Glycyrrhiza uralensis chalcone synthetase, encoding gene and application thereof
A chalcone synthase and gene technology, applied in the field of plant molecular biology, to achieve the effects of enhanced gene expression, great economic value and far-reaching significance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1, the separation of chalcone synthase gene CHS7G cDNA
[0031] 1. Preparation of plant material and isolation of total RNA
[0032] The mature seeds of Glycyrrhiza uralensis were sterilized and germinated on 1 / 2MS medium, and cultured aseptically for about 20 days in a culture room with a constant temperature of 25°C and a light cycle of 16 hours. The plants grew robustly and were ready for use in total RNA extract.
[0033] Invitrogen’s Trizol reagent was used to extract total RNA from the material. The entire operation process was guaranteed to be free of RNase contamination and strictly followed the RNA extraction process instructions of Trizol reagent. The extracted RNA was divided into small portions and frozen at -80°C for later use.
[0034] 2. Acquisition of CHS7G gene sequence:
[0035] Primers were designed according to the sequence of soybean chalcone synthase gene CHS7 (GenBank Accession No.M98871):
[0036] Gmchs7F: 5'-AGGAAAGATGGTTAGCGTAGC-3...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2. Expression vector construction and transformation of licorice hairy roots mediated by Agrobacterium rhizogenes A4.
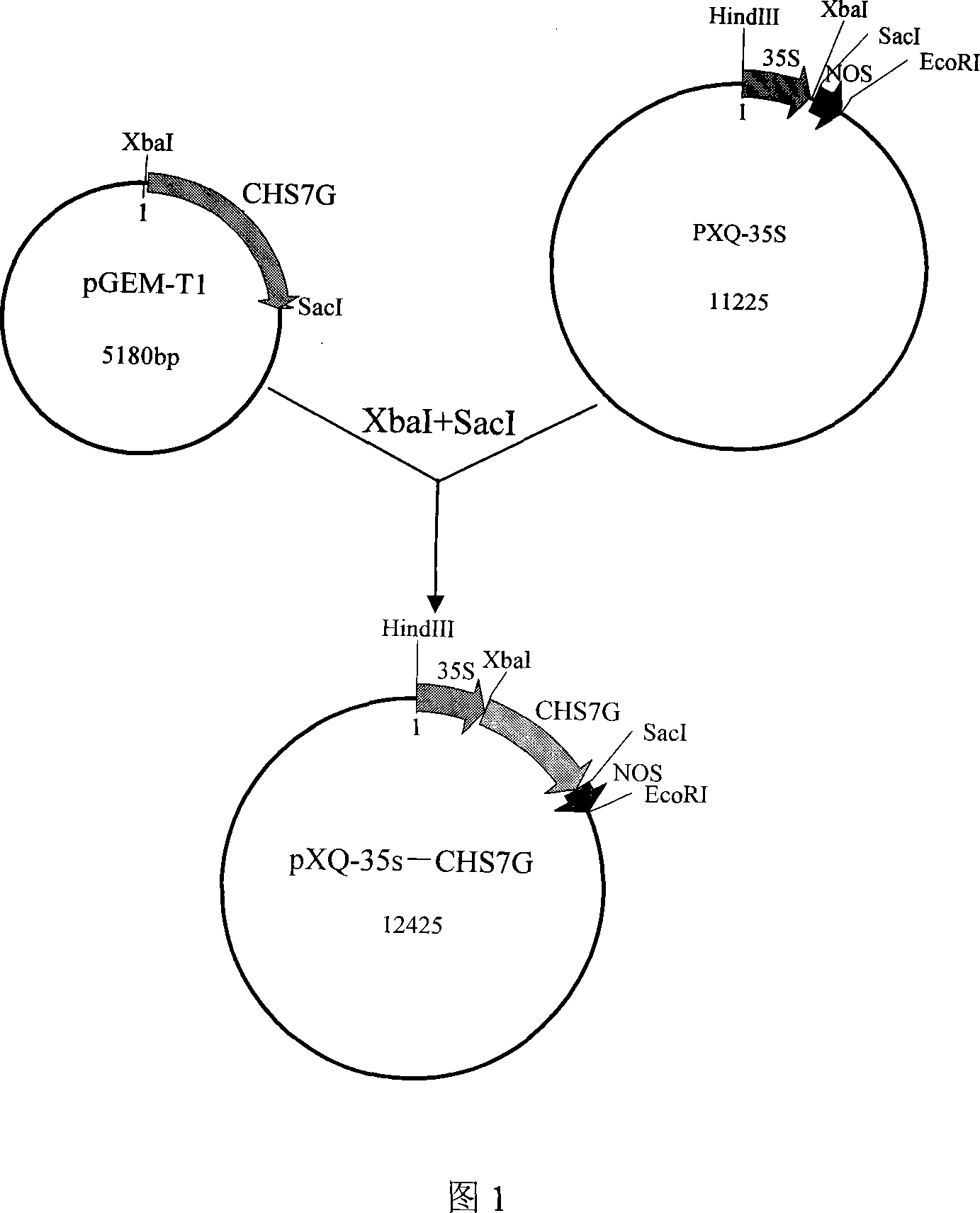
[0060] 1. Construction of plant expression vector pXQ-35s-CHS7G
[0061] The licochalcone synthase gene CHS7G was excised from the T vector using the enzyme cutting site XbaI / SacI, and after the plant expression vector pXQ-35s with the 35s promoter and nos terminator was digested with XbaI / SacI ( pCambia1301 obtained after knocking out the GUS gene) was connected to construct the expression vector pXQ-35s-CHS7G (as shown in Figure 1).
