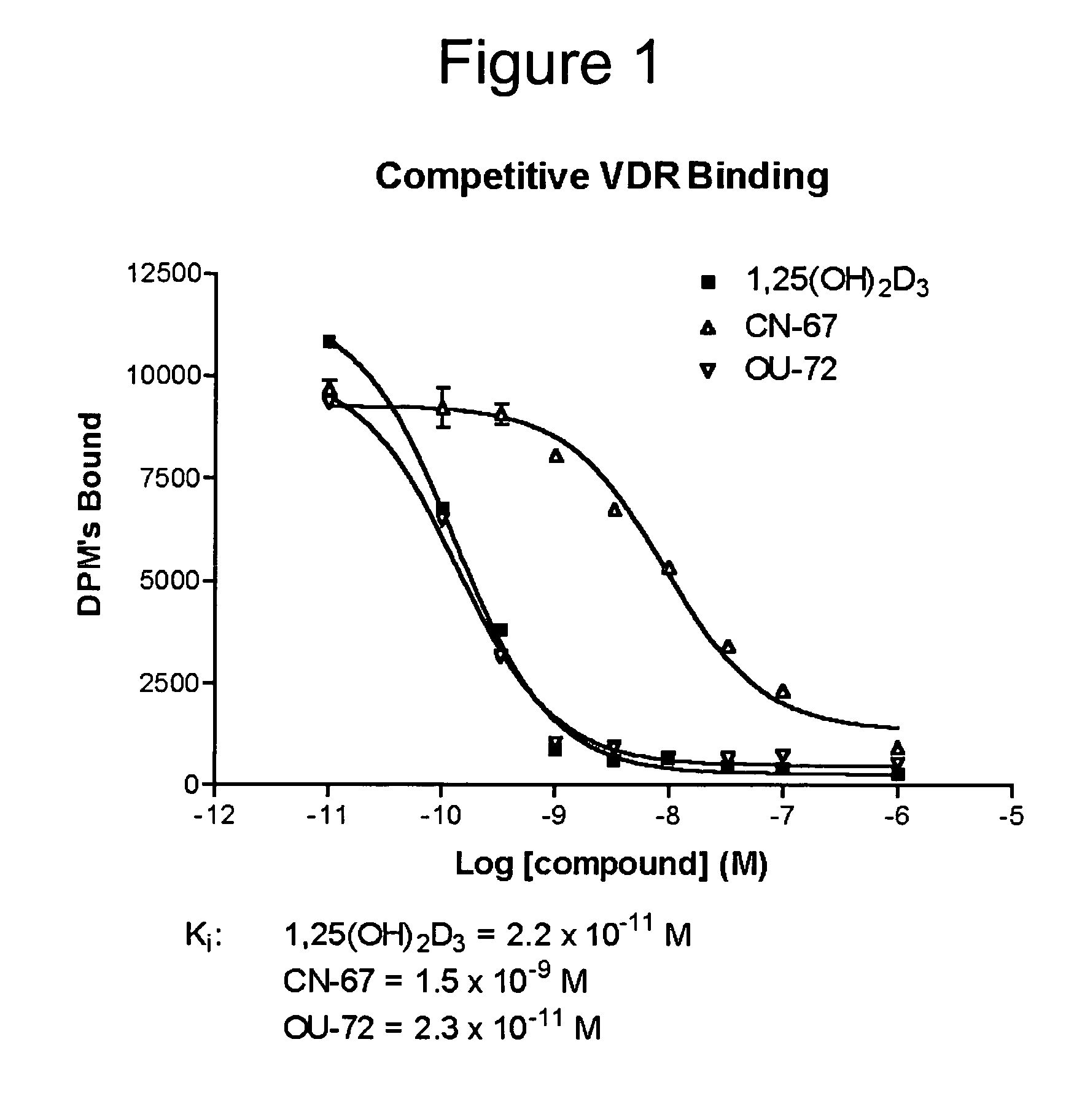
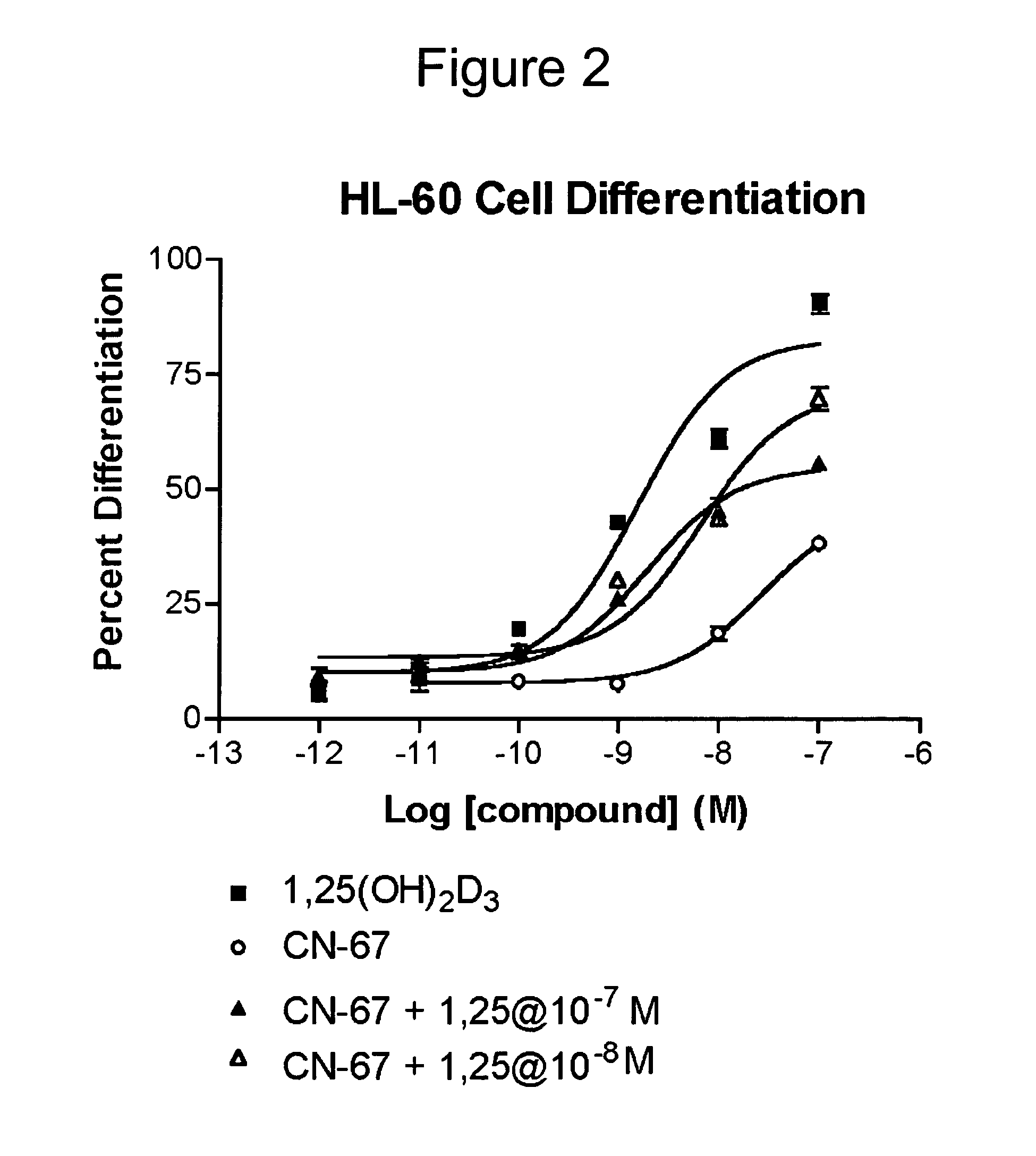
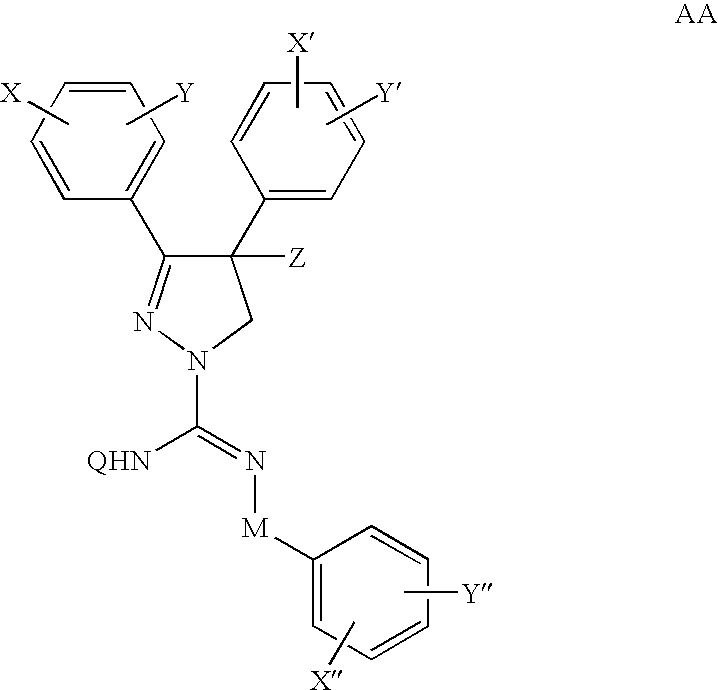
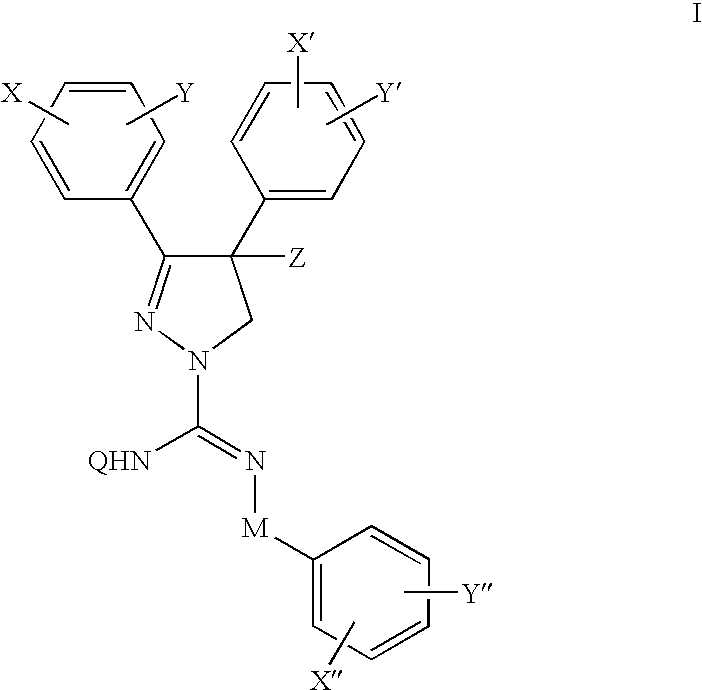
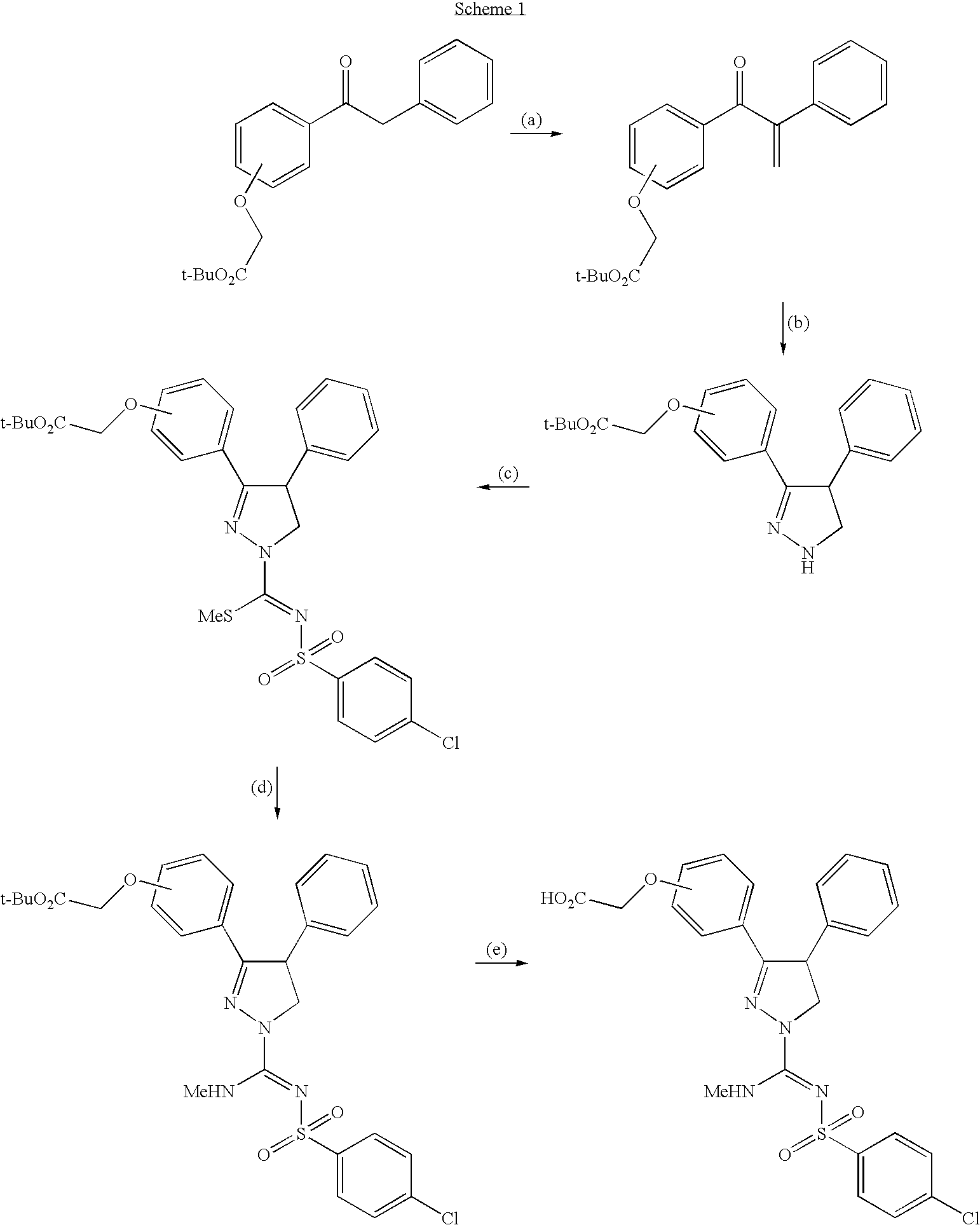
Vitamin D receptor antagonists and their use in treating asthma
Various compounds such as those having the formula I and XIV where the variables have the values described herein antagonize the vitamin D receptor and are useful in treating conditions such as asthma and in preparing medicaments for use in antagonizing the vitamin D receptor or treating conditions such as asthma
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Cannabinoid receptor antagonists/inverse agonists useful for treating metabolic disorders, including obesity and diabetes
The present invention provides novel pyrazoles that are useful as cannabinoid receptor antagonists and pharmaceutical compositions thereof and methods of using the same for treating obesity, diabetes, and / or cardiometabolic disorders.
Owner:JENRIN DISCOVERY
Azole Derivatives as Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor Antagonists
A novel azole compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof is effective as a cannabinoid CB1 receptor inverse agonist or antagonist, which is useful for preventing or treating obesity and obesity-related metabolic disorders. The prevention also provides a method for preparing same, a pharmaceutical composition containing same, and a method for preventing or treating obesity and obesity-related metabolic disorders.
Owner:THE GREEN CROSS CORP
Biphenyl compounds useful as muscarinic receptor antagonists
InactiveUS20070293461A1Long duration of actionImprove performanceBiocideOrganic chemistryCombinatorial chemistryPulmonary disease
This invention provides compounds of formula I: wherein a, b, c, d, m, n, p, r, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, and W are as defined in the specification. The compounds of formula I are muscarinic receptor antagonists. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds, processes and intermediates for preparing such compounds and methods of using such compounds to treat pulmonary disorders.
Owner:THERAVANCE BIOPHARMA R&D IP LLC
Use of ace inhibitors and/or angiostensin ii receptor antagonists for the improving and/or maintaining the skin tone and for the treatment of skin ageing
InactiveUS20090143458A1Reduced gene expressionIncrease gene expressionCosmetic preparationsBiocideNK1 receptor antagonistDepressant
The present invention relates to use of an ACE inhibitor and / or angiotensin II receptor antagonist of the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of skin ageing or wrinkling. Furthermore, the present invention relates to use of an ACE inhibitor and / or angiotensin II receptor antagonist for the preparation of a cosmetic composition.
Owner:ACE APS
Kappa opioid receptor ligands
Kappa opioid receptor antagonists are provided that yield significant improvements in functional binding assays to kappa opioid receptors relative to nor-BNI, and the use of these antagonists in treatment of disease states that are ameliorated by binding of the kappa opioid receptor such as heroin or cocaine addictions.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
Fluoro and sulphonylamino containing 3,6-disubstituted azabicyclo (3.1.0) hexane derivatives as muscarinic receptor antagonists
This invention generally relates to the derivatives of novel 3,6 disubstituted azabicyclo[3.1.0] hexane's. The compounds of this invention are MUSCARINIC receptor antagonists which are useful, inter-ail for the treatment of various diseases of the respiratory, urinary and gastrointestinal systems mediated through MUSCARINIC receptors. The invention also relates to processes for the preparation of the compounds of the invention, pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds of the present invention and the methods of treating the diseases mediated through MUSCARINIC receptors.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
6-substituted nicotinamide derivatives as opioid receptor antagonists
A compound of the formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, enantiomer, racemate, diastereomers or mixtures thereof, or a solvate thereof, formulations and methods of use thereof, as opioid receptor antagonists are disclosed wherein the variables are as described herein.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Pyrazole derivatives as cannabinoid receptor antagonists
One aspect of the invention is concerned with cannabimimetic pyrazole analogs. Another aspect of the invention is concerned with new and improved pyrazole analogs having high affinities and / or selectivities for the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. A further aspect of the invention is concerned with pharmaceutical preparations employing the inventive analogs and methods of administering therapeutically effective amounts of the inventive analogs to provide a physiological effect.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Cannabinoid receptor antagonists/inverse agonists useful for treating obesity
The present invention provides novel pyrazoles that are useful as cannabinoid receptor antagonists and pharmaceutical compositions thereof and methods of using the same for treating obesity, diabetes, and / or cardiometabolic disorders.
Owner:JENRIN DISCOVERY
Pharmaceutical Combination
Pharmaceutical combinations comprising a beta-3 adrenergic receptor agonist and a muscarinic receptor antagonist, and methods for their use are disclosed. Methods of using the pharmaceutical combinations for the treatment of one or more symptoms associated with overactive bladder, for example, frequency of urgency, nocturia, and urinary incontinence, are also disclosed.
Owner:B3AR THERAPEUTICS INC
3,6-Disubstituted azabicyclo derivatives as muscarinic receptor antagonists
This invention relates to derivatives of 3,6-disubstituted azabicyclo compounds. The compounds of this invention can function as muscarinic receptor antagonists, and can be used for the treatment of various diseases of the respiratory, urinary and gastrointestinal systems mediated through muscarinic receptors. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds of the present invention and the methods for treating the diseases mediated through muscarinic receptors.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
Kappa opioid receptor ligands
InactiveUS20090264462A1Strong specificityHigh affinityBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseΜ-opioid receptor
Kappa opioid receptor antagonists are provided that yield significant improvements in functional binding assays to kappa opioid receptors, and the use of these antagonists in treatment of disease states that are ameliorated by binding of the kappa opioid receptor such as heroin or cocaine addictions.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
Substituted 4-amino-1-(pyridylmethyl)piperidine and related compounds
This invention provides 4-amino-1-(pyridylmethyl)piperidine and related compounds and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof which are useful as muscarinic receptor antagonists. This invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds; processes and intermediates useful for preparing such compounds; and methods for treating disease conditions mediated by muscarinic receptors, such as overactive bladder, irritable bowel syndrome and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, using such compounds.
Owner:THERAVANCE BIOPHARMA R&D IP LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com