[0062] 2. Transform the recombinant plasmid pXQ-35s-CHS7G into Agrobacterium rhizogenes A4 by freeze-thaw method
[0063] A. Take 2-3 μl plasmid (concentration 1 μg / μl) to transform the freshly prepared Agrobacterium rhizogenes A4 competent cells, and place on ice for 30 minutes;
[0064] B. Immerse in liquid nitrogen for 5 minutes, 37 ℃ water bath for 5 minutes, add 500 μl of empty YEB (beef extract 5g / L, yeast...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Embodiment 3, molecular detection of transgenic hairy root system
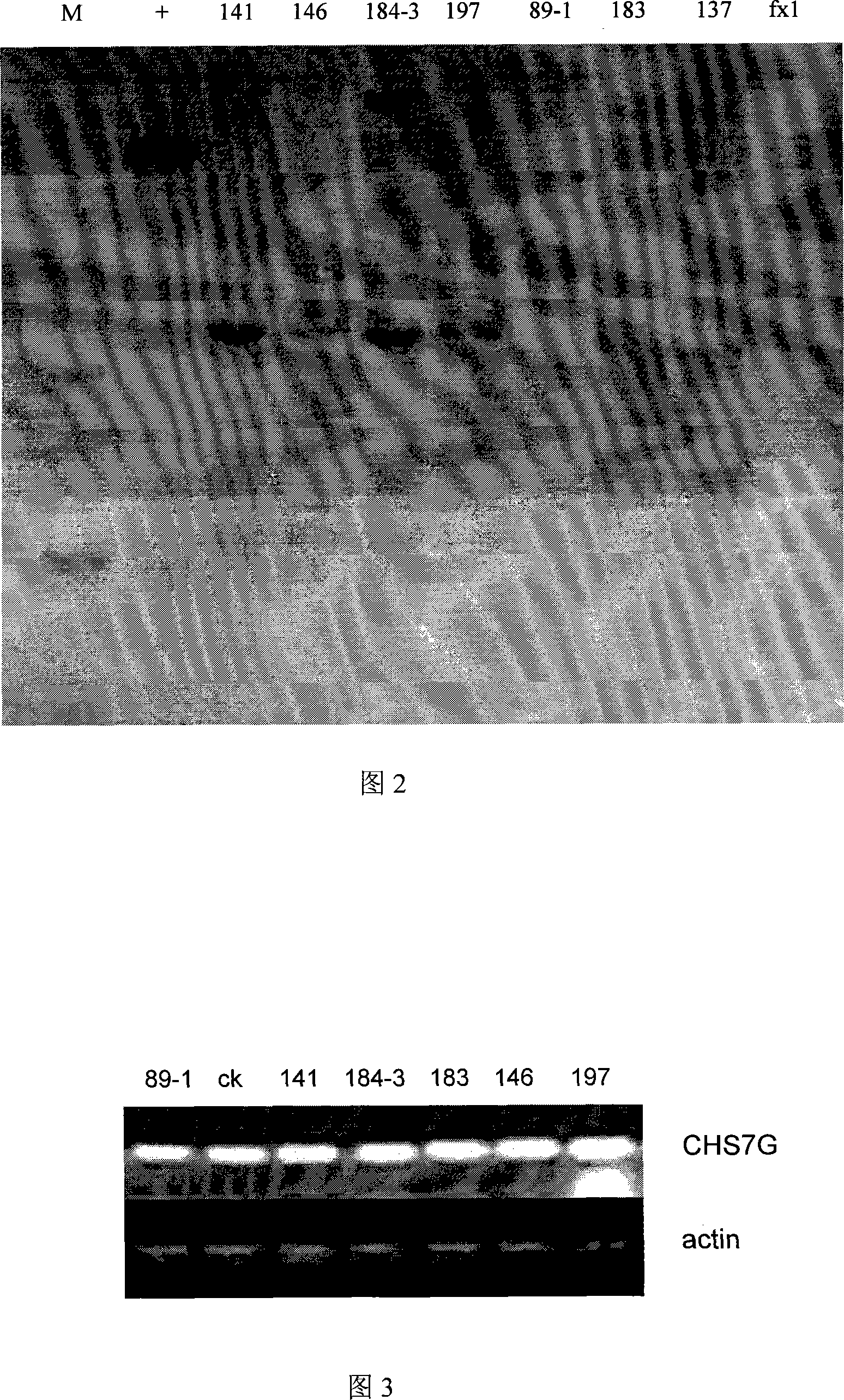
[0071] Randomly select 7 licorice hairy root lines obtained after resistance screening in Example 2, and use the CTAB method to extract total DNA (with reference to "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide"); use the DIG DNA Labeling and Detection kit of Roche Company to extract Octin labeled CHS7G gene fragment was used as a probe for Southern hybridization. All operations were carried out in strict accordance with the instructions of the kit. The hybridization results are shown in Figure 2. In Fig. 2, M is the DNA molecular weight standard (λDNA / HindIII); + is the positive control recombinant plasmid pXQ-35s-CHS7G; fx1 is the wild-type hairy root of the negative control non-transformed exogenous gene; others are obtained after resistance screening 7 licorice hairy root strains. The hybridization results showed that all 7 of the selected transgenic hairy root systems were positive, and all of them were m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com